Abstract
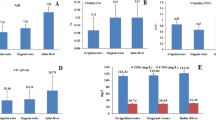
Environmental degradation has increased, mainly as a result of anthropogenic effects arising from population, industrial and agricultural growth. Water pollution is a problem that affects health, safety and welfare of the whole biota which shares the same environment. In Goiânia and metropolitan region, the main water body is the Meia Ponte River that is used for the abstraction of water, disposal of treated wastewater and effluents. In addition, this river receives wastewater from urban and rural areas. The aim in this present study was to evaluate the quality of raw water by some physical, chemical and toxicological tests. The physicochemical results found high levels of turbidity, conductivity, aluminum, phosphorus and metal iron, manganese, copper and lithium when compared to the standards of the Brazilian legislation. The values found of toxicity demonstrated a high degree of cytotoxicity and genotoxicity. Therefore, it was concluded that the Meia Ponte River has been undergoing constant environmental degradation, causing the poor quality of its waters. Thus, measures for the prevention and recovery should be adopted for the maintenance of the Meia Ponte River.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aral, H., & Vecchio-Sadus, A. (2008). Toxicity of lithium to humans and the environment—A literature review. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,70(3), 349–356.
AWWA (American Water Works Association). (1998). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (20th ed.). Washington: American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association and Water Environment Federation.
Baccan, N., de Andrade, J. C., Godinho, O. E., & Barone, J. S. (1979). Química analítica quantitativa elementar. Sao Paulo: Edgard Blucher.
Barreto, L. V., Fraga, M. D. S., Barros, F. M., Rocha, F. A., Amorim, J. D. S., Carvalho, S. R. D., et al. (2014). Relationship between stream flow and water quality in a river section. Revista Ambiente & Água,9(1), 118–129.
Batista, N. J. C., Cavalcante, A. A. D. C. M., de Oliveira, M. G., Medeiros, E. C. N., Machado, J. L., Evangelista, S. R., et al. (2016). Genotoxic and mutagenic evaluation of water samples from a river under the influence of different anthropogenic activities. Chemosphere,164, 134–141.
Bianchi, J., Mantovani, M. S., & Marin-Morales, M. A. (2015). Analysis of the genotoxic potential of low concentrations of Malathion on the Allium cepa cells and rat hepatoma tissue culture. Journal of Environmental Sciences,36, 102–111.
Botelho, R. G., Rossi, M. L., Maranho, L. A., Olinda, R. A., & Tornisielo, V. L. (2013). Evaluation of surface water quality using an ecotoxicological approach: A case study of the Piracicaba River (São Paulo, Brazil). Environmental Science and Pollution Research,20(7), 4382–4395.
Brandelero, S. M., de Siqueira, E. Q., & de Sousa, A. R. (2013). Parâmetros físico-químicos da água do Rio Meia Ponte, Goiânia-GO. RETEC-Revista de Tecnologias,5(1), 48–62.
BRASIL. (2013). Plano de ação de Recursos Hídricos da Unidade de Gestão Hídrica Meia Ponte. https://www.google.com.br/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=1&ved=0ahUKEwiD8Ia5pKzUAhVDhZAKHRrTAX4QFggnMAA&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.cbhparanaiba.org.br%2F_download.php%3Ffile%3DaHR0cDovL2NiaHBhcmFuYWliYS5vcmcuYnIvdXBsb2Fkcy9kb2N1bWVudG9zL1BSSF9QQVJBTkFJQkEvUEFSSHMvR08vUEFSSF9NZWlhUG9udGUucGRm&usg=AFQjCNEvg2bu_XLly9FSB-yt41UdVyUHXA&sig2=uAblRq9Sfni0ozI6BpiYXg&cad=rja. Accessed January 07, 2019.
Calil, P. M., Oliveira, L. D., Kliemann, H. J., & Oliveira, V. D. (2012). Caracterização geomorfométrica e do uso do solo da Bacia Hidrográfica do Alto Meia Ponte, Goiás. Revista Brasileira de Engenharia Agricola e Ambiental-Agriambi,16(4), 433–442.
Cao, Y., Lei, K., Zhang, X., Xu, L., Lin, C., & Yang, Y. (2018). Contamination and ecological risks of toxic metals in the Hai River, China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,164, 210–218.
