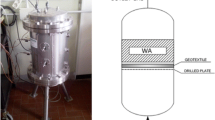
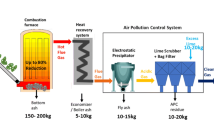
Abstract
The increasing volumes of municipal solid waste produced worldwide are encouraging the development of processes to reduce the environmental impact of this waste stream. Combustion technology can facilitate volume reduction of up to 90%, with the inorganic contaminants being captured in furnace bottom ash, and fly ash/APC residues. The disposal or reuse of these residues is however governed by the potential release of constituent contaminants into the environment. Accelerated carbonation has been shown to have a potential for improving the chemical stability and leaching behaviour of both bottom ash and fly ash/APC residues. However, the efficacy of carbonation depends on whether the method of gas application is direct or indirect. Also important are the mineralogy, chemistry and physical properties of the fresh ash, the carbonation reaction conditions such as temperature, contact time, CO2 partial pressure and relative humidity. This paper reviews the main issues pertaining to the application of accelerated carbonation to municipal waste combustion residues to elucidate the potential benefits on the stabilization of such residues and for reducing CO2 emissions. In particular, the modification of ash properties that occur upon carbonation and the CO2 sequestration potential possible under different conditions are discussed. Although accelerated carbonation is a developing technology, it could be introduced in new incinerator facilities as a “finishing step” for both ash treatment and reduction of CO2 emissions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, S. A., & Ali, M. (2004). Partnerships for solid waste management in developing countries: Linking theories to realities. Habitat International, 28, 467–479.
Ali, A. (2003). Waste management – Developing world and countries in transit. In Christensen, T. H., Cossu, R., Stegmann, R. (Eds.) Proceedings of Sardinia 2003, Ninth International Waste Management and Landfill Symposium S. Margherita di Pula. Cagliari, Italy, (on CD ROM).
Anthony, E. J., Bulewicz, E. M., Dudek, K., & Kozak, A. (2002). The long term behaviour of CFBC ash-water systems. Waste Management, 22, 99–111.
Arickx, S., Van Gerven, T., & Vandecasteele, C. (2006). Accelerated carbonation for treatment of MSWI bottom ash. Journal of Hazardous Materials, B 137, 235–243.
Astrup, T., Dijkstra, J. J., Comans, R. N. J., van der Sloot, H. A., & Christensen, T. H. (2006a). Geochemical modeling of leaching from MSWI air-pollution-control residues. Environmental Science and Technology, 40, 3551–3557.
Astrup, T., Mosbæk, H., & Christensen, T. H. (2006b). Assessment of long-term leaching from waste incineration air-pollution-control residues. Waste Management, 26, 803–814.
Astrup, T., Rosenblad, C., Trapp, S., & Christensen, T. H. (2005). Chromium release from waste incineration air-pollution-control residues. Environmental Science and Technology, 39, 3321–3329.
Baciocchi, R., Polettini, A., Pomi, R., Prigiobbe, V., Von Zedwitz, V. N., Steinfeld, A. (2006a). CO2 sequestration by direct gas–solid carbonation of APC residues. Energy and Fuels, 20, 1933–1940.
Baciocchi, R., Polettini, A., Pomi, R., Prigiobbe, V., Von Zedwitz, V. N., & Steinfeld, A. (2006b). Performance and kinetics of CO2 sequestration by direct gas–solid carbonation of APC residues. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Green House Gas Technology. Trondheim (Norway).
Baciocchi, R., Polettini, A., Pomi, R., Prigiobbe, V., Von Zedwitz, V. N., & Steinfeld, A. (2006c). Accelerated gas/solid carbonation of incinerator residues: kinetics and effects on metal mobility. In Extended abstracts of the First International Conference on Accelerated Carbonation for Environmental and Materials Engineering, June 12–14, London UK, Cement and Concrete Science (Ed.).
Bhatia, S. K., & Perlmutter, D. D. (1983). Effect of the product layer on the kinetics of the CO2-lime reaction. AIChE Journal, 29, 79–86.
Bin-Shafique, M. S., Walton, J. C., Gutierrez, N., Smith, R. W., & Tarquin, A. J. (1998). Influence of carbonation on leaching of cementitious waste forms. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 124, 463–467.
Bodénan, F., Azaroual, M., & Piantone, P. (2000). Forecasting the long-term behaviour of municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash: Rapid combined tests. In Woolley, G. R., Goumans, J. J. J. M., & Wainwright, P. (Eds.), Waste materials in construction, studies in environmental sciences 71 (pp. 475–482). Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Bodénan, F. & Deniard, Ph. (2003). Characterization of flue gas cleaning residues from European solid waste incinerators: Assessment of various Ca-based sorbent processes. Chemosphere, 51, 335–347.
