Abstract
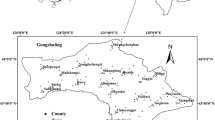
A detailed investigation was conducted to evaluate heavy metal sources and their spatial distribution in agricultural fields in the south of Tehran using statistics, geostatistics, and a geographic information system. The content of Cd, Cu, Co, Pb, Zn, Cr, and Ni were determined in 106 samples. The results showed that the primary inputs of Cr, Co, and Ni were due to pedogenic factors, while the inputs of Zn, Pb, and Cu were due to anthropogenic sources. Cd was associated with distinct sources, such as agricultural and industrial pollution. Ordinary kriging was carried out to map the spatial patters of heavy metals, and disjunctive kriging was used to quantify the probability of heavy metal concentrations higher than their recommended threshold values. The results show that Cd, Cu, Ni, and Zn exhibit pollution risk in the study area. The sources of the high pollution levels evaluated were related to the use of urban and industrial wastewater and agricultural practices. These results are useful for the development of proper management strategies for remediation practices in the polluted area.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adriano, D. C. (2001). Trace elements in terrestrial environments. Biogeochemistry, bioavailability and risks of metals. New York: Springer.
Alavi Naeini, M. R., Mozafari, A., & Najjaran, M. (2005). Geochemical and heavy mineral exploration in Tehran. Scale:1:100000. Ministry of Industries and Mines Geological survey of Iran.
Alloway, B. J. (1990). Heavy metals in soils. London: Blackie.
Alloway, B. J., & Ayres, D. C. (1993). Chemical principles of environmental pollution. London: Blackie.
Alloway, B. J., & Jackson, A. (1991). The behavior of heavy metals in sewage sludge-amended soil. Science of the Total Environment, 100, 151–176.
Aucejo, A., Ferrer, J., Gabaldón, C., Marzal, P., & Seco, A. (1997). Diagnosis of boron, fluorine, lead, nickel and zinc toxicity in citrus plantations in Villareal, Spain. Water Air Soil Pollution, 94, 349–360.
Burrough, P. A., & McDonnell, R. A. (1998). Principles of geographical information systems (p. 333). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Cambardella, C. A., Moorman, T. B., Novak, J. M., Parkin, T. B., Turco, R. F., & Konopka, A. E. (1994). Field-scale variability of soil properties in central Iowa soils. Soil Science Society of American Journal, 58, 1501–1511.
Chen, T., Liu, X. M., Zhu, M. Z., Zhao, K. L., Wu, J. J., Xu, J. M., et al. (2008). Identification of trace element sources and associated risk assessment in vegetable soils of the urban–rural transitional area of Hangzhou, China. Environmental Pollution, 151, 67–78.
Facchinelli, A., Sacchi, E., & Mallen, L. (2001). Multivariate statistical and GIS-based approach to identify heavy metal sources in soils. Environmental Pollution, 114, 313–324.
Giller, K. E., Witter, E., & McGrath, S. P. (1998). Toxicity of heavy metals to micro-organisms and microbial processes in agricultural soils. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 30, 1389–1414.
Goovaerts, P. (1997). Geostatistics for natural resources evaluation. Applied geostatistics series. New York: Oxford University Press.
Goovaerts, P. (1999). Geostatistics in soil science: State-of-the-art and perspectives. Geoderma, 89, 1–45.
Hernandez-Stefanoni, J. L., & Ponce-Hernandez, R. (2006). Mapping the spatial variability of plant diversity in a tropical forest: Comparison of spatial interpolation methods. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 117, 307–334.
Huang, S. S., Liao, Q. L., Hua, M., Wu, X. M., Bi, K. S., Yan, C. Y., et al. (2007). Survey of heavy metal pollution and assessment of agricultural soil in Yangzhong district, Jiangsu Province, China. Chemosphere, 67, 2148–2155.
Isaaks, E. H., & Srivastava, R. M. (1989). An introduction to applied geostatistics (pp. 39–52). New York:Oxford University Press.
Krige, D. G. (1951). A statistical approach to some basic mine valuation problems on the Witwatersrand. Journal of Chemical, Metallurgical and Mining Society of South Africa, 52(6), 119–139.
Krige, D. G. (1960). On the departure of ore value distributions from lognormal models in South African gold mines. Journal of Chemical, Metallurgical and Mining Society of South Africa, 61, 231–244.
Lark, R. M., & Ferguson, R. B. (2004). Mapping risk of soil nutrient deficiency or excess by disjunctive and indicator kriging. Geoderma, 118, 39–53.
Lin, Y. P., Chang, T. K., & Teng, T. P. (2001). Characterization of soil lead by comparing sequential Gaussian simulation, simulated annealing simulation and kriging methods. Environment Geology, 41, 189–199.
Liu, X. M., Wu, J. J., & Xu, J. M. (2006). Characterizing the risk assessment of heavy metals and sampling uncertainty analysis in paddy field by geostatistics and GIS. Environmental Pollution, 141, 257–264.
