Abstract
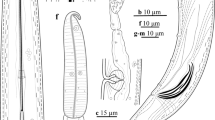
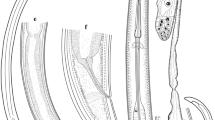
Five populations of a new dagger nematode species were recovered from natural grasslands and forests of north and northwest Iran, and described based upon morphological and molecular data in present paper. Xiphinema hyrcaniense n. sp. is characterized by 3.9–5.5 mm long females, having 102–142 μm long odontostyle, 64–88 μm long odontophore, guiding ring located at 115–147 μm distance from anterior end, two equally developed genital branches having crystalloids in tubular part of uteri and pseudo-Z-organ at their junction with pars dilatata uteri, short, rounded to dorsally more convex tail with a mucro or in few specimens, without it. Common males with 72–95 μm long spicules and four juvenile developmental stages. The new species is similar to six known species belonging to artificial morphospecies group 5, especially looking closest to X. montenegrinum in its general morphology, but could be separated by ontogenesis of tail shape and morphometric indices. In molecular phylogenetic analyses using partial large subunit, and internal transcribe spacer 1 ribosomal DNA (LSU D2-D3 and ITS1 rDNA) sequences, the new species formed a clade with X. cretense and Xiphinema sp. in LSU; and in ITS1 tree, with X. dentatum and X. paradentatum.








Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
12 April 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-021-02272-1
Notes
The name of the new species is derived from Hyrcania, meaning “Wolf’s Land”, the ancient region located in southeast of the Caspian Sea, the occurrence region of the type population of the new species
References
Barsi, L., Fanelli, E., & De Luca, F. (2017). A new record of Xiphinema dentatum Sturhan, 1978 and description of X. paradentatum sp. n. (Nematoda: Dorylaimida) from Serbia. Nematology, 19, 925–949.
Barsi, L., Lamberti, F., & Agostinelli, A. (1998). Xiphinema densispinatum sp. n. from Bosnia and Herzegovina and X. montenegrinum sp. n. from Montenegro, Yugoslavia (Nematoda: Dorylaimida). Nematologia Mediterranea, 26, 67–77.
Bravo, M. A., & Roca, F. (1995). Xiphinema cadavalense sp. n. (Nemata: Longidoridae) from Portugal. Fundamental and Applied Nematology, 18, 17–20.
Cobb, N. A. (1913). New nematode genera found inhabiting fresh water and non-brackish soils. Journal of the Washington Academy of Sciences, 3, 432–444.
Cohn, E. (1970). Observations on the feeding and symptomatology of Xiphinema and Longidorus on selected host roots. Journal of Nematology, 2, 167–173.
Cohn, E. (1975). Relations between Xiphinema and Longidorus and their host plants. In F. Lamberti , C. E. Taylor & J. W. Seinhorst ( Eds.). Nematode vectors of plant viruses (pp. 365–385). London: Plenum Press.
Coomans, A., Huys, R., Heyns, J., & Luc, M. (2001). Character analysis, phylogeny and biogeography of the genus Xiphinema Cobb, 1913 (Nematoda: Longidoridae). Annales Sciences Zoologiques, 287, 1–239.
Dalmasso, A. (1969). Étude anatomique et taxonomique des genres Xiphinema, Longidorus et Paralongidorus (Nematoda: Dorylaimida). Mémoires du Museum National d’Histoire Naturelle, Nouvelle Série, Série A, Zoologie, 61, 34–82.
Decraemer, W., & Robbins, R. T. (2007). The who, what and where of Longidoridae and Trichodoridae. Journal of Nematology, 39, 295–297.
Decraemer, W., & Geraert, E. (2013). Ectoparasitic nematodes. In R. N. Perry & M. Moens (Eds.), Plant Nematology (2nd ed., pp. 179–216). Wallingford, UK ; Cambridge, MA, USA: CABI.
De Grisse, A. T. (1969). Redescription ou modifications de quelques techniques utilisées dans l’étude des nematodes phytoparasitaires. Mededelingen Rijksfakulteiteit Landbouwwetenschappen. Gent, 34, 351–369.
de Man, J. G. (1884). Die frei in der reinen Erde und im süssen Wasser lebenden Nematoden der niederländischen Fauna (pp. 1–206). Leiden.
Gutiérrez-Gutiérrez, C., Palomares-Rius, J. E., Cantalapiedra-Navarrete, C., Landa, B. B., Esmenjaud, D., & Castillo, P. (2010). Molecular analysis and comparative morphology to resolve a complex of cryptic Xiphinema species. Zoologica Scripta, 39, 483–498.
He, Y., Subbotin, S. A., Rubtsova, T. V., Lamberti, F., Brown, D. J. F., & Moens, M. (2005). A molecular phylogenetic approach to Longidoridae (Nematoda: Dorylaimida). Nematology, 7, 111–124.