Bone, B. D., Knox, K., Picken, A., & Robinson, H. D. (2003). The effect of carbonation on leachate quality from landfilled municipal solid waste (MSW) incinerator residues. In Christensen, T. H., Cossu, R., & Stegmann, R. (Eds.), Proc. Sardinia 2003, Ninth International Waste Management and Landfill Symposium S. Margherita di Pula. Cagliari, Italy. (on CD ROM).
CEU (1999). Council directive 1999/31/EC of 26 April 1999 on the landfill of waste. Official Journal of the European Communities, L128, 1–19.
Cornelis, G., Van Gerven, T., & Vandecasteele, C. (2006). Antimony leaching from uncarbonated and carbonated MSWI bottom ash. Journal of Hazardous Materials, B 137, 1284–1292.
Damodaran, N., Robinson, A., David, E., & Kalas-Adams, N. (2003). Urban Solid Waste Generation and Management in India. In Christensen, T. H., Cossu, R., & Stegmann, R. (Eds.), Proc. Sardinia 2003, Ninth International Waste Management and Landfill Symposium S. Margherita di Pula. Cagliari, Italy. (on CD ROM).
DEFRA (Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs) (2006): Municipal waste management in the European Union. Retrieved from http://www.defra.gov.uk/environment/statistics/waste/kf/wrkf08.htm.
Dijkstra, J. J., van Zomeren, A., Meeussen, J. C. L., & Comans, R. N. J. (2006). Effect of accelerated aging of MSWI bottom ash on the leaching mechanisms of copper and molybdenum. Environmental Science & Technology, 40, 4481–4487.
Dinsdale, J. Environment Agency (2006). Municipal waste incineration. Retrieved from http://www.environmentagency.gov.uk/yourenv/eff/1190084/resources_waste/213982/203410/.
Ecke, H. (2003). Sequestration of metals in carbonated municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) fly ash. Waste Management, 23, 631–640.
Euractiv (EU News and Policy Positions) (2005). Commission opts for hands off approach on waste policy. Retrieved from http://www.euractiv.com/en/environment/commission-opts-hands-approachwaste-policy/article-151198.
Eusden, J. D., Eighmy, T. T., Hockert, K., Holland, E., & Marsella, K. (1999). Petrogenesis of municipal solid waste combustion bottom ash. Applied Geochemistry, 14, 1073–1091.
Fernández-Bertos, M., Simons, S. J. R., Hills, C. D., & Carey, P. J. (2004a). A review of accelerated carbonation technology in the treatment of cement-based materials and sequestration of CO2. Journal of Hazardous Materials, B112, 193–205.
Fernández-Bertos, M., Li, X., Simons, S. J. R., Hills, C. D., & Carey, P. J. (2004b). Investigation of accelerated carbonation for the stabilization of MSW incinerator ashes and the sequestration of CO2. Green Chemistry, 6(8), 428–436.
Fernández-Bertos, M., Simons, S. J. R., Hills, C. D., & Carey, P. J. (2006). Kinetic studies of carbonation of MSWI ashes. In Cement and Concrete Science (Ed.), Extended abstracts of the First International Conference on Accelerated Carbonation for Environmental and Materials Engineering. London UK.
Hänchen, M., Prigiobbe, V., Storti, G., & Mazzotti, M. (2006). Mineral carbonation: Kinetic study of olivine dissolution and carbonate precipitation. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Green House Gas Technology. Trondheim (Norway).
Hjelmar, O. (1996). Disposal strategies for municipal solid waste incineration residues. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 47, 345–368.
Huijgen, W. J. J., & Comans, R. N. J. (2003). Carbon dioxide sequestration by mineral carbonation: Literature review. ECN-C-03016 (February 2003). Report downloadable from http://www.ecn.nl.
Huijgen, W. J. J., & Comans, R. N. J. (2006). Carbonation of steel slag for CO2 sequestration: leaching of products and reaction mechanisms. Environmental Science and Technology, 40, 2790–2796.
Huijgen, W. J. J., Witkamp, G. J., & Comans, R. N. J. (2005). Mineral CO2 sequestration by steel slag carbonation. Environmental Science and Technology, 39, 9676–9682.
Huijgen, W. J. J., Witkamp, G. J., & Comans, R. N. J. (2006). Mechanisms of aqueous wollastonite carbonation as a possible CO2 sequestration process. Chemical Engineering Science, 61, 4242–4251.
