Abstract
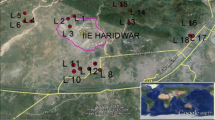
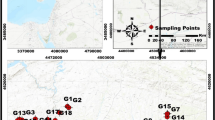
Levels of selected metals Na, Ca, Mg, K, Fe, Mn, Cr, Co, Ni, Cd, Pb and Mn were estimated by flame atomic absorption spectrophotometry in groundwater samples from Kasur, a significant industrial city of Pakistan. Salient mean concentration levels were recorded for: Na (211 mg/l), Ca (187 mg/l), Mg (122 mg/l), K (87.7 mg/l), Fe (2.57 mg/l) and Cr (2.12 mg/l). Overall, the decreasing metal concentration order was: Na > Ca > Mg > K > Fe > Cr > Zn > Co > Pb > Mn > Ni > Cd. Significantly positive correlations were found between Na–Cr (r = 0.553), Na–Mn (r = 0.543), Mg–Fe (r = 0.519), Mg–Cr (r = 0.535), Pb–K (r = 0.506) and Pb–Ni (r = 0.611). Principal Component Analysis and Cluster Analysis identified tannery effluents as the main source of metal contamination of the groundwater. The present metal data showed that Cr, Pb and Fe levels were several times higher than those recommended for water quality by WHO, US-EPA, EU and Japan. The elevated levels of Cr, recorded as 21–42 fold higher compared with the recommended quality values, were believed to originate from the tanning industry of Kasur.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Aiyesanmi, A. F., Ipinmoroti, K. O., & Adeeyinwo, C. E. (2004). Baseline geochemical characteristics of groundwater within okitipupa south-east belt of the bituminous sands field of Nigeria. International Journal of Environmental Studies, 61, 49–57.
Amajor, L. I. (1986). Geochemical characteristics of groundwaters in Port Harcourt and environs (pp. 366–374). Proc. NIWASA Symposium. Ikeja, Lagos.
American Public Health Association (APHA), American Water Works Association (AWWA) and Water Pollution Control Federation (WPCF) 1989. Standard methods for the examinations of water and wastewaters. New York: American Public Health Association.
Barman, S. C., Sahu, R. K., Bhargava, S. K., & Chatterjee, C. (2000). Distribution of heavy metals in wheat, mustard and grown in the field irrigated with industrial effluent. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 64, 489–496.
Calderon, R. L. (2000). The epidemiology of chemical contaminants of drinking water. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 38, S13–S20.
Everitt, B. S. (1993). Cluster analysis. London: Heineman.
Ezeigbo, H. I. (1989). Geological and hydrological influences on the Nigeria environment. Water Resources, 1, 37–44.
Facchinelli, A., Sacchi, E., & Mallen, L. (2001). Multivariate statistical and GIS-based approach to identify heavy metal sources in soils. Environmental Pollution, 114, 313–324.
Federal Bureau of Statistics (2003). Pakistan statistical year book 2003. Government of Pakistan: Federal Bureau of Statistics.
Fernandez, H., Conti, L. F., & Patchineelam, S. R. (1994). An assessment of the pollution of heavy metals in Jacarepagua Basin, Rio De Janeiro, Brazil: A statistical approach. Environment & Technology, 269, 87–94.
Hair, J. F., Jr., Anderson, R. E., Tatham, R. L., & Back, W. C. (1988). Multivariate data analysis (5th ed.). Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
Hopke, P. K. (1992). Factor and correlation analysis of multivariate environmental data. In C. N. Hewitt (Ed.), Methods of environmental data analysis (pp. 139–180). London, UK: Elsevier.
Ipinmoroti, K. O. (1993). Water quality of shallow wells located close to dumpsite in Akure, Nigeria. Pakistan Journal of Scientific and Industrial Research, 36, 137–141.
Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA)-EPA Joint Report (2000). Environmental investigations in Pakistan.
Jarup, L. (2002). Cadmium overload and toxicity. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation, 17(Suppl. 2), 35–39.
Jha, P. K., Subramanian, V., Sitasawad, R., & Van Grieken, R. (1990). Heavy metals in water and sediments of the Yamuna river (a tributary of the Ganga) Science of the Total Environment, 95, 7–27.
Jobson, J. D. (1991). Applied multivariate data analysis. New York: Springer.
Jolliffe, I. T. (1986). Principal component analysis. New York: Springer.
