Abstract
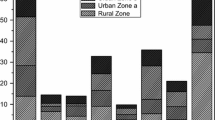
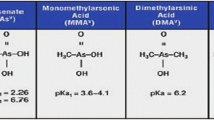
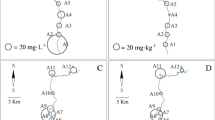
Arsenic is a toxic and carcinogenic element. Its toxicity depends on its oxidation state and its concentration. The aim of this paper is to determine, for the first time, the concentration levels of arsenic in water and sediment during the spring/summer period of 2009 in Sevojno, a region in West Serbia with a long industrial tradition, as well as to determine the model of arsenic distribution in water/sediment system and the level of its compatibility with the existing theoretical model. Adsorption is a continual process in the environment. It plays a very important role in the transport and fate of pollutants, especially in sediment. The adsorption of arsenic was examined using the Freundlich adsorption isotherm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agbaba, J., & Dalmatia, B. (2006). Drinking water quality control. Novi Sad: Novi Sad University, pp. 197–251.
Beard, J., & Cruces, L. (1998). New Science, 28, 10.
Bednar, A. J., Garbarino, J. R., Burkhardat, M. R., Ranville, J. F., & Wildeman, T. R. (2004). Field and laboratory arsenic speciation methods and their application to natural-water analysis. Water Research, 38, 355–364.
Benett, P. M., Jepson, P. D., Law, R. J., Jones, B. R., Kuiken, T., Baker, J. R., et al. (2001). Exposure to heavy metals and infectious disease mortality in harbour poropises from England and Wales. Environmental Pollution, 1, 33–40.
Bowen, H. J. M. (1979). Environmental geochemistry of the elements. New York: Academic Press.
Chow, J. T. (1978). Lead in natural waters. In: J. O. Nriagu (Ed.), The biogeochemistry of lead in the environment, Part A, ecological cycling (pp. 185–218). Nth Holland: Elsevier.
De Zuane, J. (Ed.) (1997). Handbook of drinking water quality (2nd ed.). New York: Wiley.
Ðorđević, S., & Dražić, V. (2000). Physical chemistry (pp. 453–454). Belgrade, Faculty of technology and metallurgy.
European Commission (2000). Air pollution by As, Cd and Ni compounds. Working group on As, Cd and Ni compounds position paper (p. 361). Version Final, October 2000. DG Environment, EC.
Fergusson, J. E. (1990). The heavy elements: Chemistry, environmental impact and health effect. Oxford: Pergamon Press.
Ferreccio, C. R., Gonzales, C. W., Solari, J. S., & Noder, C. N. (1996). Revista Médica de Chile, 124, 119.
Gregus, Z., Gyurasics, A., & Csanaky, I. (2000). Biliary and urinary excretion of inorganic arsenic: Monomethylarsonous acid as a major biliary metabolite in rats. Toxicological Sciences, 56, 18–25.
Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality, Recommendations (2nd ed.). 2, Geneva: World Health Organisation (1996).
Hopenhayn, C., Biggs, M. L., Smith, A. H., Kalman, D. A., & Moore, L. E. (1996). Environmental Health Perspectives, 104, 620–628.
Hughes, M. F. (2002). Arsenic toxicity and potential mechanisms of action. Toxicology Letters, 133, 1–16.
Hunt, L. E., & Howard, A. G. (1994). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 28, 33–38.
Igwe, J. C., & Abia, A. A. (2007). Adsorption isotherm studies of Cd (II), Pb (II) and Zn (II) ions bioremediation from aquedus solution using unmodified and EDTA-modified maize cob, Ecl. Quim. Sao Paolo, 32(1), pp. 33–42.
Kabata-Pendias, A., & Pendias, H. (1992). Trace elements in soils and plants. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Lazrus, L. A., Lorang, E., & Lodge, P. J. (1970). Lead and other metal ions in United States precipitation. Environmental Science & Technology, 4, 55–58.
Marković, Z. (1995). The River Ðetinja-macrozoobenthos in the assessment of water quality, the Ministry of Environment Republic of Serbia and Research Center Uzice, Uzice, pp. 7–8.
Mojsilović, S., Baklajić, D., & Ðokovi´c, I. (1977). Basic geological map of SFRY. Belgrade : Institute of Geological and Geophysical Research.
Ning, R. Y. (2002). Arsenic removal by reverse osmosis. Desalination, 143, 237–241.
Official Gazette RS, No. 31/82 (1982). Belgrade: Regulation on Dangerous Substances in Water.
Rao, M., & Bhole, A. G. (2001). Chromium removal by adsorption using fly ash and bagasse. Journal of Indian Water Works Association, XXXIII(1), 97–100.
Shih, M. C. (2005). An overview of arsenic removal by pressure-driven membrane processes. Desalination, 172, 85–97.
Singh, K., & Srivastava, B. (2001). Basic color removal of wastewater by adsorption on rice husk carbon. Indian Journal of Chemical Technology, 8, 133–139.
Vukašinović-Pešić, V., Okanović, M., Blagojević, N., & Rajaković, L. J. (2005). The source, characteristics and distribution of arsenic in the environment. Chemical Industry and Chemical Engineering Quaterly, 11(1), 44–48.
Zakharyan, R. A., Sampayo-Reyes, A., Healy, S. M., Tsaprailis, G., Board, P. G., Liebler, D. C., et al. (2001). Human monomethylarsonic (MMAV) reductase is a member of the glutathione-S-transferase superfamily. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 14, 1051–1057.
Zouboulis, A., & Katsoyiannis, I. (2002). Removal of arsenates from contaminated water by coagulation-direct filtration. Separation Science and Technology, 37(12), 2859–2873.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aksentijević, S., Kiurski, J. & Vasić, M.V. Arsenic distribution in water/sediment system of Sevojno. Environ Monit Assess 184, 335–341 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-1971-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-1971-4