Abstract
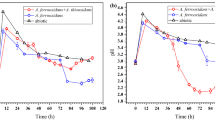
Bioleaching of As from the soil in an abandoned Ag–Au mine was carried out using Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans. A. ferrooxidans is an iron oxidizer and A. thiooxidans is a sulfur oxidizer. These two microbes are acidophilic and chemoautotrophic microbes. Soil samples were collected from the Myoungbong and Songcheon mines. The main contaminant of the soil was As, with an average concentration of 4,624 mg/kg at Myoungbong and 5,590 mg/kg at Songcheon. A. ferrooxidans and A. thiooxidans generated lower pH conditions during their metabolism process. The bioleaching of As from soil has a higher removal efficiency than chemical leaching. A. ferrooxidans could remove 70 % of the As from the Myoungbong and Songcheon soils; however, A. thiooxidans extracted only 40 % of the As from the Myoungbong soil. This study shows that bioleaching is an effective process for As removal from soil.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boon, M., Snijder, M., Hansford, G., & Heijnen, J. (1998). The oxidation kinetics of zinc sulphide with Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Hydrometallurgy, 48(2), 171–186.
Borůvka, L., Kozák, J., Mühlhanselová, M., Donátová, H., Nikodem, A., & Němeček, K. (2012). Effect of covering with natural topsoil as a reclamation measure on brown-coal mining dumpsites. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 113, 118–123.
Bosecker, K. (2001). Microbial leaching in environmental clean-up programmes. Hydrometallurgy, 59(2–3), 245–248.
Bosecker, K. (2006). Bioleaching: metal solubilization by microorganisms. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 20(3–4), 591–604.
Businelli, D., Massaccesi, L., Said-Pullicino, D., & Gigliotti, G. (2009). Long-term distribution, mobility and plant availability of compost-derived heavy metals in a landfill covering soil. Science of the Total Environment, 407(4), 1426–1435.
Chen, S. Y., & Lin, J. G. (2001). Effect of substrate concentration on bioleaching of metal-contaminated sediment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 82(1), 77–89.
Chutia, P., Kato, S., Kojima, T., & Satokawa, S. (2009). Arsenic adsorption from aqueous solution on synthetic zeolites. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 162(1), 440–447.
Giménez, J., Martínez, M., de Pablo, J., Rovira, M., & Duro, L. (2007). Arsenic sorption onto natural hematite, magnetite, and goethite. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 141(3), 575–580.
Gu, X., & Wong, J. W. C. (2004). Identification of inhibitory substances affecting bioleaching of heavy metals from anaerobically digested sewage sludge. Environmental Science and Technology, 38(10), 2934–2939.
Korean Ministry of Environment (2010). Soil Environment Standard Test, Soil Environment Preservation Act.
Lee, J.-S., Chon, H.-T., Kim, K.-W., & Kim, J.-Y. (2003). Risk assessment of toxic heavy metals in abandoned metal mine areas. Journal of the Korean Society for Geosystem Engineering (in Korea), 40, 264–273.
Liu, Y. G., Zhou, M., Zeng, G. M., Wang, X., Li, X., & Fan, T. (2008). Bioleaching of heavy metals from mine tailings by indigenous sulfur-oxidizing bacteria: Effects of substrate concentration. Bioresource Technology, 99(10), 4124–4129.
Ok, Y. S., Kim, S.-C., Kim, D.-K., Skousen, J. G., Lee, J.-S., Cheong, Y.-W., Kim, S.-J., & Yang, J. E. (2011a). Ameliorants to immobilize Cd in rice paddy soils contaminated by abandoned metal mines in Korea. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 33, 23–30.
Ok, Y. S., Lim, J. E., & Moon, D. H. (2011b). Stabilization of Pb and Cd contaminated soils and soil quality improvements using waste oyster shells. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 33(1), 83–91.
Schippers, A., Jozsa, P. G., Sand, W., Kovacs, Z. M., & Jelea, M. (2000). Microbiological pyrite oxidation in a mine tailings heap and its relevance to the death of vegetation. Geomicrobiology Journal, 17(2), 151–162.
Silverman, M. P., & Lundgren, D. G. (1959). Studies on the chemoautotrophic iron bacterium Ferrobacillus ferrooxidans I. An improved medium and a harvesting procedure for securing high cell yields. Journal of Bacteriology, 77(5), 642–647.
Sreekrishnan, T., Tyagi, R., Blais, J., & Campbell, P. (1993). Kinetics of heavy metal bioleaching from sewage sludge—I. Effects of process parameters. Water Research, 27(11), 1641–1651.
Stookey, L. L. (1970). Ferrozine—A new spectrophotometric reagent for iron. Analytical Chemistry, 42(7), 779–781.
Zhang, W., Singh, P., Paling, E., & Delides, S. (2004). Arsenic removal from contaminated water by natural iron ores. Minerals Engineering, 17(4), 517–524.
Zhang, J., Zhang, X., Ni, Y., Yang, X., & Li, H. (2007). Bioleaching of arsenic from medicinal realgar by pure and mixed cultures. Process Biochemistry, 42(9), 1265–1271.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ko, MS., Park, HS., Kim, KW. et al. The role of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans in arsenic bioleaching from soil. Environ Geochem Health 35, 727–733 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-013-9530-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-013-9530-2