IAWG (The International Ash Working Group) (1995). An international perspective on characterization and management of residues from municipal solid waste incineration. Final document.
Ibànez, R., Andrés, A., Viguri, J. R., Ortiz, I., & Irabien, J. A. (2000). Characterization and management of incinerator wastes. Journal of Hazardous Materials, A79, 215–227.
IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change) (2005). IPCC special report on carbon dioxide capture and storage. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Jia, L., & Anthony, E. J. (2000). Pacification of FBC ash in a pressurized TGA. Fuel, 79, 1109–1114.
Johanneson, B., & Utgennant, P. (2001). Microstructural changes caused by carbonation of cement mortar. Cement and Concrete Research, 31, 925–931.
Johnson, D. C. (2000). Accelerated carbonation of waste calcium silicate materials. SCI Lecture Papers Series.
Jung, C. H., Matsuto, T., Tanaka, N., & Okada, T. (2004). Metal distribution in incineration residues of municipal solid waste (MSW) in Japan. Waste Management, 24, 381–391.
Kirby, C. S., & Rimstidt, J. D. (1993). Mineralogy and surface properties of municipal solid waste ash. Environmental Science & Technology, 27, 652–660.
Kodama, S., Nishimoto, T., Yogo, K., & Yamada, K. (2006). Design and evaluation of a new CO2 fixation process using alkaline-earth metal wastes. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Green House Gas Technology. Trondheim (Norway).
Lackner, K. S. (2002). Carbonate chemistry for sequestering fossil carbon. Annual Review for Energy and the Environment, 27, 193–232.
Lackner, K. S., Butt, D. P., & Wendt, C. H. (1997). Progress on binding CO2 in mineral substrates. Energy Conversion and Management, 38, S259–264.
Lackner, K. S., Wendt, C. H., Butt, D. P., Joyce, E. L., Jr., & Sharp, D. H. (1995). Carbon dioxide disposal in carbonate minerals. Energy, 20, 1153–1170.
Lange, L. C., Hills, C. D., & Poole, A. B. (1996). The effect of accelerated carbonation on the properties of cement-solidified waste forms. Waste Management, 16, 757–763.
Li, X., Hills, C. D., Carey, P., & Simons, S. J. R. (2006). Accelerated carbonation of municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) APC residues. In Cement and Concrete Science (Ed.), Extended abstracts of the First International Conference on Accelerated Carbonation for Environmental and Materials Engineering. London UK.
Maroto-Valer, M. M., Fauth, D. J., Kutcha, M. E., Zhang, Y., & Andrésen, J. M. (2005). Activation of magnesium rich minerals as carbonation feedstock materials for CO2 sequestration. Fuel Processing Technology, 86, 1627–1645.
Meima, J. A., & Comans, R. N. J. (1997). Geochemical modeling of weathering reactions in municipal solid waste incinerator bottom ash. Environmental Science & Technology, 31(5), 1269–1276.
Meima, J. A., & Comans, R. N. J. (1999). The leaching of trace elements from municipal solid waste incinerator bottom ash at different stages of weathering. Applied Geochemistry, 14, 159–171.
Meima, J. A., van der Weijden, R. D., Eighmy, T. T., & Comans, R. N. J. (2002). Carbonation processes in municipal solid waste incinerator bottom ash and their effect on the leaching of copper and molybdenum. Applied Geochemistry, 17, 1503–1513.
O’Connor, W. K., Dahlin, D. C., Rush, G. E., Gerdemann, S. J., Penner, L. R., & Nilsen, D. N. (2005). Aqueous mineral carbonation: mineral availability, pretreatment, reaction parameters, and process studies. Albany, OR: Albany Research Center.
Papadakis, V. G., Vayenas, C. G., & Fardis, M. N. (1991). Experimental investigation and mathematical modeling of the concrete carbonation problem. Chemical Engineering Science, 46(5/6), 1333–1338.
Park, A., & Fan, L. S. (2004). CO2 mineral sequestration: Physically activated dissolution of serpentine and pH swing process. Chemical Engineering Science, 59, 5241–5247.
Park, A., Jadhav, R., & Fan, L. S. (2003). CO2 mineral sequestration: Chemically enhanced aqueous carbonation of serpentine. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 81, 885–890.
Pettersson, C., Ephraim, J., & Allard, B. (1994). On the composition and properties of humic substances isolated from deep groundwater and surface waters. Organic Geochemistry, 21, 443–451.
