Abstract
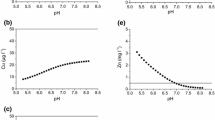
Central European floodplain soils are often contaminated with potentially toxic metals. The prediction of their aqueous concentrations is a prerequisite for an assessment of environmental concerns. We tested the aqueous concentrations of cadmium (Cd), copper (Cu), nickel (Ni), lead (Pb) and zinc (Zn) derived from multi-surface adsorption modelling (on hydrous iron, aluminum and manganese oxides, clay and soil organic matter) against those analyzed in situ in the soil solution of four horizons of floodplain soils at the Elbe River, Germany. The input data for the reactive metals were derived from a seven-step sequential extraction scheme or from extraction with 0.43 M nitric acid (HNO3) and evaluated in four modelling scenarios. In all scenarios, measured and modelled concentrations were positively related, except partially for Pb. Close reproduction of the measured data was obtained using measured data of accompanying cations and anions together with amounts of reactive metals from both the sequential extraction or from 0.43 M HNO3 extraction, except for Cu, which was often strongly overestimated, and partially Cd. We recommend extraction with 0.43 M HNO3 to quantify reactive metals in soil because the modelling results were metal-specific with better or equal results using the single extractant, the application of which is also less laborious. Approximations of ion concentrations and water contents yielded similar results. Modelled solid-phase speciation of metals varied with pH and differed from that from sequential extraction. Multi-surface modelling may be an effective tool to predict both aqueous concentrations and solid-phase speciation of metals in soil.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
BBodSchV. (1999). Verordnung zur Durchführung des Bundes-Bodenschutzgesetzes (Bundes-Bodenschutz- und Altlastenverordnung, BBodSchV vom 16.7.1999). BGBl, I.1554.
Bonten, L. T. C., Groenenberg, J. E., Meesenburg, H., & de Vries, W. (2011). Using advanced surface complexation models for modelling soil chemistry under forest: Solling forest, Germany. Environmental Pollution, 159, 2831–2839.
Bonten, L. T. C., Groenenberg, J. E., Weng, L., & van Riemsdijk, W. H. (2008). Use of speciation and complexation models to estimate heavy metal sorption in soils. Geoderma, 146, 303–310.
Cancès, B., Ponthieu, M., Castrec-Rouelle, M., Aubry, E., & Benedetti, M. F. (2003). Metal ions speciation in a soil and its solution: Experimental data and model results. Geoderma, 113, 341–355.
Dijkstra, J. J., Meeussen, J. C. L., & Comans, R. N. J. (2004). Leaching of heavy metals from contaminated soils: An experimental and modeling study. Environmental Science and Technology, 38, 4390–4395.
Du Laing, G., Rinklebe, R., Vandecasteele, B., Meers, E., & Tack, F. M. G. (2009). Trace metal behaviour in estuarine and riverine floodplain soils and sediments: A review. Science of the Total Environment, 407, 3972–3985.
Dzombak, D. A., & Morel, F. M. M. (1990). Surface complexation modeling: Hydrous ferric oxide. New York: Wiley.
Ford, R. G., Kemner, K. M., & Bertsch, P. M. (1999). Influence of sorbate-sorbent interactions on the crystallization kinetics of nickel- and lead-ferrihydrite coprecipitates. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 63, 39–48.
Fulda, B., Voegelin, A., Maurer, F., Christl, I., & Kretzschmar, R. (2013). Copper redox transformation and complexation by reduced and oxidized soil humic acid. 1. X-ray absorption spectroscopy study. Environmental Science and Technology, 47, 10903–10911.
Groenenberg, J. E., & Lofts, S. (2014). The use of assemblage models to describe trace element partitioning, speciation, and fate: A review. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 33, 2181–2196.
Groenenberg, J. E., Römkens, P. F. A. M., Comans, R. N. J., Luster, J., Pampura, T., Shotbolt, L., et al. (2010). Transfer functions for solid-solution partitioning of cadmium, copper, nickel, lead and zinc in soils: derivation of relationships for free metal ion activities and validation with independent data. European Journal of Soil Science, 61, 58–73.
Gustafsson, J. P. (2013). Visual MINTEQ 3.0 program, http://www.lwr.kth.se/english/OurSoftWare/Vminteq/index.html.
Händel, M., Rennert, T., & Totsche, K. U. (2013). Synthesis of cryptomelane- and birnessite-type manganese oxides at ambient pressure and temperature. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 405, 44–50.
ISO/DIS 17586. (2016). Soil quality: Extraction of trace elements using dilute nitric acid. Draft International Standard. Reference number: ISO/DIS 17586:2016(E). ISO/TC 190/SC 3 Secretariat: DIN.
Karamalidis, A. K., & Dzombak, D. A. (2011). Surface complexation modeling: Gibbsite. New York: Wiley.
Kim, N. D., & Fergusson, J. E. (1991). Effectiveness of commonly used sequential extraction technique in determining the speciation of cadmium in soils. Science of the Total Environment, 105, 191–209.
Kinniburgh, D. G., van Riemsdijk, W. H., Koopal, L. K., Borkovec, M., Benedetti, M. F., & Avena, M. J. (1999). Ion binding to natural organic matter: Competition, heterogeneity, stoichiometry and thermodynamic consistency. Colloids and Surfaces A, 151, 147–166.
Kraepiel, A. M. L., Keller, K., & Morel, F. M. M. (1998). On the acid-base chemistry of permanently charged minerals. Environmental Science and Technology, 32, 2829–2838.
