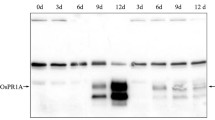
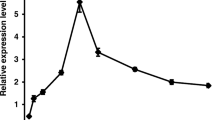
Abstract
Bacterial blight caused by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo) is a major disease of rice worldwide. Xoo secretes effector proteins (T3Es) directly into the rice cell through a hrp-encoded specialized type III secretion apparatus to induce blight. We examined the function of XopF, one of the conserved effectors in Xoo, using a null mutant developed through a PCR-based homologous recombination strategy. We studied inducible, hrp-dependent expression pattern of xopF. We confirmed that XopF is translocated in rice cytosol through T3SS using adenylate cyclase activity assay. XopF regulate the in planta Xoo growth and suppress PAMP-triggered immune (PTI) response in rice. Xoo wild but not mutant, Xoo ∆xopF produced intense blight lesions upon inoculation using leaf clipping method. Further, Xoo ∆xopF showed significant reduction in planta colonization relative to the wild strain. The relative expression analysis of PTI marker genes, PR10, OsWRKY13, OsRLCK16, and OsFLS2 indicated that these genes were up-regulated 1.5 to 5 fold upon challenge-inoculation with Xoo ∆xopF indicating the role of XopF in suppressing PTI in rice. Xoo ∆xopF mutant induced more callose deposition in infected rice leaves. XopF::EYFP fusion gene product was localized to the plasma membrane when transiently expressed in Nicotiana benthamiana as well as in living onion epidermal cells. Collectively, the present study shows that XopF repress basal PTI response in plants, and thus favours Xoo growth and pathogenicity in rice.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramovitch, R. B., Janjusevic, R., Erec Stebbins, C., & Martin, G. B. (2006). Type III effector AvrPtoB requires intrinsic E3 ubiquitin ligase activity to suppress plant cell death and immunity. Proceedings of National Academy of Sciences of the United States, 103, 2851–2856.
Akimoto-Tomiyama, C., Furutani, A., Tsuge, S., Washington Erica, J., Nishizawa, Y., Minami, E., & Ochiai, H. (2012). XopR, a Type III effector secreted by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae, suppresses microbe-associated molecular pattern triggered immunity in Arabidopsis thaliana. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 25, 505–514.
Alfano, J. R., & Collmer, A. (1997). The type III (Hrp secretion pathway of plant pathogenic bacteria: trafficking harpins, Avr proteins, and death. Journal of Bacteriology, 179, 5655–5662.
Alfano, J. R., & Collmer, A. (2004). Type III secretion system effector proteins: double agents in bacterial disease and plant defense. Annual Reiew Phytopathology, 42, 385–414.
Amaral, A.M. do., Toledo, C.P., Baptista, J.C., Machado, M.A. (2005). Transformation of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri by electroporation. Fitopatologia Brasileira [online], 30, 292–294.
Ausubel, F. M. (2005). Are innate immune signalling pathways in plants and animals conserved? Nature Immunology, 6, 973–979.
Bartetzko, V., Sonnewald, S., Vogel, F., Hartner, K., Stadler, R., Hammes, U. Z., & Frederik, B. (2009). The Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria type III effector protein XopJ inhibits protein secretion: evidence for interference with cell wall–associated defense responses. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 22, 655–664.
Casper-Lindley, C., Dahlbeck, D., Clark, E. T., & Staskawicz, B. J. (2002). Direct biochemical evidence for type III secretion dependent translocation of the AvrBs2 effector protein into plant cells. Proceedings of National Academy of Sciences of the United States, 99(12), 8336–8341.
Cheong, H., Kim, C. Y., Jeon, J. S., Lee, B. M., Sun Moon, J., & Hwang, I. (2013). Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae type III effector XopN targets OsVOZ2 and a putative thiamine synthase as a virulence factor in rice. PLoS ONE, 8(9), e73346. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0073346.
Datsenko, K. A., & Wanner, B. L. (2000). One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proceedings of National Academy of Sciences of the United States, 97(12), 6640–6645.