Carvalho, K. Q., Lima, S. B., Passig, F. H., Gusmão, L. K., Souza, D. C., Kreutz, C., et al. (2015). Influence of urban area on the water quality of the Campo River basin, Paraná State, Brazil. Brazilian Journal of Biology,75(4), 96–106.
Caserta, D., Graziano, A., Monte, G. L., Bordi, G., & Moscarini, M. (2013). Heavy metals and placental fetal-maternal barrier: A mini-review on the major concerns. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences,17(16), 2198–2206.
CETESB. (2009). Significado ambiental e sanitário das variáveis de qualidade das águas e dos sedimentos e metodologias analíticas e de amostragem. Série Relatórios. São Paulo: CETESB, Available at: http://cetesb.sp.gov.br/aguas-interiores/wp-content/uploads/sites/32/2013/11/variaveis.pdf. Accessed January 07, 2019.
CETESB (Companhia de Tecnologia e Saneamento Ambiental). (2012). Guia de coleta e preservação de amostras de água, sedimento, comunidades aquáticas e efluentes líquidos. Organizadores, Carlos Jesus Brandão (et al.), São Paulo.
Chauhan, A., Goyal, P., & Varma, A. (2015). In-vitro antibiotic resistance and heavy metal tolerance patterns of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria isolated from effluent treated water of Delhi, India. Current Pharmaceutical Research,5(2), 1449–1458.
Chen, M., Lu, G., Wu, J., Yang, C., Niu, X., Tao, X., et al. (2018). Migration and fate of metallic elements in a waste mud impoundment and affected river downstream: A case study in Dabaoshan Mine, South China, China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,164, 474–483.
Chowdhury, S., & Balasubramanian, R. (2014). Recent advances in the use of graphene-family nanoadsorbents for removal of toxic pollutants from wastewater. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science,204, 35–56.
Christofoletti, C. A., Pedro-Escher, J., & Fontanetti, C. S. (2013). Assessment of the genotoxicity of two agricultural residues after processing by diplopods using the Allium cepa assay. Water, Air, and Soil pollution,224(4), 1523.
Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente (CONAMA). (2005). Resolução número 357, de 17 de março de 2005. www.mma.gov.br/port/conama/res/res05/res35705.pdf. Accessed June 7, 2017.
Costa, A. C., Domingues, G., Duesman, E., de Almeida, I. V., & Vicentini, V. E. P. (2015). Cytotoxicity of waters of the River Peixe (São Paulo-Brazil), in meristematic root cells of Allium cepa L. Bioscience Journal,31(1), 248–258.
Delpla, I., Jung, A. V., Baures, E., Clement, M., & Thomas, O. (2009). Impacts of climate change on surface water quality in relation to drinking water production. Environment International,35(8), 1225–1233.
DeWeber, J. T., & Wagner, T. (2014). A regional neural network ensemble for predicting mean daily river water temperature. Journal of Hydrology,517, 187–200.
Düsman, E., Luzza, M., Savegnago, L., Lauxen, D., Vicentini, V. E. P., Tonial, I. B., et al. (2014). Allium cepa L. as a bioindicator to measure cytotoxicity of surface water of the Quatorze River, located in Francisco Beltrão, Paraná, Brazil. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment,186(3), 1793–1800.
Dyer, F., ElSawah, S., Croke, B., Griffiths, R., Harrison, E., Lucena-Moya, P., et al. (2014). The effects of climate change on ecologically-relevant flow regime and water quality attributes. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment,28(1), 67–82.
Falis, M., Špalková, M., & Legáth, J. (2014). Effects of heavy metals and pesticides on survival of Artemia franciscana. Acta Veterinaria Brno,83(2), 95–99.
Fant, C., Srinivasan, R., Boehlert, B., Rennels, L., Chapra, S. C., Strzepek, K. M., et al. (2017). Climate change impacts on US water quality using two models: HAWQS and US basins. Water,9(2), 118.
Fels, L. E., Hafidi, M., & Ouhdouch, Y. (2016). Artemia salina as a new index for assessment of acute cytotoxicity during co-composting of sewage sludge and lignocellulose waste. Waste Management,50, 194–200.