Lee, C., Chon, H., & Jung, M. (2001). Heavy metal contamination in the vicinity of the Daduk Au–Ag–Pb–Zn mine in Korea. Applied Geochemistry, 16, 1377–1386.
Lin, Y.-P., Teng, T.-P., & Chang, T.-K. (2002). Multivariate analysis of soil heavy metal pollution and landscape pattern in Changhua County in Taiwan. Landscape and Urban Planning, 62, 19–35.
Lin, C. H., Wu, Y. L., Chang, K. H., & Lai, C. H. (2004). A method for locating influential pollution sources and estimating their contributions. Environmental Modeling & Assessment, 9, 129–136.
Mance, G. (1987). Pollution threats of heavy metals in aquatic environment. London: Elsevier.
Moon, C. H., Lee, Y. S., Yoon, T. H. (1994). Variation of trace Cu, Pb and Zn in sediment and water of an urban stream resulting from domestic effluents. Water Research, 28, 985–991.
Nolte, J. (1988). Pollution source analysis of river water and sewage sludge. Environmental Technology Letters, 9, 857–868.
Nriagu, J. O., & Pacyna, J. M. (1988). Quantitative assessment of world-wide contamination of air, water and soils by trace metals. Nature, 333, 134–139.
Oguzie, E. E., Agochukwu, I. B., Onuchukwu, A. I., & Offem, J. O. (2002). Ground water contamination: A simulation study of buried waste metallic contaminant penetration through the aquifers. Journal of the Chemical Society of Nigeria, 27, 82–84.
Packham, R. F. (1996). Drinking water quality and health. In R. M. Harrison (Ed.), Pollution, causes, effects and control (pp. 52–65). UK: The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Radojevic, M., & Bashkin, V. N. (1999). Practical environmental analysis. Cambridge CB4 0WF, UK: The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Ramesh, R., Ramanathan, A. L., Ramesh, S., Purvaja, R., & Subramanian, V. (2000). Distribution of rare earth elements in the surficial sediments of the Himalaya river system. Geochemical Journal, 34, 295–319.
Razo, I., Carrizales, L., Castro, J., Díaz-Barriga, F., & Monroy, M. (2004). Arsenic and heavy metal pollution of soil, water and sediments in a semi-arid climate mining area in Mexico. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 152, 129–152.
Samina, J., Jaffar, M., & Shah, M. H. (2004). Physico-chemical profiling of groundwater along Hazara strip, Pakistan. Journal of the Chemical Society of Pakistan, 26, 288–292.
Sandhu, S. S., Warren, W. J., & Nelson, P. (1976). Trace inorganics in rural potable water and their correlation to possible sources. Water Research, 12, 257–261.
Santos, E. E., Lauria, D. C., Porto, C. L., & Silveira, D. E. (2004). Assessment of daily intake of trace elements due to consumption of foodstuffs by adult inhabitants of Rio de Janeiro city. Science of the Total Environment, 327, 69–79.
Speir, T. W., Van Schaik, A. P., Percival, H. J., Close, M. E., & Pang, L. (2003). Heavy metals in soil, plants and ground water following high-rate sewage sludge application to land. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 150, 319–358.
StatSoft, Inc. (1999). STATISTICA for Windows (Computer program manual). Tulsa, OK: StatSoft, Inc.
Tahri, M., Benyaich, F., Bounakhla, M., Bilal, E., Gruffat, J. J., Moutte, J., et al. (2005). Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contents in soils, sediments and water in the region of Meknes (central Morocco). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 102(1–3), 405–417.
Vallee, B., & Ulmer, D. O. (1972). Biochemical effects of mercury, cadmium and lead. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 41, 91–128.
Vidal, M., Melgar, J., Lopez, A., & Santoalla, M. C. (2000). Spatial and temporal hydrochemical changes in ground water under the contaminating effects of fertilizers and wastewater. Journal of Environmental Management, 60, 215–225.
Watt, G. C. M., Britton, A., Gilmour, H. G., Moore, M. R., Murray, G. D., & Robertson, S. J. (2000). Public health implications of new guidelines for lead in drinking water: A case study in an area with historically high water lead levels. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 38, S73–S79.
Yeung, I. M. H. (1999). Multivariate analysis of the Hong Kong Victoria harbour water quality data. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 59, 331–342.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tariq, S.R., Shah, M.H., Shaheen, N. et al. Statistical source identification of metals in groundwater exposed to industrial contamination. Environ Monit Assess 138, 159–165 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-9753-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-9753-8