Abstract
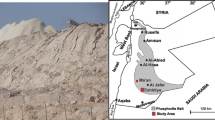
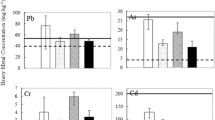
The management of phosphogypsum (PG) heap, located south of the Sfax city in Tunisia, has been going on for decades. But dumping this solid waste still poses environmental problems. Even though valorized as amendment to agriculture soils, the sanitary impact of this practice is not seriously considered. To assess the risk of the transference of contaminants from PG to agricultural soil-plants food chain, a wild plant species Salicornia arabica grown in PG-contaminated field and tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) and oat (Avena sativa) grown in laboratory using different rates (10, 20 and 30%) of PG amendment, were tested. The cadmium, lead, chromium, nickel, copper and zinc concentrations in soils and plants were determined by atomic absorption spectrometry and by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry, respectively. Measurements showed that Ni, Cu and Pb levels in the amended soils were below international standards except for Cd and Cr which exceeded Chinese, FAO/WHO and European allowable standard limits. Gathered results showed that the more the PG rate increases, the more the bioconcentration factors of heavy metals increased in plants, particularly in the roots. This is a prospective study assuming direct or indirect exposure scenario of different human cohorts by consuming varied common food stuffs. The Human Exposure to Soil Pollutants evaluation and United State Environment Protection Agency models were adopted for the hazard quotient calculation to assess the acceptability of sanitary risk related to each metal. The direct and indirect health risk assessments varied in the decreasing order: children, adolescents and then adults. Therefore, the PG amendment must not exceed the rate of 10%.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi, A. M., Iqbal, J., Khan, M. A., & Shah, M. H. (2013). Health risk assessment and multivariate apportionment of trace metals in wild leafy vegetables from Lesser Himalayas, Pakistan. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 92, 237–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.02.011.
Abusin, S. A. A., & Mandikiana, B. W. (2020). Towards sustainable food production systems in Qatar: Assessment of the viability of aquaponics. Global Food Security. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gfs.2020.100349.
Ajam, L., Felfoul Hayet, S., Ben Ouezdou, M., Reguigui, N., & Mensi, R. (2009). Essais physiques, mécanique et chimiques sur les Briques cuites fabriquées à partir du phosphogypse. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/313526931.
Al-Hwaiti, M., & Al-Khashman, O. (2015). Health risk assessment of heavy metals contamination in tomato and green pepper plants grown in soils amended with phosphogypsum waste materials. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 37(2), 287–304. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-014-9646-z.
Al-Hwaiti, M., Ranville, J., & Ross, P. E. (2010). Bioavailability and mobility of trace metals in phosphogypsum from Aqaba and Eshidiya, Jordan. Chemie Der Erde-geochemistry, 70, 283–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemer.2010.03.001.
Allan, C. A., Strauss, B. J. G., Burger, H. G., Forbes, E. A., & McLachlan, R. I. (2008). Testosterone therapy prevents gain in visceral adipose tissue and loss of skeletal muscle in nonobese aging men. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 93(1), 139–146. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2007-1291.
Al-Othman, Z. A., Ali, R., Al-Othman, A. M., Ali, J., & Habila, M. A. (2016). Assessment of toxic metals in wheat crops grown on selected soils, irrigated by different water sources. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 9, S1555–S1562.
Angelova, V., Babrikov, T., & Ivanov, K. (2009). Bioaccumulation and distribution of lead, zinc, and cadmium in crops of Solanaceae family. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 40, 2248–2263. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103620902961227.
anses. (2013). Avis de l’Agence nationale de sécurité sanitaire de l’alimentation, de l’environnement et du travail relatif «aux effets du plomb sur la santé associés à des plombémies inférieures à 100 µg/L» (p. 146). Saisine n° 2011-SA-0219. Maisons-Alfort.
anses. (2018). Avis de l’Agence nationale de sécurité sanitaire de l’alimentation, de l’environnement et du travail relatif au risque d’excès d’apport en iode lié à la consommation d’algues dans les denrées alimentaires (p. 25). Maisons-Alfor, (2017-SA-0086).