Fonseca, R. C., Souza, N. A. D., Correa, T. C. L., Garcia, L. F., Reis, L. G. V. D., & Rodriguez, A. G. (2013). Assessment of toxic potential of Cerrado fruit seeds using Artemia salina bioassay. Food Science and Technology (Campinas),33(2), 251–256.
Freire, R., Bonifácio, C. M., Freitas, F. H., Schneider, R. M., & Tavares, C. R. G. (2013). Nitrogen forms and total phosphorus in water courses: A study at Maringá stream, Paraná State. Acta Scientiarum: Technology,35(4), 711–716.
Ghosh, P., Thakur, I. S., & Kaushik, A. (2017). Bioassays for toxicological risk assessment of landfill leachate: A review. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,141, 259–270.
Gomes, A. I., Pires, J. C., Figueiredo, S. A., & Boaventura, R. A. (2014). Optimization of river water quality surveys by multivariate analysis of physicochemical, bacteriological and ecotoxicological data. Water Resource Management,28(5), 1345–1361.
Hanh, P. T. M., Sthiannopkao, S., Kim, K. W., & Hung, N. Q. (2010). Anthropogenic influence on surface water quality of the Nhue and Day sub-river systems in Vietnam. Environmental Geochemistry and Health,32(3), 227–236.
Hannah, D. M., & Garner, G. (2015). River water temperature in the United Kingdom: Changes over the 20th century and possible changes over the 21st century. Progress in Physical Geography,39(1), 68–92.
Hara, R. V., & Marin-Morales, M. A. (2017). In vitro and in vivo investigation of the genotoxic potential of waters from rivers under the influence of a petroleum refinery (São Paulo State—Brazil). Chemosphere,174, 321–330.
Huang, B., Li, Z., Chen, Z., Chen, G., Zhang, C., Huang, J., et al. (2015). Study and health risk assessment of the occurrence of iron and manganese in groundwater at the terminal of the Xiangjiang River. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,22(24), 19912–19921.
Islam, M. S., Ahmed, M. K., Raknuzzaman, M., Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M., & Islam, M. K. (2015). Heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment: A preliminary assessment of an urban river in a developing country. Ecological Indicators,48, 282–291.
Islam, M. A., Romić, D., Akber, M. A., & Romić, M. (2018). Trace metals accumulation in soil irrigated with polluted water and assessment of human health risk from vegetable consumption in Bangladesh. Environmental Geochemistry and Health,40(1), 59–85.
Jiang, Z., Qin, R., Zhang, H., Zou, J., Shi, Q., Wang, J., et al. (2014). Determination of Pb genotoxic effects in Allium cepa root cells by fluorescent probe, microtubular immuno fluorescence and comet assay. Plant and Soil,383(1–2), 357–372.
Johnson, M. F., Wilby, R. L., & Toone, J. A. (2014). Inferring air-water temperature relationships from river and catchment properties. Hydrological Processes,28(6), 2912–2928.
Khallef, M., Liman, R., Konuk, M., Ciğerci, İ. H., Benouareth, D., Tabet, M., et al. (2015). Genotoxicity of drinking water disinfection by-products (bromoform and chloroform) by using both Allium anaphase-telophase and comet tests. Cytotechnology,67(2), 207–213.
Khan, S., Shahnaz, M., Jehan, N., Rehman, S., Shah, M. T., & Din, I. (2013). Drinking water quality and human health risk in Charsadda district, Pakistan. Journal of Cleaner Production,60, 93–101.
Kibria, G., Hossain, M. M., Mallick, D., Lau, T. C., & Wu, R. (2016). Monitoring of metal pollution in waterways across Bangladesh and ecological and public health implications of pollution. Chemosphere,165, 1–9.
Kumarasamy, P., James, R. A., Dahms, H. U., Byeon, C. W., & Ramesh, R. (2014). Multivariate water quality assessment from the Tamiraparani river basin, Southern India. Environmental Earth Sciences,71(5), 2441–2451.
Lebrun, J. D., Uher, E., Tusseau-Vuillemin, M. H., & Gourlay-Francé, C. (2014). Essential metal contents in indigenous gammarids related to exposure levels at the river basin scale: Metal-dependent models of bioaccumulation and geochemical correlations. Science of the Total Environment,466, 100–108.