Lair, G. J., Zehetner, F., Fiebig, M., Gerzabek, M. H., van Gestel, C. A. M., Hein, T., et al. (2009). How do long-term development and periodical changes of river–floodplain systems affect the fate of contaminants? Results from European rivers. Environmental Pollution, 157, 3336–3346.
McKenzie, R. M. (1980). The adsorption of lead and other heavy metals on oxides of manganese and iron. Australian Journal of Soil Research, 18, 61–73.
Mejia, J., Roden, E. E., & Ginder-Vogel, M. (2016). Influence of oxygen and nitrate on Fe (hydr)oxide mineral transformation and soil microbial communities during redox cycling. Environmental Science and Technology, 50, 3580–3588.
Milne, C. J., Kinniburgh, D. G., van Riemsdijk, W. H., & Tipping, E. (2003). Generic NICA-Donnan model parameters for metal-ion binding by humic substances. Environmental Science and Technology, 37, 958–971.
Peña, J., Kwon, K. D., Refson, K., Bargar, J. R., & Sposito, G. (2010). Mechanisms of nickel sorption by a bacteriogenic birnessite. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 74, 3076–3089.
Ren, Z.-L., Sivry, Y., Dai, J., Tharaud, M., Cordier, L., & Benedetti, M. F. (2015). Multi-element stable isotopic dilution and multi-surface modelling to assess the speciation and reactivity of cadmium and copper in soil. European Journal of Soil Science, 66, 973–982.
Rennert, T., Meißner, S., Rinklebe, J., & Totsche, K. U. (2010). Dissolved inorganic contaminants in a floodplain soil: Comparison of in situ soil solutions and laboratory techniques. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 209, 489–500.
Rennert, T., & Rinklebe, J. (2010). Release of Ni and Zn from contaminated floodplain soils under saturated flow conditions. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 205, 93–105.
Rinklebe, J., Stubbe, A., Staerk, H.-J., Wennrich, R., & Neue, H. U. (2005). Factors controlling the dynamics of As, Cd, Zn and Pb in alluvial soils of the Elbe river (Germany). In W. G. Lyon, J. Hong, & R. K. Reddy (Eds.), Proceedings of environmental science and technology (pp. 265–270). New Orleans: American Science Press.
Sauvé, S., McBride, M. B., Norvell, W. A., & Hendershot, W. H. (1997). Copper solubility and speciation of in situ contaminated soils: Effects of copper level, pH and organic matter. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 100, 133–149.
Scheinost, A. C., Kretzschmar, R., Pfister, S., & Roberts, D. R. (2002). Combining selective sequential extractions, X-ray absorption spectroscopy, and principal component analysis for quantitative zinc speciation in soil. Environmental Science and Technology, 36, 5021–5028.
Schröder, T. J., van Riemsdijk, W. H., van der Zee, S. E. A. T. M., & Vink, J. P. M. (2008). Monitoring and modelling of the solid-solution partitioning of metals and As in a river floodplain redox sequence. Applied Geochemistry, 23, 2350–2363.
Schwertmann, U. (1964). Differenzierung der Eisenoxide des Bodens durch Extraktion mit saurer Ammoniumoxalat-Lösung. Zeitschrift für Pflanzenernährung, Düngung und Bodenkunde, 105, 194–202.
Shaheen, S., & Rinklebe, J. (2014). Geochemical fractions of chromium, copper, and zinc and their vertical distribution in floodplain soil profiles along the Central Elbe River, Germany. Geoderma, 228–229, 142–159.
Tipping, E., Hetherington, N. B., Hilton, J., Thompson, D. W., Bowles, E., & Hamilton-Taylor, J. (1985). Artifacts in the use of selective chemical extraction to determine distributions of metals between oxides of manganese and iron. Analytical Chemistry, 57, 1944–1946.
Tonkin, J. W., Balistrieri, L. S., & Murray, J. W. (2004). Modeling sorption of divalent metal cations on hydrous manganese oxide using the diffuse double layer model. Applied Geochemistry, 19, 29–53.
Weng, L., Temminghoff, E. J. M., Lofts, S., Tipping, E., & van Riemsdijk, W. H. (2002). Complexation with dissolved organic matter and solubility control of heavy metals in a sandy soil. Environmental Science and Technology, 36, 4804–4810.
Weng, L., Temminghoff, E. J. M., & van Riemsdijk, W. H. (2001). Contribution of individual sorbents to the control of heavy metal activity in a sandy soil. Environmental Science and Technology, 35, 4436–4443.
Wolt, J. D. (1994). Soil solution chemistry. New York: Wiley.
Zeien, H., & Brümmer, G. W. (1989). Chemische Extraktionen zur Bestimmung von Schwermetallbindungsformen in Böden. Mitteilungen der Deutschen Bodenkundlichen Gesellschaft, 59, 505–509.
Acknowledgments
Various data were gained by a research grant of the Ministry of Agriculture and Environment, of the European Fond for Regional Development (EFRE) and the Department of Environmental Protection (LAU) of the Federal German state of Saxony-Anhalt (FKZ: 76213/08/01), for which the authors thank. We also thank Mrs. A. Böttcher, Mr. H. Dittrich, Mr. T. Swaton, Dr. M. Overesch and Mr. C. Vandenhirtz for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rennert, T., Rabus, W. & Rinklebe, J. Modelling the concentrations of dissolved contaminants (Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn) in floodplain soils. Environ Geochem Health 39, 331–344 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-016-9859-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-016-9859-4