Ashraf, U., Mahmood, M. H.-R., Hussain, S., Abbas, F., Anjum, S. A., & Tang, X. (2020). Lead (Pb) distribution and accumulation in different plant parts and its associations with grain Pb contents in fragrant rice. Chemosphere, 248, 126003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126003.
Assche, F. V., & Clijsters, H. (1990). Effects of metals on enzyme activity in plants. Plant, Cell and Environment, 13(3), 195–206. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.1990.tb01304.x.
Ben Ali, M. (2009). Mesure du gaz “radon” à l’intérieur d’une chambre construite avec des briques à base de Phosphogypse (p. 143). FST/CNSTN, Tunis: Faculté des Sciences de Tunis. https://inis.iaea.org/collection/NCLCollectionStore/_Public/43/035/43035379.pdf.
Ben Hmida, R., & Elkaroui Elkadhi, H. (2014). The short-term effects of air pollution on health in Sfax (Tunisia): An ARDL cointegration procedure. In 2014 international conference and utility exhibition on conference: Green energy for sustainable development (ICUE), At Pattaya, Thailand (pp. 1–5), ISBN: 978-1-4799-2628-2.
Bhatnagar, J. P., & Awasthi, S. K. (2000). Prevention of Food Adulteration Act (Act no. 37 of 1954) alongwith Central & State Rules (as amended for 1999). New Delhi: Ashoka Law House.
Bisson, M., & Marilière, M. (2018). Bilan des choix de VTR disponibles sur le portail des substances chimiques de l’INERIS (p. 60). DRC-17-163632-11568A.
Bonnard, R. (2003). Evaluation de l’impact sur la santé des rejets atmosphériques des tranches charbon d’une grande installation de combustion, Partie 2: Exposition par voies indirectes (p. 45). INERIS DRC-03-45956/ERSA-n°92-RBn-/GT-GIC, (Version 4).
Bonnard, R., Hulot, C., & Leveque, S. (2001). Méthode de calcul des Valeurs de Constat d’Impact dans les sols (p. 54). INERIS DRC-01-25587/DESP-R01.
Boulvert, E. (2017). Coefficients de transfert des éléments traces métalliques vers les plantes, utilisés pour l’évaluation de l’exposition Application dans le logiciel MODUL’ERS. Rapport INERIS-DRC-17-163615-01452A.
Bowen, H. J. M. (1979). Environmental chemistry of the elements. London: Academic Press.
Campos, M. P., Costa, L. J. P., Nisti, M. B., & Mazzilli, B. P. (2017). Phosphogypsum recycling in the building materials industry: Assessment of the radon exhalation rate. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 172, 232–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2017.04.002.
Canet, R., Chaves, C., Pomares, F., & Albiach, R. (2003). Agricultural use of sediments from the Albufera Lake (eastern Spain). Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 95(1), 29–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-8809(02)00171-8.
Casas, S. (2005). Modélisation de la bioaccumulation de métaux traces (Hg, Cd, Pb, Cu et Zn) chez la moule, Mytilus galloprovincialis, en milieu méditerranéen (PhD thesis). Université du Sud Toulon Var. https://tel.archives-ouvertes.fr/tel-00009551/document.
Castañé, C., van der Blom, J., & Nicot, P. C. (2020). Tomatoes. In M. L. Gullino, R. Albajes, & P. C. Nicot (Eds.), Integrated pest and disease management in greenhouse crops (pp. 487–511). Cham: Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-22304-5_17.
Castro, E., Mañas, P., & De las Heras, J. (2009). A comparison of the application of different waste products to a lettuce crop: Effects on plant and soil properties. Scientia Horticulturae, 123(2), 148–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2009.08.013.
Caussy, D., Gochfeld, M., Gurzau, E., Neagu, C., & Ruedel, H. (2003). Lessons from case studies of metals: Investigating exposure, bioavailability, and risk. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 56(1), 45–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0147-6513(03)00049-6.
Champ, M. (2018). Devrions-nous manger plus de céréales complètes? Cahiers de Nutrition et de Diététique, 53(1), 22–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnd.2017.12.001.
Chandrajith, R., & Dissanayake, C. B. (2009). Phosphate mineral fertilizers, trace metals and human health. Journal of the National Science Foundation of Sri Lanka, 37(3), 153. https://doi.org/10.4038/jnsfsr.v37i3.1219.