Li, P., Qian, H., Howard, K. W., Wu, J., & Lyu, X. (2014). Anthropogenic pollution and variability of manganese in alluvial sediments of the Yellow River, Ningxia, northwest China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment,186(3), 1385–1398.
Libralato, G., Prato, E., Migliore, L., Cicero, A. M., & Manfra, L. (2016). A review of toxicity testing protocols and endpoints with Artemia spp. Ecological Indicators,69, 35–49.
Liman, R., Ciğerci, İ. H., & Öztürk, N. S. (2015). Determination of genotoxic effects of Imazethapyr herbicide in Allium cepa root cells by mitotic activity, chromosome aberration, and comet assay. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology,118, 38–42.
Liu, X., Song, Q., Tang, Y., Li, W., Xu, J., Wu, J., et al. (2013). Human health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil—Vegetable system: A multi-medium analysis. Science of the Total Environment,463, 530–540.
Loss, A., Pereira, M. G., Beutler, S. J., Perin, A., & Anjos, L. H. C. (2012). Densidade e fertilidade do solo sob sistemas plantio direto e integração lavoura-pecuária no Cerrado, Amazon. Journal of Agriculture and Environmental Sciences,55(4), 260–268.
Lu, Y., Xu, X., Li, T., Xu, Y., & Wu, X. (2012). The use of a brine shrimp (Artemia salina) bioassay to assess the water quality in Hangzhou section of Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal. Bulletin of Environment Contamination and Toxicology,88(3), 472–476.
Luo, Y., Ficklin, D. L., Liu, X., & Zhang, M. (2013). Assessment of climate change impacts on hydrology and water quality with a watershed modeling approach. Science of the Total Environment,450, 72–82.
Magdaleno, A., Juárez, Á. B., Dragani, V., Saenz, M. E., Paz, M., & Moretton, J. (2014). Ecotoxicological and genotoxic evaluation of Buenos Aires city (Argentina) hospital wastewater. Journal of Toxicology,2014, 1–10.
Masood, F., & Malik, A. (2013). Mutagenicity and genotoxicity assessment of industrial wastewaters. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,20(10), 7386–7397.
Meyer, B. N., Ferrigni, N. R., Putnan, J. E., Jacobsen, L. B., Nichols, D. E., & Aughlin, J. (1982). Brine shrimp: A convenient general bioassay for active plant constituents. Journal of Medicinal Plants Research,45(1), 31–34.
Miner, C. A., Dakhin, A. P., Zoakah, A. I., Zaman, M., & Bimba, J. (2016). Physical and microbiological quality of drinking water sources in Gwafan Community, Plateau State, Nigeria. Pyrex Journal of Research in Environmental Studies,3(1), 01–06.
Mishra, S., Kumar, A., Yadav, S., & Singhal, M. K. (2018). Assessment of heavy metal contamination in water of Kali River using principle component and cluster analysis, India. SWRM,4(3), 573–581.
Mohamed, A. H., Sheir, S. K., Osman, G. Y., & Azeem, H. H. A. (2014). Toxic effects of heavy metals pollution on biochemical activities of the adult brine shrimp, Artemia salina. Canadian Journal of Pure & Applied Sciences,8(3), 3019–3028.
Mustapha, A., Aris, A. Z., Juahir, H., Ramli, M. F., & Kura, N. U. (2013). River water quality assessment using environmentric techniques: Case study of Jakara River basin. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,20(8), 5630–5644.
Naresh, K., Singh, A., & Priya, S. (2013). To study the physico-chemical properties and bacteriological examination of hot spring water from Vashisht region in Distt. Kullu of HP, India. International Research Journal of Environmental Sciences,2(8), 28–31.
Neto, J. B. S., Júnior, M. G. S., Ucker, F. E., Alonso, R. R. P., & Lima, M. L. (2016). Diagnósticos dos recursos hídricos: Disponibilidade e demanda para a região metropolitana de Goiânia. RENEFARA,8(8), 149–167.
Netto, E., Madeira, R. A., Silveira, F. Z., Fiori, M. A., Angioleto, E., Pich, C. T., et al. (2013). Evaluation of the toxic and genotoxic potential of acid mine drainage using physicochemical parameters and bioassays. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology,35(3), 511–516.
