Abstract
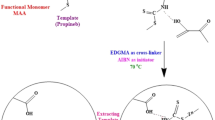
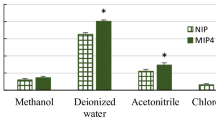
A molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) was prepared using chlorsulfuron (CS), a herbicide as a template molecule, methacrylic acid as a functional monomer, ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EDMA) as a cross-linker, methanol and toluene as a porogen, and 2,2-azobisisobutyronitrile as an initiator. The binding behaviors of the template chlorsulfuron and its analog on MIP were evaluated by equilibrium adsorption experiments, which showed that the MIP particles had specific affinity for the template CS. Solid-phase extraction (SPE) with the chlorsulfuron molecularly imprinted polymer as an adsorbent was investigated. The optimum loading, washing, and eluting conditions for chlorsulfuron molecularly imprinted polymer solid-phase extraction (CS-MISPE) were established. The optimized CS-MISPE procedure was developed to enrich and clean up the chlorsulfuron residue in water, soils, and wheat plants. Concentrations of chlorsulfuron in the samples were analyzed by HPLC-UVD. The average recoveries of CS spiked standard at 0.05~0.2 mg L−1 in water were 90.2~93.3%, with the relative standard deviation (RSD) being 2.0~3.9% (n = 3). The average recoveries of 1.0 mL CS spiked standard at 0.1~0.5 mg L−1 in 10 g soil were 91.1~94.7%, with the RSD being 3.1~5.6% (n = 3). The average recoveries of 1.0 mL CS spiked standard at 0.1~0.5 mg L−1 in 5 g wheat plant were 82.3~94.3%, with the RSD being 2.9~6.8% (n = 3). Overall, our study provides a sensitive and cost-effective method for accurate determination of CS residues in water, soils, and plants.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayano, E., Kanazawa, H., Ando, M., & Nishimura, T. (2004). Determination and quantitation of sulfonylurea and urea herbicides in water samples using liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization mass spectrometric detection. Analytica Chimica Acta, 507, 211–218.
Baggiani, C., Anfossi, L., & Giovannoli, C. (2007). Solid phase extraction of food contaminants using molecular imprinted polymers. Analytica Chimica Acta, 591, 29–39.
Baggiani, C., Baravalle, P., Giraudi, G., & Tozzi, C. (2007). Molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction method for the high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of fungicide pyrimethanil in wine. Journal of Chromatography. A, 1141, 158–164.
Bastide, J., Cambon, J. P., Breton, F., Piletsky, S. A., & Rouillon, R. (2005). The use of molecularly imprinted polymers for extraction of sulfonylurea herbicides. Analytica Chimica Acta, 542, 97–103.
Bhardwaj, G. (2007). From pioneering invention to sustained innovation: Herbicides at DuPont. Chemical Heritage, 25(1), 34–36.
Claude, B., Morin, P., Lafosse, M., Belmont, A. S., & Haupt, K. (2008). Selective solid-phase extraction of a triterpene acid from a plant extract by molecularly imprinted polymer. Talanta, 75, 344–350.
Djozan, D., & Ebrahimi, B. (2008). Preparation of new solid phase micro extraction fiber on the basis of atrazine-molecular imprinted polymer: Application for GC and GC/MS screening of triazine herbicides in water, rice and onion. Analytica Chimica Acta, 616, 152–159.
Dong, X. Z., Wang, N., Wang, S. L., Zhang, X. W., & Fan, Z. J. (2004). Synthesis and application of molecularly imprinted polymer on selective solid-phase extraction for the determination of monosulfuron residue in soil. Journal of Chromatography. A, 1057, 13–19.
Fan, Z. J., Liu, F. M., & Qian, C. F. (1999). The present situation and development of sulfonylurea herbicides. Pesticides, 38, 6–9.
Feng, Q. Z., Zhao, L. X., Yan, W., Lin, J. M., Zheng, Z. X., & Hazard, J. (2009). Molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction combined with high performance liquid chromatography for analysis of phenolic compounds from environmental water samples. Materials, 167, 282–288.
Knopp, A., Knopp, D., & Niessner, R. (1999). Metsulfuron-methyl in different water types. Environmental Science and Technology, 33, 358–361.
Krynitsky, A. J. (1997). Determination of sulfonylurea herbicides in water by capillary electrophoresis and by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Journal of AOAC International, 80, 392–400.
Li, X. Y., Wang, G. J., Sun, J. G., Zheng, Y. T., Yan, B., Xie, H. T., et al. (2007). Determination and pharmacokinetic study of a novel sulfonylurea: Potential hypoglycemic agent in rat plasma. Chromatographia, 65, 13–18.
Liu, X. J., Chen, Z. Y., Zhao, R., Shangguan, D. H., Liu, G. Q., & Chen, Y. (2007). Uniform-sized molecularly imprinted polymer for metsulfuron-methyl by one-step swelling and polymerization method. Talanta, 71, 1205–1210.
Liu, Y. Q., Hoshina, K., & Haginaka, J. (2010). Monodispersed, molecularly imprinted polymers for inchonidine by precipitation polymerization. Talanta, 80, 1713–1718.