Chang, L. W., Meier, J. R., & Smith, M. K. (1997). Application of plant and earthworm bioassays to evaluate remediation of a lead-contaminated soil. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 32(2), 166–171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002449900170.
Charfi Fourati, F., Bouaziz, J., & Belayouni, H. (2015). Valorisation du phosphogypse de Tunisie en vue de son utilisation comme substituant au gypse naturel dans la fabrication du ciment. Déchets, sciences et techniques. https://doi.org/10.4267/dechets-sciences-techniques.1550.
Chen, Y., Liu, Y., Ding, Y., Wang, X., & Xu, J. (2015). Overexpression of PtPCS enhances cadmium tolerance and cadmium accumulation in tobacco. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture, 121(2), 389–396.
Chevalier, A. (1922). Les Salicornes et leur emploi dans l’alimentation: étude historique, botanique, économique. Journal d’agriculture traditionnelle et de botanique appliquée, 2(16), 697–785. https://doi.org/10.3406/jatba.1922.1484.
Chijioke, N. O., Uddin Khandaker, M., Tikpangi, K. M., & Bradley, D. A. (2020). Metal uptake in chicken giblets and human health implications. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 85, 103332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2019.103332.
COM. (2006). 231 final (p. 130). Communication from the Commission of the Council, the European Parliament, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions, Thematic Strategy for Soil Protection, Brussels.
Cuadri, A. A., Navarro, F. J., García-Morales, M., & Bolívar, J. P. (2014). Valorization of phosphogypsum waste as asphaltic bitumen modifier. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 279, 11–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.06.058.
Darrouzes, J. (2007). Spectromètre de masse à plasma à couplage inductif (ICP-MS) à cellule de collision/réaction (CC/R) pour l’analyse clinique. Performances et applications à l’analyse élémentaire et à la spéciation. Annales de Toxicologie Analytique, 19(1), 103–111. https://doi.org/10.1051/ata:2007015.
DHAenC (Department of Health and Aging and enHealth Council). (2012). Environmental health risk assessment: Guidelines for assessing human health risks from environmental hazards [R]. Canberra: ACT.
Dor, F., Daniau, C., Empereur-Bissonnet, P., Zmirou, D., Bonvallot, N., Duboudin, C., et al. (2005). Estimation de l’impact sanitaire d’une pollution environnementale et évaluation quantitative des risques sanitaires. Ed. InVS/Afsse, 160.
Dubuisson, C., & Lioret, S. (2007). Résultats de l’étude INCA 2: Évolution des consommations alimentaires depuis INCA 1. Colloque PNNS (La situation nutritionnelle en France en 2007), 35 p. https://www.anses.fr/fr/system/files/PASER-Co-INCA2conso.pdf.
Dupuis, C., & Saffre, A.-S. (2018). Unité d’incinération de déchets non dangereux située à Amilly (45) Evaluation de l’état des milieux et des risques sanitaires, Version 3 (p. 187). Rapport ARIA/2017.014(17.014).
El Zrelli, R., Courjault-Radé, P., Rabaoui, L., Castet, S., Michel, S., & Bejaoui, N. (2015). Heavy metal contamination and ecological risk assessment in the surface sediments of the coastal area surrounding the industrial complex of Gabes city, Gulf of Gabes, SE Tunisia. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 101(2), 922–929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.10.047.
El Zrelli, R., Rabaoui, L., Abda, H., Daghbouj, N., Pérez-López, R., Castet, S., et al. (2019a). Characterization of the role of phosphogypsum foam in the transport of metals and radionuclides in the Southern Mediterranean Sea. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 363, 258–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.09.083.
El Zrelli, R., Rabaoui, L., van Beek, P., Castet, S., Souhaut, M., Grégoire, M., et al. (2019b). Natural radioactivity and radiation hazard assessment of industrial wastes from the coastal phosphate treatment plants of Gabes (Tunisia, Southern Mediterranean Sea). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 146, 454–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.06.075.
FAO/WHO. (2001). Food additives and contaminants (p. 1–289). Codex Alimentarius Commission. Joint FAO/WHO Food Standards Program, ALI-NORM 01/12A.