Nostro, P. L., Ninham, B. W., Carretti, E., Dei, L., & Baglioni, P. (2015). Specific anion effects in Artemia salina. Chemosphere,135, 335–340.
Oliveira, L. F. C., Calil, P. M., Rodrigues, C., Kliemann, H. J., & Oliveira, V. Á. (2013). Potencial do uso dos solos da bacia hidrográfica do alto rio Meia Ponte, Goiás/potential use by attributes morphometric soil of the upper Meia Ponte watershed, Goiás. Revista Ambiente & Água,8(1), 222.
Patel, P., Raju, N. J., Reddy, B. S. R., Suresh, U., Sankar, D. B., & Reddy, T. V. K. (2018). Heavy metal contamination in river water and sediments of the Swarnamukhi River basin, India: Risk assessment and environmental implications. Environmental Geochemistry and Health,40(2), 609–623.
Peng, H., Zheng, X., Chen, L., & Wei, Y. (2016). Analysis of numerical simulations and influencing factors of seasonal manganese pollution in reservoirs. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,23(14), 14362–14372.
Peter, D. H., Castella, E., & Slaveykova, V. I. (2017). Lateral and longitudinal patterns of water physico-chemistry and trace metal distribution and partitioning in a large river floodplain. Science of the Total Environment,587, 248–257.
Phan, K., Phan, S., Se, S., Sieng, H., Huoy, L., & Kim, K. W. (2018). Assessment of water quality and trace metal contaminations in Mondolkiri province in the northeastern part of Cambodia. Environmental Geochemistry and Health,41(1), 1–9.
Pohren, R. S., Costa, T. C., & Vargas, V. M. F. (2013). Investigation of sensitivity of the Allium cepa test as an alert system to evaluate the genotoxic potential of soil contaminated by heavy metals. Water, Air, and Soil pollution,224(3), 1–10.
Poitrasson, F., Vieira, L. C., Seyler, P., Pinheiro, G. M. S., Mulholland, D. S., Bonnet, M. P., et al. (2014). Iron isotope composition of the bulk waters and sediments from the Amazon River basin. Chemical Geology,377, 1–11.
Powers, S. M., Bruulsema, T. W., Burt, T. P., Chan, N. I., Elser, J. J., Haygarth, P. M., et al. (2016). Long-term accumulation and transport of anthropogenic phosphorus in three river basins. Nature Geoscience,9(5), 353–356.
Prado, R., García, R., Rioboo, C., Herrero, C., & Cid, A. (2015). Suitability of cytotoxicity endpoints and test microalgal species to disclose the toxic effect of common aquatic pollutants. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,114, 117–125.
Qin, R., Jiang, W., & Liu, D. (2013). Aluminum can induce alterations in the cellular localization and expression of three major nucleolar proteins in root tip cells of Allium cepa var. agrogarum L. Chemosphere,90(2), 827–834.
Qin, R., Wang, C., Chen, D., Björn, L. O., & Li, S. (2015). Copper induced root growth inhibition of Allium cepa var. agrogarum L. involves disturbances in cell division and DNA damage. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry,34(5), 1045–1055.
Rank, J., & Nielsen, M. H. (1994). Evaluation of the Allium anaphase-telophase test in relation to genotoxicity screening of industrial wastewater. Mutation Research/Environmental Mutagenesis and Related Subjects,312(1), 17–24.
Reza, R., & Singh, G. (2010). Heavy metal contamination and its indexing approach for river water. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology,7(4), 785–792.
Rodrigues, G. Z. (2016). Uso do bioensaio com Allium cepa L. e análises físico-químicas e microbiológicas para avaliação da qualidade do Rio da Ilha, RS, Brasil. Acta Toxicológica Argentina,24(2), 97–104.
Saha, N., Rahman, M. S., Ahmed, M. B., Zhou, J. L., Ngo, H. H., & Guo, W. (2017). Industrial metal pollution in water and probabilistic assessment of human health risk. Journal of Environmental Management,185, 70–78.
Sahu, R., Gupta, K. A., Agarwal, N. K., & Sinha, S. (2013). Impacts of urban wastes on the physic-chemical characteristics of river Gomti at Luchnow. Research in Environment and Life Sciences,6(1), 1–4.