Huson, D. H., & Scornavacca, C. (2012). Dendroscope 3: An interactive tool for rooted phylogenetic trees and networks. Systematic Biology, 61, 1061–1067.
Jahanshahi Afshar, F. (2019). The first molecular phylogenetic study of Xiphinema robbinsi Pedram, Niknam & Decraemer, 2008 (Nematoda: Longidoridae) based on specimens from the type locality. Nematology, 21, 333–335.
Jahanshahi Afshar, F., Shahryari, F., Mokhtassi-Bidgoli, A., Castillo, P., Mirzaie Fouladvand, Z., & Pedram, M. (2020). Occurrence of Xiphinema santos Lamberti, Lemos, Agostinelli & D’Addabo 1993 (Nematoda: Longidoridae), a X. americanum-group member in Iran. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 157, 281–291.
Jahanshahi Afshar, F., Pedram, M., & Mobasseri, M. (2021). Description of Xiphinema persicum n. sp. (Nematoda: Longidoridae), a X. americanum-group species from Iran. European Journal of Plant Pathology.https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-021-02201-2
Jahanshahi Afshar, F. J., Shahryari, F., Gharibzadeh, F., Pourjam, E., & Pedram, M. (2019). Description of Xiphinema azarbaijanense n. sp. (Nematoda; Longidoridae) from West Azarbaijan province, northwestern Iran. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 155, 417–434.
Katoh, K., & Standley, D. M. (2013). MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30, 772–780.
Kiontke, K., Gavin, N. P., Raynes, Y., Roehrig, C., Piano, F., & Fitch, D. H. A. (2004). Caenorhabditis phylogeny predicts convergence of hermaphroditism and extensive intron loss. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101, 9003–9008.
de Kruger, J. C. (1988). The uterine differentiation in Xiphinema. Phytophylactica, 20, 233–251.
Lamberti, F., Castillo, P., Gómez-Barcina, A., & Agostinelli, A. (1992). Description of six new species of Xiphinema (Nematoda, Dorylaimida) from the Mediterranean region. Nematologia Mediterranea, 20, 125–139.
Larget, B., & Simon, D. L. (1999). Markov chain Monte Carlo algorithms for the Bayesian analysis of phylogenetic trees. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 16, 750–759.
Loof, P. A. A., & Coomans, A. (1972). The oesophageal gland nuclei of Longidoridae (Dorylaimida). Nematologica, 21, 213–233.
Loof, P. A. A., & Luc, M. (1990). A revised polytomous key for the identification of species of the genus Xiphinema Cobb, 1913 (Nematoda: Longidoridae) with exclusion of the Xiphinema americanum group. Systematic Parasitology, 16, 35–66.
Loof, P. A. A., & Luc, M. (1993). A revised polytomous key for the identification of species of the genus Xiphinema Cobb, 1913 (Nematoda: Longidoridae) with exclusion of the X. americanum group: Supplement 1. Systematic Parasitology, 24, 185–189.
Loof, P. A. A., Luc, M., & Baujard, P. (1996). A revised polytomous key for the identification of species of the genus Xiphinema Cobb, 1913 (Nematoda: Longidoridae) with exclusion of the X. americanum group: Supplement 2. Systematic Parasitology, 33, 23–29.
Luc, M., & Coomans, A. (1988). Xiphinema smoliki n. sp. and Longidorus pawneensis n. sp. (Nemata: Longidoridae) from Colorado, USA. Revue de nématologie, 11, 137–142.
Luc, M., & Dalmasso, A. (1964). Trois nouveaux Xiphinema associés à la vigne (Nematoda: Dorylaimidae). Nematologica, 9, 531–541.
Luc, M., Loof, P. A. A., & Coomans, A. (1986). Description of Xiphinema thorneanum n. sp. and observations on some species of the genus (Nemata: Longidoridae). Revue de Nématologie, 9, 337–346.
MacFarlane, S. A., Zasada, I., Lemaire, O., & Demangeat, G. (2016). Nematode-Borne Plant Viruses. In J. K. Brown (Ed.), Vector-mediated transmission of plant pathogens (pp. 365–378). St. Paul: APS Press.
Mirzaie Fouladvand, Z., Pourjam, E., Castillo, P., & Pedram, M. (2019). Genetic diversity, and description of a new dagger nematode, Xiphinema afratakhtehnsis sp. nov., (Dorylaimida: Longidoridae) in natural forests of southeastern Gorgan, northern Iran. PloS one, 14, e0214147.
Micoletzky, H. (1927). Neue und seltene freilebende Nematoden aus dem Wolgagebiet (Kama). Zoologischer Anzeiger, 73, 113–123.