Polettini, A., & Pomi, R. (2004). The leaching behaviour of incineration bottom ash as affected by accelerated ageing. Journal of Hazardous Materials, B113(1–3), 209–215.
Polettini, A., Pomi, R., & Ragaglia, M. (2005). Accelerated ageing as a tool for sustainable disposal of incinerator bottom ash. In Cossu, R., Stegmann, R. (Eds.), Proc. Sardinia 2005, Tenth International Waste Management and Landfill Symposium, S. Margherita di Pula (CA). (on CD ROM).
Reddy, K. J., Gloss, S. P., & Wang, L. (1994). Reaction of CO2 with alkaline solid wastes to contaminant mobility. Water Research, 28(6), 1377–1382.
Rendek, E., Ducom, G., & Germain, P. (2006a). Carbon dioxide sequestration in municipal solid waste incinerator (MSWI) bottom ash. Journal of Hazardous Materials, B128, 73–79.
Rendek, E., Ducom, G., & Germain, P. (2006b). Influence of organic matter on municipal solid waste incinerator bottom ash carbonation. Chemosphere, 64, 1212–1218.
Sabbas, T., Polettini, A., Pomi, R., Astrup, T., Hjelmar, O., Mostbauer, P., et al. (2003). Management of municipal solid waste incineration residues. Waste Management, 23, 61–88.
Sakita S., Shimaoka T., Nishigaki M., & Tanaka T. (2006). Carbonation treatment of lead in municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash for beneficial use. In Cement and Concrete Science (Ed.), Extended abstracts of the First International Conference on Accelerated Carbonation for Environmental and Materials Engineering. London, UK.
Short, N. R., Purnell, P., & Page, C. L. (2001). Preliminary investigations into the supercritical carbonation of cement pastes. Journal of Material Science, 36, 35–41.
Shtepenko, O. L., Hills, C. D., Coleman, N. J., & Brough, A. (2005). Characterization and preliminary assessment of a sorbent produced by accelerated mineral Carbonation. Environmental Science and Technology, 39, 345–354.
Speiser, C., Baumann, T., & Niessner, R. (2000). Morphological and chemical characterization of calcium-hydrate phases formed in alteration processes of deposited municipal solid waste incinerator bottom ash. Environmental Science and Technology, 34, 5030–5037.
Steketee, J. J., Rutten, S., & de Bode, A. (2006). Accelerated carbonation of MSWI bottom ash on a practical scale. In Cement and Concrete Science (Ed.), Extended abstracts of the First International Conference on Accelerated Carbonation for Environmental and Materials Engineering. London, UK.
Stolaroff, J. K., Lowry, G. V., & Keith, D. W. (2005). Using CaO- and MgO-rich industrial waste streams for carbon sequestration. Energy Conversion & Management, 46, 687–699.
Tawfic, T. A., Reddy, K. J., & Gloss, S. P. (1995). Reaction of CO2 with clean coal technology ash to reduce trace element mobility. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 84, 385–398.
Todorovic, J., & Ecke, H. (2006). Demobilization of critical contaminants in four typical waste-to-enery ashes by carbonation. Waste Management, 26, 430–441.
Urban Age (1999). What cities do with their waste, 6, 32–33.
Van Balen, K. (2005). Carbonation reaction of lime, kinetics at ambient temperature. Cement and Concrete Research, 35, 647–657.
Van Gerven, T., Cornelis, G., Vandoren, E., Garrabrants, A. C., Sanchez, F., Kosson, D. S., et al. (2006). Effects of progressive carbonation on heavy metal leaching from waste-containing cement matrices. AIChE Journal, 52(2), 826–837.
Van Gerven, T., Van Keer, E., Arickx, S., Jaspers, M., Wauters, G., & Vandecasteele, C. (2005). Carbonation of MSWI-bottom ash to decrease heavy metal leaching, in view of recycling. Waste Management, 25, 291–300.
Zevenbergen, C., & Comans, R. N. J. (1994). Geochemical factors controlling the mobilization of major elements during weathering of MSWI bottom ash. In Goumans, J. J. J. M., van der Sloot, H. A., & Aalbers (Eds.), Environmental aspects of construction with waste materials (pp. 179–194). Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Ziock, H. J., Lackner, K. S., & Harrison, D. P. (2000). Zero emission coal power, a new concept. In Proc. of the 1st US National Conference on Carbon Dioxide Sequestration. Washington DC: DOE Publications.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Costa, G., Baciocchi, R., Polettini, A. et al. Current status and perspectives of accelerated carbonation processes on municipal waste combustion residues. Environ Monit Assess 135, 55–75 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-9704-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-9704-4