Fernández, B., Lobo, L., & Pereiro, R. (2018). Atomic absorption spectrometry: Fundamentals, instrumentation and capabilities. In P. Worsfold, C. Poole, A. Townshend, & M. Miró (Eds.), Encyclopedia of analytical science (3rd ed., p. 7). Amsterdam: Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-409547-2.14116-2.
Garty, J. (2001). Biomonitoring atmospheric heavy metals with lichens: Theory and application. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 20(4), 309–371. https://doi.org/10.1080/20013591099254.
Gebrekidan, A., Weldegebriel, Y., Hadera, A., & Van der Bruggen, B. (2013). Toxicological assessment of heavy metals accumulated in vegetables and fruits grown in Ginfel river near Sheba Tannery, Tigray, Northern Ethiopia. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 95, 171–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.05.035.
Guan, Y., Shao, C., & Ju, M. (2014). Heavy metal contamination assessment and partition for industrial and mining gathering areas. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 11, 7286–7303. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110707286.
Gupta, N., Khan, D. K., & Santra, S. C. (2012). Heavy metal accumulation in vegetables grown in a long-term wastewater-irrigated agricultural land of tropical India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184(11), 6673–6682. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2450-7.
Hachicha, M. (2007). Les sols salés et leur mise en valeur en Tunisie. Science et changements planétaires / Sécheresse, 18, 45–50.
Hakanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: A sedimentological approach. Water Research, 14(8), 975–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8.
Hammami, N., Athmouni, K., Lahmar, I., Ben Abdallah, F., & Belghith, K. (2019). Antioxidant potential of Salicornia arabica lipid extract and their protective effect against cadmium induced oxidative stress in erythrocytes isolated from rats. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization, 13(4), 2705–2712. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-019-00191-8.
Hazerbouck, B. (2005). Etude des modèles d’évaluation de l’exposition et des risques liés aux sols pollués: Modélisation du transfert de vapeurs du soussol ou du vide sanitaire vers l’air intérieur (p. 17). INERIS DRC-05-57278-DESP/R03a.
He, J., Qin, J., Long, L., Ma, Y., Li, H., Li, K., et al. (2011). Net cadmium flux and accumulation reveal tissue-specific oxidative stress and detoxification in Populus × canescens. Physiologia Plantarum, 143(1), 50–63. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2011.01487.x.
Hembrom, S., Singh, B., Gupta, S. K., & Nema, A. K. (2020). A comprehensive evaluation of heavy metal contamination in foodstuff and associated human health risk: A global perspective. In P. Singh, R. P. Singh, & V. Srivastava (Eds.), Contemporary environmental issues and challenges in era of climate change (pp. 33–63). Singapore: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-32-9595-7_2.
Hentati, O., Abrantes, N., Caetano, A. L., Bouguerra, S., Gonçalves, F., Römbke, J., et al. (2015). Phosphogypsum as a soil fertilizer: Ecotoxicity of amended soil and elutriates to bacteria, invertebrates, algae and plants. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 294, 80–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.03.034.
Hernandez, L., Probst, A., Probst, J. L., & Ulrich, E. (2003). Heavy metal distribution in some French forest soils: Evidence for atmospheric contamination. The Science of the Total Environment, 312(1–3), 195–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(03)00223-7.
Huang, X., Duan, S., Wu, Q., Yu, M., & Shabala, S. (2020). Reducing cadmium accumulation in plants: Structure-function relations and tissue-specific operation of transporters in the spotlight. Plants, 9(2), 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9020223.
INS. (2016a). Flash Démographique, Statistiques Tunisie, n°1. http://www.ins.tn/sites/default/files/publication/pdf/Bulletin%20n%C2%B01-2016-v3.pdf.
INS. (2016b). Flash Consommation et Niveau de Vie, Statistiques Tunisie, n°1. http://www.ins.nat.tn/sites/default/files/publication/pdf/Bulletin%20-cons-2016-fr2-2.pdf.
ISO. (2005). Soil quality: Chronic toxicity in higher plants. ISO 22030. Geneva: International Organization for Standardization.
ISO. (2012). Soil quality: Determination of the effects of pollutants on soil flora, Part 2: Effects of contaminated soil on the emergence and early growth of higher plants. ISO 11269-2. Geneva: International Organiztion for Standardization.