Martin, P. D., Jones, G. R., Stringer, F., & Wilson, I. D. (2004). Comparison of extraction of a blocker from plasma onto a molecularly imprinted polymer with liquid–liquid extraction and solid phase extraction methods. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 35, 1231–1239.
Martínez, R. C., Gonzalo, E. R., & Hernández, E. H. (2006). Behaviour of triazine herbicides and their hydroxylated and dealkylated metabolites on a propazine-imprinted polymer comparative study in organic and aqueous media. Analytica Chimica Acta, 559, 186–194.
Molinelli, A., Weiss, R., & Mizaikoff, B. (2002). Advanced solid phase extraction using molecularly imprinted polymers for the determination of quercetin in red wine. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 50, 1804–1808.
Penmetsa, K. V., Leidy, R. S., & Shea, D. (1997). Enantiomeric and isomeric separation of herbicides using cyclodextrin-modified capillary zone electrophoresis. Journal of Chromatography. A, 790, 225–234.
Pimentel, D., & Levitan, L. (1986). Pesticides: Amounts applied and amounts reaching pests. Bioscience, 36, 86–91.
Polati, S., Bottaro, M., Frascarolo, P., Gosetti, F., Gianotti, V., & Gennaro, M. C. (2006). HPLC-UV and HPLC-MSn multiresidue determination of amidosulfuron, azimsulfuron, nicosulfuron, rimsulfuron, thifensulfuron methyl, tribenuron methyl and azoxistrobine in surface waters. Analytica Chimica Acta, 579, 146–151.
She, Y. X., Cao, W. Q., Shi, X. M., Lv, X. L., Liu, J. J., Wang, R. Y., et al. (2010). Class-specific molecularly imprinted polymers for the selective extraction and determination of sulfonylurea herbicides in maize samples by high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography B, 878, 2047–2053.
Sondhia, S. (2008). Determination of imazosulfuron persistence in rice crop and soil. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 137, 205–211.
Song, N. H., Zhang, S., Hong, M., & Yang, H. (2010). Impact of dissolved organic matter on bioavailability of chlorotoluronn to wheat. Environmental Pollution, 158, 906–912.
Sun, Z., Schussler, W., Sengl, M., Niessner, R., & Knoppa, D. (2008). Selective trace analysis of diclofenac in surface andwastewater samples using solid-phase extractionwith a new molecularly imprinted polymer. Analytica Chimica Acta, 620, 73–81.
Tang, K. J., Chen, S. W., Gu, X. H., Wang, H. J., Dai, J., & Tang, J. (2008). Preparation of molecularly imprinted solid phase extraction using bensulfuron-methyl imprinted polymer and clean-up for the sulfonylurea-herbicides in soybean. Analytica Chimica Acta, 614, 112–118.
Tang, K. J., Gu, X. H., Zhu, S., Tang, J., & Wang, H. J. (2009). Spectrum analysis and adsorption characteristics of bensulfuronmethyl molecularly imprinted polymers. China Acta Chimica Sinica, 67, 687–692.
Tran, A. T. K., Hyne, R. V., & Doble, P. (2007). Determination of commonly used polar herbicides in agricultural drainage waters in Australia by HPLC. Chemosphere, 67, 944–953.
Wang, N., Dong, X. Z., Zhang, X. W., Lv, X. Y., Hou, J. F., & Fan, Z. J. (2004). Synthesis and the recognition properties of the monosulfuron imprinted polymer. J Instrum Anal, 23, 13–17.
Wu, W. X., Li, L., Yang, G. L., Li, Z. W., & Zhang, G. Q. (2006). Characteristics of molecular recognition of triadimefon imprinting polymer. Chin, Journal of Hebei Univerersity (Natural Science Edition), 26, 396–400.
Wu, Y., Yang, C. Z., & Liu, Y. (2008). Determination of chlorimuron-ethyl in soybeans by GC-MS. Chin J Anal Lab, 27, 80–83.
Wu, Y. J., Fu, X. W., & Yang, H. (2011). Cloud point extraction with Triton X-114 for separation of metsulfuron-methyl, chlorsulfuron, and bensulfuron-methyl from water, soil, and rice and analysis by high-performance liquid chromatography. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology. doi:10.1007/s00244-010-9626-y.
Xia, X. R., & Leidy, R. B. (2002). A simplified liquid-solid extraction technique for the analyses of pesticide residues in soil samples. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 73, 179–190.
Ye, G. B., Zhang, W., Cui, X., Pan, C. P., & Jiang, S. R. (2006). Determination and quantitation of ten sulfonylureaherbicides in soil samples using liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization mass spectrometric detection. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 34, 1207–1212.
Zhu, X. F., Cao, Q., Hou, N. B., Wang, G. S., & Ding, Z. T. (2006a). The preparation and the recognition property of molecularly imprinted polymer of podophyllotoxin. Analytica Chimica Acta, 561, 171–177.
Zhu, X. L., Yang, J., Su, Q. D., Cai, J. B., & Gao, Y. (2006b). Monocrotophos—Specific molecularly imprinted polymers and its spectroscopic study. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 26, 1817–1820.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support of the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (no. KYZ200918) for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, X.W., Wu, Y.J., Qu, J.R. et al. Preparation and utilization of molecularly imprinted polymer for chlorsulfuron extraction from water, soil, and wheat plant. Environ Monit Assess 184, 4161–4170 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2252-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2252-y