Mirzaei, S., Pourjam, E., & Pedram, M. (2015). Molecular characterisation of, and new data on, two populations of Xiphinema ingens Luc & Dalmasso, 1964 (Nematoda: Longidoridae) from Iran. Nematology, 17, 125–138.
Mobasseri, M., Hutchinson, M. C., Jahanshahi Afshar, F., & Pedram, M. (2019). New evidence of nematode endosymbiont bacteria coevolution based on one new and one known dagger nematode species of Xiphinema americanum-group (Nematoda, Longidoridae). PLoS One, 14, e0217506.
Nunn, G.B. (1992). Nematode molecular evolution. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK.
Nylander, J. A. A. (2004). MrModeltest v2. Program distributed by the author. Evolutionary Biology Centre: Uppsala University.
Palomares-Rius, J. E., Escobar, C., Cabrera, J., Vovlas, A., & Castillo, P. (2017). Anatomical alterations in plant tissues induced by plant-parasitic nematodes. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8, 1987.
Pedram, M. (2018). Nematodes of the family Longidoridae. Plant-parasitic nematodes in Iran. Science Reference in collaboration with the Iranian Society of Nematology, 627–667.
Rambaut, A., & Drummond, A. J. (2009). Tracer version 1.5 [computer program] http://beast.bio.ed.ac.uk/.
Robbins, R. T., Brown, D. J. F., Halbrendt, M. J., & Vrain, T. C. (1996). Compendium of juvenile stages of Xiphinema species (Nematoda: Longidoridae). Russian Journal of Nematology, 4, 163–171.
Ronquist, F., & Huelsenbeck, J. P. (2003). MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics, 19, 1572–1574.
Roshan-Bakhsh, A., Pourjam, E., Pedram, M., Robbins, R. T., & Decraemer, W. (2014). Description of Xiphinema castilloi sp. n. (Dorylaimida: Longidoridae) from Iran and its phylogenetic relationships. Nematology, 16, 359–368.
Siddiqi, M. R. (2000). Tylenchida Parasites of Plants and Insects (2nd ed. p. 833). Wallingford: UK, CABI publishing.
Sturhan, D. (1978). Zwei neue Xiphinema-Arten aus Deutschland (Nematoda, Dorylaimida). Nematologica, 24, 19–28.
Subbotin, S., Perry, R., Warry, A., & Halford, P. (2000). Variations in ribosomal DNA sequences and phylogeny of Globodera parasitising solanaceous plants. Nematology, 2, 591–604.
Taylor, C. E., & Brown, D. J. F. (1997). Nematode vectors of plant viruses. Wallingford: CAB International.
Thorne, G. (1939). The monograph of the nematodes of the superfamily Dorylaimoidea. Capita Zoologica, 8, 1–261.
Tzortzakakis, E. A., Archidona-Yuste, A., Cantalapiedra-Navarrete, C., Nasiou, E., Lazanaki, M. S., Kabourakis, E. M., Palomares-Rius, J. E., & Castillo, P. (2014). Integrative diagnosis and molecular phylogeny of dagger and needle nematodes of olives and grapevines in the island of Crete, Greece, with description of Xiphinema cretense n. sp. (Nematoda, Longidoridae). European Journal of Plant Pathology, 140, 563–590.
Tzortzakakis, E. A., Archidona-Yuste, A., Cantalapiedra-Navarrete, C., Nasiou, E., Palomares-Rius, J. E., & Castillo, P. (2015). Description and molecular characterisation of Xiphinema herakliense n. sp. (Nematoda: Longidoridae) from wild and cultivated olives in Crete. Nematology, 17, 231–245.
Acknowledgements
The soil samples from Gilan province, studied in present study, were kindly provided by Dr. Yousef Panahandeh. This help is appreciated. The technical helps of Dr. Mohammad Reza Atighi and Dr. Farahnaz Jahanshahi Afshar are appreciated. We thank Tarbiat Modares University and Iranian National Science Foundation (INSF) for financial supports.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Informed consent
The authors certify that they have accepted the principles of ethical standards and that guidelines of professional conduct have been followed. The funders had no role in designing of this study, collecting and analyzing of the data, preparing the manuscript and are not involved in evaluating or publishing process of this research.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
The soil samples analyzed in this study were collected from the natural public regions that are not under protection against soil samplings.
Conflict of interest
All the authors certify that they do not have any conflict of interest, the presented data are original and the presented data are not published, and are not under evaluation for publication elsewhere, all prevailing local, national and international regulations and conventions, and normal scientific ethical practices, have been respected. They also certify that the final version of this manuscript has been reviewed by all authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fadakar, S., Pourjam, E., Barsi, L. et al. A new species of the genus Xiphinema Cobb 1913 (Nematoda: Longidoridae) from north and northwest Iran. Eur J Plant Pathol 160, 557–574 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-021-02264-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-021-02264-1