Ivanova, J., Kamenova, K., Petrova, E., Vladov, I., Gluhcheva, Y., & Dorkov, P. (2020). Comparative study on the effects of salinomycin, monensin and meso-2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid on the concentrations of lead, calcium, copper, iron and zinc in lungs and heart in lead-exposed mice. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, 58, 126429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2019.126429.
Jain, D., Kour, R., Bhojiya, A. A., Meena, R. H., Singh, A., Mohanty, S. R., et al. (2020). Zinc tolerant plant growth promoting bacteria alleviates phytotoxic effects of zinc on maize through zinc immobilization. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 13865. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-70846-w.
Jalali, J., Gaudin, P., Capiaux, H., Neji, Saidi M., Ammar, E., & Lebeau, T. (2019). Environmental impact of phosphogypsum piles in Tunisia. Environmental Ecotoxicological Safety, 174, 12–25.
Khan, S., Abd El-Latif, H., Min, Q., Shafiqur, R., & Ji-Zheng, H. (2010). Effects of Cd and Pb on soil microbial community structure and activities. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 17(2), 288–296. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-009-0134-4.
Khan, S., Chao, C., Waqas, M., Arp, H. P. H., & Zhu, Y.-G. (2013a). Sewage sludge biochar influence upon rice (Oryza sativa L.) yield, metal bioaccumulation and greenhouse gas emissions from acidic paddy soil. Environmental Science and Technology, 47(15), 8624–8632. https://doi.org/10.1021/es400554x.
Khan, A., Khan, S., Khan, M. A., Qamar, Z., & Waqas, M. (2015). The uptake and bioaccumulation of heavy metals by food plants, their effects on plants nutrients, and associated health risk: A review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22(18), 13772–13799. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4881-0.
Khan, K., Lu, Y., Khan, H., Ishtiaq, M., Khan, S., Waqas, M., et al. (2013b). Heavy metals in agricultural soils and crops and their health risks in Swat District, northern Pakistan. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 58, 449–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2013.05.014.
Khan, S., Reid, B. J., Li, G., & Zhu, Y.-G. (2014). Application of biochar to soil reduces cancer risk via rice consumption: A case study in Miaoqian village, Longyan, China. Environment International, 68, 154–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2014.03.017.
Khelifi, F., Melki, A., Hamed, Y., Adamo, P., & Caporale, A. G. (2019). Environmental and human health risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in soil, sediments, and ore-processing wastes from a mining area of southwestern Tunisia. Environmental Geochemistry and Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00434-z.
Kumar, V., Pandita, S., Singh Sidhu, G. P., Sharma, A., Khanna, K., Kaur, P., et al. (2021). Copper bioavailability, uptake, toxicity and tolerance in plants: A comprehensive review. Chemosphere, 262, 127810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127810.
Kuryatnyk, T., Angulski da Luz, C., Ambroise, J., & Pera, J. (2008). Valorization of phosphogypsum as hydraulic binder. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 160(2–3), 681–687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.03.014.
Lakhdar-Toumi, S., & Bereksi-Reguig, K. (2016). In vivo study of anti-lithiasis and diuretic effects of two grains decoction: Hordeum vulgare and Avena sativa. Phytothérapie, 14(5), 304–308. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10298-015-0995-2.
Li, W., Khan, M. A., Yamaguchi, S., & Kamiya, Y. (2005). Effects of heavy metals on seed germination and early seedling growth of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Growth Regulation, 46(1), 45–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-005-6324-2.
Li, Y., Wang, Y., Gou, X., Su, Y., & Wang, G. (2006). Risk assessment of heavy metals in soils and vegetables around non-ferrous metals mining and smelting sites, Baiyin, China. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 18(6), 1124–1134. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(06)60050-8.
Liu, W., Zhao, J., Ouyang, Z., Söderlund, L., & Liu, G. (2005). Impacts of sewage irrigation on heavy metal distribution and contamination in Beijing, China. Environment International, 31(6), 805–812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2005.05.042.
Loska, K., & Wiechuła, D. (2003). Application of principal component analysis for the estimation of source of heavy metal contamination in surface sediments from the Rybnik Reservoir. Chemosphere, 51, 723–733.