Goel, A. K., Lundberg, D., Torres, M. A., Matthews, R., Akimoto-Tomiyama, C., Farmer, L., Dangle, J. L., & Grant, S. R. (2008). The Pseudomonas syringae type III effector HopAM1 enhances virulence on water-stressed plants. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 21, 361–370.
Gu, K., Yang, B., Tian, D., Wu, L., Wang, D., Sreekala, C., Yang, F., Chu, Z., Wang, G. L., White, F. F., & Yin, Z. (2005). R gene expression induced by a type-III effector triggers disease resistance in rice. Nature, 435, 1122–1125.
Jelenska, J., Yao, N., Vinatzer, B. A., Wright, C. M., Brodsky, J. L., & Greenberg, J. T. (2007). A J domain virulence effector of Pseudomonas syringae remodels host chloroplasts and suppresses defenses. Currrent Biology, 17, 499–508.
Jiang, B. L., He, Y. Q., Cen, W. J., Wei, H. Y., Jiang, G. F., Jiang, W., Hang, X. H., Feng, J. X., Lu, G. T., Tang, D. J., & Tang, J. L. (2008). The type III secretion effector XopXccN of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris is required for full virulence. Research in Microbiology, 159, 216–220.
Jones, J. D. G., & Dangl, J. L. (2006). Plant immune system. Nature, 444, 323–329.
Kauffman, H. E., Reddy, A. P. K., Hsieh, S. P. Y., & Merca, S. D. (1973). An improved technique for evaluating resistance to rice varieties of Xanthomonas oryzae. Plant Disease Report, 57, 537–541.
Kim, J. G., Taylor, K. W., Hotson, A., Keegan, M., Schmelz, E. A., & Mudgett, M. B. (2008). XopD SUMO protease affects host transcription, promotes pathogen growth, and delays symptom development in Xanthomonas-infected tomato leaves. Plant Cell, 20, 1915–1929.
Kim, J. G., Li, X., Roden, J. A., Taylor, K. W., Aakre, C. D., Su, B., Lalonde, S., Kirik, A., Chen, Y., Baranage, G., McLane, H., Martin, G. B., & Mudgett, M. B. (2009). Xanthomonas T3S effector XopN suppresses PAMP-triggered immunity and interacts with a Tomato atypical receptor-like kinase and TFT1. Plant Cell, 21, 1305–1323.
Kumar, R., & Mondal, K. K. (2013). XopN T3SS effector is required for growth and pathogenicity by Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. punicae, the causal agent of bacterial blight of pomegranate. Physiological Molecular Plant Pathology, 84, 36–43.
Lee, B. M., Park, Y. J., Park, D. S., Kang, H. W., Kim, J. G., Song, E. S., Park, I. C., Yoon, U. H., Hahn, J. H., Koo, B. S., Lee, G. B., Kim, H., Park, H. S., Yoon, K. O., Kim, J. H., Jung, C., Koh, N. H., Seo, J. S., & Go, S. J. (2005). The genome sequence of Xanthomonas oryzae pathovar oryzae KACC10331, the bacterial blight pathogen of rice. Nucleic Acids Research, 33, 577–586.
Mondal, K.K., Mani, C., Sinha, P., Singh, U.D., & Gogoi, R. (2012). Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae causing bacterial blight in rice is well adapted to elevated CO2 and temperature. In 3rd International Agronomy Congress, Nov. 26–30, New Delhi, India.
Mondal, K.K., Juanaid, A., Verma, G., Mani, C., & Manju. (2013). XopF-T3E is required for growth, pathogenicity and for suppression of PTI response by Indian strain of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae, causing bacterial blight of rice. In 4th Int Conf Bacterial Blight of Rice, Dec 2–4, Hyderabad, India.
Mondal, K. K., Meena, B. R., Junaid, A., Verma, G., Mani, C., Majumder, D., Manju, Kumar, S., & Banik, S. (2014). Pathotyping and genetic screening of type III effectors in Indian strains of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae causing bacterial leaf blight of rice. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology, 86, 98–106.
Mudgett, M. B. (2005). New insights to the function of phytopathogenic bacterial type III effectors in plants. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 56, 509–531.