Santos, R. M. B., Fernandes, L. S., Pereira, M. G., Cortes, R. M. V., & Pacheco, F. A. L. (2015). A framework model for investigating the export of phosphorus to surface waters in forested watersheds: Implications to management. Science of the Total Environment,536, 295–305.
Serpa, D., Keizer, J. J., Cassidy, J., Cuco, A., Silva, V., Gonçalves, F., et al. (2014). Assessment of river water quality using an integrated physicochemical, biological and ecotoxicological approach. Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts,16(6), 1434–1444.
Sikder, M. T., Kihara, Y., Yasuda, M., Mihara, Y., Tanaka, S., Odgerel, D., et al. (2013). River water pollution in developed and developing countries: Judge and assessment of physicochemical characteristics and selected dissolved metal concentration. CLEAN—Soil Air Water,41(1), 60–68.
Silveira, M. A. D., Ribeiro, D. L., Santos, T. A., Vieira, G. M., Cechinato, C. N., Kazanovski, M., et al. (2016). Mutagenicity of two herbicides widely used on soybean crops by the Allium cepa test. Cytotechnology,68(4), 1215–1222.
Singh, M., Das, A., Singh, D., Maiti, P., Shabbir, M., & Das, A. (2014). High genotoxicity of shipyard contaminants on Allium cepa and calf thymus DNA. Environmental Chemistry Letters,12(2), 321–327.
StatSoft Inc. (2012). STATISTICA (data analysis software system), version 7. 2004. Tulsa, USA, 150.
Tang, W., Zhao, Y., Wang, C., Shan, B., & Cui, J. (2013). Heavy metal contamination of overlying waters and bed sediments of Haihe basin in China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,98, 317–323.
Tedesco, S. B., & Laughinghouse, I. V. (2012). Bioindicator of genotoxicity: The Allium cepa test. Intech Open Access Publisher.
Udiba, U. U., Stella, A., Balli, G., Dawaki, S. I., Oddy-Obi, I. C., & Agboun, T. D. T. (2015). Toxicity potential of Allium cepa L. as a bioindicator of heavy metal pollution status of River Galma basin around Dakace Industrial Layout, Zaria, Nigeria. International Journal of Biological Sciences and Applications,2(6), 76–85.
Varol, M. (2013). Dissolved heavy metal concentrations of the Kralkızı, Dicle and Batman dam reservoirs in the Tigris River basin, Turkey. Chemosphere,93(6), 954–962.
Varol, M., Gökot, B., Bekleyen, A., & Şen, B. (2012). Spatial and temporal variations in surface water quality of the dam reservoirs in the Tigris River basin, Turkey. CATENA,92, 11–21.
Veiga, A. M., Santos, C. C. P., Cardoso, M. R. D., & Lino, N. C. (2013). Caracterização hidromorfológica da bacia do Rio Meia Ponte. Caminhos de Geografia,14(46), 126–138.
WHO. (2019). Health topics environmental health. http://www.searo.who.int/topics/environmental_health/en/. Accessed January 07, 2019.
Xu, Y., Chen, T., Cui, F., & Shi, W. (2016). Effect of reused alum-humic-flocs on coagulation performance and floc characteristics formed by aluminum salt coagulants in humic-acid water. Chemical Engineering Journal,287, 225–232.
Xu, X., Lu, Y., Zhang, D., Wang, Y., Zhou, X., Xu, H., et al. (2015). Toxic Assessment of Triclosan and Triclocarban on Artemia salina. Bulletin of Environment Contamination and Toxicology,95(6), 728–733.
Yang, Y., He, Z., Wang, Y., Fan, J., Liang, Z., & Stoffella, P. J. (2013). Dissolved organic matter in relation to nutrients (N and P) and heavy metals in surface runoff water as affected by temporal variation and land uses—A case study from Indian River Area, south Florida, USA. Agricultural Water Management,118, 38–49.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES). My sincere acknowledgments to the Sanitation Company of Goiás State (SANEAGO). The authors thank you the CAPES (Coordination of Improvement of Higher Level Personnel), by student scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gomes, R.P., de Paula Silva, J.A., Carvalho Junior, M.C. et al. Evaluation of the raw water quality: physicochemical and toxicological approaches. Environ Geochem Health 41, 2425–2442 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00292-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00292-9