Maazoun, H., & Bouassida, M. (2018). On phosphogypsum management challenges. In Proceedings of GeoMEast 2018 international Congress and exhibition: “Sustainable civil infrastructures: Structural integrity”, Egypt.
Maazoun, H., & Bouassida, M. (2019a). Phosphogypsum management perspectives. Massive valorization or massive storage? Acta Scientific Agriculture, 3(8), 184–189.
Maazoun, H., & Bouassida, M. (2019b). Phosphogypsum management challenges in Tunisia. In S. Hemeda & M. Bouassida (Eds.), Contemporary issues in soil mechanics (pp. 88–104). Cham: Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01941-9_7.
Mahmoud, E., & Abd El-Kader, N. A. (2015). Heavy metal immobilization in contaminated soils using phosphogypsum and rice straw compost. Land Degradation and Development, 26(8), 819–824. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.2288.
Marie, D., & Olivier, D. (2005). Evaluation et gestion du risque sanitaire lié au dépassement de la limite de qualité du chrome dans l’eau de distribution (p. 88). Rennes: Atelier Santé Environnement ENSP.
Martínez-Valverde, I., Periago, M. J., Provan, G., & Chesson, A. (2002). Phenolic compounds, lycopene and antioxidant activity in commercial varieties of tomato (Lycopersicum esculentum). Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 82(3), 323–330. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.1035.
Medina, A., Vassilev, N., Barea, J. M., & Azcón, R. (2005). Application of Aspergillus niger-treated agrowaste residue and Glomus mosseae for improving growth and nutrition of Trifolium repens in a Cd-contaminated soil. Journal of Biotechnology, 116(4), 369–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2004.12.009.
Mohanna, C., Guiot, J., Marini, K., Cramer, W., Picard, N., Walter, S., et al. (2019). Le rôle des forêts méditerranéennes dans l’Accord de Paris Role of Mediterranean forests in the Paris Agreement (p. 176).
Molas, J., & Baran, S. (2004). Relationship between the chemical form of nickel applied to the soil and its uptake and toxicity to barley plants (Hordeum vulgare L.). Geoderma, 122(2–4), 247–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2004.01.011.
Monteiro, M., Santos, C., Mann, R., Soares, A., & Lopes, T. (2007). Evaluation of cadmium genotoxicity in Lactuca sativa L. using nuclear microsatellites. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 60, 421–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2006.12.018.
Müller, G., Müller, G., & Putz, G. (1969). Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine river. Geo Journal, 5, 109–118.
Munzuroglu, O., & Geckil, H. (2002). Effects of metals on seed germination, root elongation, and coleoptile and hypocotyl growth in Triticum aestivum and Cucumis sativus. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 43(2), 203–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-002-1116-4.
Nadem, S., Baghdadi, M. E., Rais, J., & Barakat, A. (2015). Evaluation de la contamination en métaux lourds des sédiments de l’estuaire de Bou Regreg (Côte atlantique, Maroc) (p. 8).
Nayak, S., Mishra, C. S. K., Guru, B. C., & Rath, M. (2011). Effect of phosphogypsum amendment on soil physico-chemical properties, microbial load and enzyme activities. Journal of Environmental Biology, 32(5), 613–617.
Ngo, R. (2016). Evaluation des Risques Sanitaires Site de 60 290 Laigneville (60) de la Société Montupet, Annexes 2 EC14-00099, (2), p. 147.
Ogundele, L. T., Adejoro, I. A., & Ayeku, P. O. (2019). Health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil samples from an abandoned industrial waste dumpsite in Ibadan, Nigeria. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191(5), 290. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7454-8.
Olatunji, A. S., Abimbola, A. F., & Afolabi, O. O. (2009). Geochemical assessment of industrial activities on the quality of sediments and soils within the Lsdpc Industrial Estate, Odogunyan, Lagos, Nigeria. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Geochemical-Assessment-of-Industrial-Activities-on-Olatunji-Abimbola/51be4dde3aa9c2f560a1e7326bee59596482a895.