Nurnberger, T., Brunner, F., Kemmerling, B., & Piater, L. (2004). Innate immunity in plants and animals: striking similarities and obvious differences. Immunological Reviews, 198, 249–266.
Ochiai, H., Inoue, Y., Takeya, M., Sasaki, A., & Kaku, H. (2005). Genome sequence of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae suggests contribution of large numbers of effector genes and insertion sequences to its race diversity. Japanese Journal of Agricultural Research Q, 39, 275–287.
Salzberg, S.L., Sommer, D.D., Schatz, M.C., Phillippy, A.M., Rabinowicz, P.D., Tsuge, S., Furutani, A., Ochiai, H., Delcher, A.L., Kelley, D., Madupu, R., Puiu, D., Radune, D., Shumway, M., Trapnell, C., Aparna, G., Jha, G., Pandey, A., Patil, P.B., Ishihara, H., Meyer, D.F., Szurek, B., Verdier, V., Koebnik, R., Dow, J.M., Ryan, R.P., Hirata, H., Tsuyumu, S., Won Lee, S., Seo, Y.S., Sriariyanum, M., Ronald, P.C., Sonti, R.V., Van Sluys, M.A., Leach, J.E., White, F.F., Bogdanove, A.J. (2008). Genome sequence and rapid evolution of the rice pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae PXO99A. BMC Genomics, 9, 204.
Singh, U.D., Gogoi, R., & Mondal, K.K. (2011). Molecular approach for augmenting disease resistance in cereals: rice and maize. In Plant Pathology in India: Vision 2030, pp. 21–30, Indian Phytopathological Society, New Delhi, India. 294 pp.
Song, C., & Yang, B. (2010). Mutagenesis of 18 Type III effectors reveals virulence function of XopZpxo99 in Xanthomonas oryzae pv.oryzae. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 23, 893–902.
Tsuge, S., Fukunaka, R., Oku, T., Tsuno, K., Ochiai, H., Inoue, Y., Kaku, H., & Kubo, Y. (2002). Expression of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae hrp genes in XOM2, a novel synthetic medium. Journal of General Plant Pathology, 68,363–371.
White, F. F., Potnis, N., Jones, J. B., & Koebnik, R. (2009). The type III effectors of Xanthomonas. Molecular Plant Pathology, 10, 749–766.
Xu, K., Huang, X., Wu, M., Wang, Y., Chang, Y., Liu, K., Zhang, J., Zhang, Y., Zhang, F., Yi, L., Li, T., Wang, R., Tan, G., & Li, C. (2014). A rapid, highly efficient and economical method of Agrobacterium-mediated in planta transient transformation in living onion epidermis. PLoS ONE, 9(1), e83556. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0083556.
Yang, B., Sugio, A., & White, F. F. (2005). Avoidance of host recognition by alterations in the repetitive and C-terminal regions of AvrXa7, a type III effector of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 18, 142–149.
Zhang, J., Shao, F., Li, Y., Cui, H., Chen, L., Li, H., Zou, Y., Long, C., Lan, L., Chai, J., Chen, S., Tang, X., & Zhou, J. M. (2007). A Pseudomonas syringae effector inactivates MAPKs to suppress PAMP-induced immunity in plants. Cell Host & Microbe, 1, 175–185.
Acknowledgments
The work is supported by the project grant received from Department of Biotechnology, Government of India (Grant No. BT/PR14870/AGR/02/767/2010). The authors thank Dr. MB Mudgett, Associate Professor, Department of Biology, Stanford University, USA for providing the EYFP constructs and valuable suggestions during plasmid constructs development. The senior author thanks Dr. Shelly Praveen and her associates for help during confocal microscopic study. We are thankful to the Head, Division of Plant Pathology, Indian Agricultural Research Institute, New Delhi, India for necessary support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary figure 1
(JPEG 420 kb)
Supplementary figure 2
(JPEG 137 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mondal, K.K., Verma, G., Manju et al. Rice pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae employs inducible hrp-dependent XopF type III effector protein for its growth, pathogenicity and for suppression of PTI response to induce blight disease. Eur J Plant Pathol 144, 311–323 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-015-0768-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-015-0768-7