Manta, D. S., Angelone, M., Bellanca, A., Neri, R., & Sprovieri, M. (2002). Heavy metals in urban soils: A case study from the city of Palermo (Sicily), Italy. Science of the Total Environment, 300, 229–243.
McGrath, D., Zhang, C. S., & Owen, C. T. (2004). Geostatistical analyses and hazard assessment on soil lead in Silvermines, area Ireland. Environmetal Pollution, 127, 239–248.
Micó, C., Recatalá, L., Peris, M., & Sánchez, J. (2006). Assessing heavy metal sources in agricultural soils of an European Mediterranean area by multivariate analysis. Chemosphere, 65, 863–872.
Micó, C., Peris, M., Recatalá, L., & Sánchez, J. (2007). Baseline values for heavy metals in agricultural soils in an European Mediterranean region. Science of the Total Environment, 378, 13–17.
Nalder, I. A., & Wein, R. W. (1998). Spatial interpolation of climatic normals: Test of a new method in the Canadian boreal forest. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 92, 211–225.
Nicholson, F. A., Smith, S. R., Alloway, B. J., Carlton-Smith, C., & Chambers, B. J. (2003). An inventory of heavy metals inputs to agricultural soils in England and Wales. Science of the Total Environment, 311, 205–219.
Okoronkwo, N. E., Igwe, I. C., & Onwuchekwa, E. C. (2005). Risk and health implications of polluted soils for crop production. African Journal of Biotechnology, 4, 521–1524.
Robinson, T. P., & Metternicht, G. (2006). Testing the performance of spatial interpolation techniques for mapping soil properties. Computer and Electronic in Agriculture, 50, 97–108.
Rodrigues, S., Pereira, M. E., Sarabando, L., Lopes, L., Cachada, A., & Duarte, A. (2006). Spatial distribution of total Hg in urban soils from an Atlantic coastal city (Aveiro, Portugal). Science of the Total Environment, 368, 40–46.
Rodriguez, J. A., Lopez-Arias, M., & Grau corbi, J. M. (2006). Heavy metals contents in agricultural topsoils in the Ebro basin (Spain). Application of the multivariate geostatistical methods to study spatial variations. Environmental Pollution, 144, 1001–1012.
Rodriguez, J. A., Nanos, N., Grau, J. M., Gil, L., & Lopez-Arias, M. (2008). Multiscale analysis of heavy metal contents in Spanish agricultural topsoils. Chemosphere, 70, 1085–1096.
Romic, M., & Romic, D. (2003). Heavy metals distribution in agricultural topsoils in urban area. Environmental Pollution, 43, 795–805.
Ross, S. M. (1994). Toxic metals in soil–plant systems. Chichester: Wiley.
Salmasi, R., & Tavassoli, A. (2006). Pollution of south of Tehran ground waters with heavy metals. International journal Environmental science and Technology, 3, 147–152.
Shi, J. C., Wang, H. Z., Xu, J. M., Wu, J. J., Liu, X. M., Zhu, H. P., et al. (2007). Spatial distribution of heavy metals in soils: A case study of Changxing, China. Environmental Geology, 52, 1–10.
Steiger, B., Webster, R., Schulin, R., & Lehmann, R. (1996). Mapping heavy metals in polluted soil by disjunctive kriging. Environmental Pollution, 94, 205–215.
USEPA (1996). United States environmental protection agency, method 3050B: Acid digestion of sediments, sludges, soils, & oils, SW-846. Washington, DC: USEPA.
USEPA (2001). Our built & natural environments, a technical review of the interactions between land use, transportation, and environmental quality. Washington, DC: USEPA.
Vicente-Serrano, S. M., Saz-Sánchez, M. A., & Cuadrat, J. M. (2003). Comparative analysis of interpolation methods in the middle Ebro Valley (Spain): Application to annual precipitation and temperature. Climate Research, 24, 161–180.
Webster, R., & Oliver, M. (2001). Geostatistics for environmental scientists. In Statistics in Practice. Chichester: Wiley.
Willmott, C. J. (1982). Some comments on the evaluation of model performance. Bulletin American Meteorological Society, 63, 1309–1313.
Yargholi, B. (2007). Investigation of the Firuzabad wastewater quality-quantity variation for agricultural use. Final report. Iranian Agricultural Engineering Research Institute.
Yargholi, B., Azimi, A. A., Baghvand, A., Liaghat, A. M., & Fardi, G. A. (2008). Investigation of cadmium absorption and accumulation in different parts of some vegetables. American–Eurasian journal. Agriculture and Environment Science, 3, 357–364.
Zhang, C. (2006). Using multivariate analyses and GIS to identify pollutants and their spatial patterns in urban soils in Galway, Ireland. Environmental Pollution, 142, 501–511.
Zhang, X. Y., Lin, F. F., Wong, M. T. F., Feng, X. L., & Wang, K. (2008). Identification of soil heavy metal sources from anthropogenic activities and pollution assessment of Fuyang County, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 154, 439–449.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1671-5
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hani, A., Pazira, E. Heavy metals assessment and identification of their sources in agricultural soils of Southern Tehran, Iran. Environ Monit Assess 176, 677–691 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1612-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1612-3