Omrane, F., Gargouri, I., Khadhraoui, M., Elleuch, B., & Zmirou-Navier, D. (2018). Risk assessment of occupational exposure to heavy metal mixtures: A study protocol. BMC Public Health, 18(1), 314. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-018-5191-5.
Palacios, A. M., Hurley, K. M., De-Ponce, S., Alfonso, V., Tilton, N., Lambden, K. B., et al. (2020). Zinc deficiency associated with anaemia among young children in rural Guatemala. Maternal & Child Nutrition, 16(1), e12885. https://doi.org/10.1111/mcn.12885.
Papastefanou, C., Stoulos, S., Ioannidou, A., & Manolopoulou, M. (2006). The application of phosphogypsum in agriculture and the radiological impact. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 89, 188–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2006.05.005.
Parth Sarthi, P., & Singh, A. K. (2013). A simple approach about the characteristics of available surface water in Bihar State of India. Geosciences, 3(2), 68–76. https://doi.org/10.5923/j.geo.20130302.05.
Pereira, R., Antunes, S. C., Marques, S. M., & Gonçalves, F. (2008). Contribution for tier 1 of the ecological risk assessment of Cunha Baixa uranium mine (Central Portugal): I soil chemical characterization. The Science of the Total Environment, 390(2–3), 377–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.08.051.
Praveena, S. M., Radojevic, M., & Abdullah, M. H. (2007). The assessment of mangrove sediment quality in Mengkabong Lagoon: An index analysis approach. Science Education, 2(3), 60–68.
Qu, C., Sun, K., Wang, S., Huang, L., & Bi, J. (2012). Monte Carlo simulation-based health risk assessment of heavy metal soil pollution: A case study in the Qixia mining area, China. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal, 18(4), 733–750. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2012.688697.
Reijnders, L. (2007). Cleaner phosphogypsum, coal combustion ashes and waste incineration ashes for application in building materials: A review. Building and Environment, 42(2), 1036–1042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2005.09.016.
Robert-Nadeau, F. (2012). Evaluation des risques toxicologiques et écotoxicologiques d’un terrain contaminé par les métaux (p. 68). Québec: Centre universitaire de formation en environnement Université de Sherbrooke.
Rogival, D., Scheirs, J., & Blust, R. (2007). Transfer and accumulation of metals in a soil–diet–wood mouse food chain along a metal pollution gradient. Environmental Pollution, 145(2), 516–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2006.04.019.
Rosenblum, H., Wessler, J. D., Gupta, A., Maurer, M. S., & Bikdeli, B. (2020). Zinc deficiency and heart failure: A systematic review of the current literature. Journal of Cardiac Failure. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cardfail.2020.01.005.
Saidane, O., Courties, A., & Sellam, J. (2020). Les fibres alimentaires contre l’arthrose: quels éléments de preuve? Revue du Rhumatisme, 87(1), 4–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rhum.2019.08.004.
Semedo, H. M. (2018). Le Colloque International sur la Pollution du Sol (GSOP18). http://www.fao.org/about/meetings/global-symposium-on-soil-pollution/fr/.
Semenzin, E., Critto, A., Carlon, C., Rutgers, M., & Marcomini, A. (2007). Development of a site-specific Ecological Risk Assessment for contaminated sites: Part II. A multi-criteria based system for the selection of bioavailability assessment tools. The Science of the Total Environment, 379(1), 34–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.02.034.
SEPA. (2005). The limits of pollutants in food. State Environmental Protection Administration, China, GB 2762-2005.
Sfar Felfoul, H., Clastres, P., Ben Ouezdou, M., & Carles-Gibergues, A. (2002). Properties and perspectives of valorization of phosphogypsum the example of Tunisia. In Proceedings of international symposium on environmental pollution control and waste management (pp. 510–520).
Singh, V. (2009). Cereal grains structure & composition. São Paulo, Brazil. http://www.iea.usp.br/midiateca/apresentacao/singhbiofuels2.pdf.
Singh, R., Gautam, N., Mishra, A., & Gupta, R. (2011). Heavy metals and living systems: An overview. Indian Journal of Pharmacology, 43(3), 246–253. https://doi.org/10.4103/0253-7613.81505.
Singh, A. K., Sathya, M., Verma, S., & Jayakumar, S. (2018). Health risk assessment of heavy metals in crop grains grown on open soils of Kanwar wetland, India. Euro-Mediterranean Journal for Environmental Integration. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-018-0073-x.
Singh, R., Singh, D. P., Kumar, N., Bhargava, S. K., & Barman, S. C. (2010). Accumulation and translocation of heavy metals in soil and plants from fly ash contaminated area. Journal of Environmental Biology, 31(4), 421–430.
Stasinos, S., & Zabetakis, I. (2013). The uptake of nickel and chromium from irrigation water by potatoes, carrots and onions. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 91, 122–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.01.023.
Tchounwou, P. B., Centeno, J. A., & Patlolla, A. K. (2004). Arsenic toxicity, mutagenesis, and carcinogenesis—A health risk assessment and management approach. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 255(1–2), 47–55. https://doi.org/10.1023/b:mcbi.0000007260.32981.b9.
Union, E. (2006). Commission Regulation (EC) No. 1881/2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Official Journal of the European Union, 364, 5–24.
US EPA. (2005). US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Guidance for developing ecological soil screening levels. Washington, DC: Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response.
Velea, T., Gherghe, L., Predica, V., & Krebs, R. (2009). Heavy metal contamination in the vicinity of an industrial area near Bucharest. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 16(1), 27–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-008-0073-5.
World Population Prospects. (2015). United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, File POP/2: Average annual rate of population change by major area, region and country (Vol. 1, pp. 1950–2100).
Xu, D., Chen, Z., Sun, K., Yan, D., Kang, M., & Zhao, Y. (2013a). Effect of cadmium on the physiological parameters and the subcellular cadmium localization in the potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 97, 147–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.07.021.
Xu, D., Zhou, P., Zhan, J., Gao, Y., Dou, C., & Sun, Q. (2013b). Assessment of trace metal bioavailability in garden soils and health risks via consumption of vegetables in the vicinity of Tongling mining area, China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 90, 103–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.12.018.
Yang, J., Lv, F., Zhou, J., Song, Y., & Li, F. (2017). Health risk assessment of vegetables grown on the contaminated soils in Daye City of Hubei Province, China. Sustainability, 9(11), 2141. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9112141.
Yazğan, B., Baltaci, A. K., Mogulkoc, R., & Avunduk, M. C. (2020). Effects of zinc supplementation on metallothionein levels in ischemic renal tissue. Biotechnic and Histochemistry. https://doi.org/10.1080/10520295.2019.1691264.
Yong, Y., Fu-Suo, Z., Hua-Fen, L., & Rong-Feng, J. (2008). Accumulation of cadmium in the edible parts of six vegetable species grown in Cd-contaminated soils. Journal of Environmental Management, 90(2), 1117–1122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2008.05.004.
Zanetti, D., Godoi, L. A., Estrada, M. M., Engle, T. E., Pacheco, M. V. C., Pereira, J. M. V., et al. (2020). Influence of a mineral supplement containing calcium, phosphorus and micronutrients on intake, digestibility, performance and mineral status of young Nellore bulls in a feedlot. Animal Production Science, 60(2), 277–287. https://doi.org/10.1071/AN17595.
Zechmeister, H. G., Riss, A., & Hanus-Illnar, A. (2004). Biomonitoring of atmospheric heavy metal deposition by mosses in the vicinity of industrial sites. Journal of Atmospheric Chemistry, 49(1), 461–477. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-004-1260-5.
Zhuang, P., McBride, M. B., Xia, H., Li, N., & Li, Z. (2009). Health risk from heavy metals via consumption of food crops in the vicinity of Dabaoshan mine, South China. Science of the Total Environment, 407(5), 1551–1561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.10.061.
Zota, A. R., Schaider, L. A., Ettinger, A. S., Wright, R. O., Shine, J. P., & Spengler, J. D. (2011). Metal sources and exposures in the homes of young children living near a mining-impacted Superfund site. Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology, 21(5), 495–505. https://doi.org/10.1038/jes.2011.21.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Tunisian Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ben Chabchoubi, I., Bouguerra, S., Ksibi, M. et al. Health risk assessment of heavy metals exposure via consumption of crops grown in phosphogypsum-contaminated soils. Environ Geochem Health 43, 1953–1981 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00777-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00777-y