Abstract
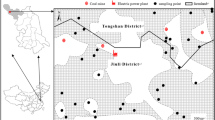
Cadmium (Cd) in coal, fly ash, slag, atmospheric deposition, soils and sediments collected from Tianjin, northern China, were measured to provide baseline information and determine possible Cd sources and potential risk. The concentrations of Cd in coal, fly ash and atmospheric deposition were much higher than the soil background values. Fallout from coal-fired thermal power plants, heating boilers and industrial furnaces has increased the Cd concentration in soils and sediments in Tianjin. The concentrations of Cd in soils of suburban areas were significantly higher than in rural areas, suggesting that coal burning in Tianjin may have an important impact on the local physical environment. Cd from coal combustion is readily mobilized in soils. It is soluble and can form aqueous complexes and permeate river sediments. The high proportion of mobile Cd affects the migration of Cd in soils and sediments, which may pose an environmental threat in Tianjin due to the exposure to Cd and Cd compounds via the food chain. This study may provide a window for understanding and tracing sources of Cd in the local environment and the risk associated with Cd bioaccessibility.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez-Ayuso, E., Querol, X., & Tomás, A. (2006). Environmental impact of a coal combustion-desulphurisation plant: Abatement capacity of desulphurisation process and environmental characterisation of combustion by-products. Chemosphere, 65, 2009–2017.
Bertin, G., & Averbeck, D. (2006). Cadmium: Cellular effects, modifications of biomolecules, modulation of DNA repair and genotoxic consequences (a review). Biochimie, 88, 1549–1559.
Bhanarkar, A. D., Gavane, A. G., Tajne, D. S., Tamhane, S. M., & Nema, P. (2008). Composition and size distribution of particles emissions from a coal-fired power plant in India. Fuel, 87, 2095–2101.
Chen, W. P., Krage, N., Wu, L. S., Pan, G. X., Khosrivafard, M., & Chang, A. C. (2008). Arsenic, cadmium, and lead in California cropland soils: Role of phosphate and micronutrient fertilizers. Journal of Environmental Quality, 37, 689–695.
Cheng, Y. M., Zhu, L. Y., Tian, S. Y., & Liang, X. W. (2009). Distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments from the Haihe River and the Bohai Sea. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 29(11), 2420–2426. (In Chinese).
China National Environmental Monitoring Center. (1990). China soil element background values. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. (In Chinese).
Cloquet, C., Carignan, J., Libourel, G., Sterckeman, T., & Perdrix, E. (2006). Tracing source pollution in soils using cadmium and lead isotopes. Environmental Science and Technology, 40, 2525–2530.
Jiang, D. L. (1990). Soil species records of Tianjin. Tianjin: Tianjin Science and Technology Press. (In Chinese).
Kaasalainen, M., & Yli-Halla, M. (2003). Use of sequential extraction to assess metal partitioning in soils. Environment Pollution, 126, 225–233.
Li, C., Wen, T. X., Li, Z., Dickerson, R. R., Yang, Y., Zhao, Y., et al. (2010). Concentrations and origins of atmospheric lead and other trace species at a rural site in northern China. Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres, 115, D00k23. doi:10.1029/2009JD013639.
Li, S. Y., Liu, G. X., & Miao, F. M. (1994). The distribution and environmental background values of the heavy metals in sediment of the Bohai Sea. China Environmental Science, 14(5), 370–376. (In Chinese).
Liu, L., Li, F. S., Xiong, D. Q., & Song, C. Y. (2006). Heavy metal contamination and their distribution in different size fractions of the surficial sediment of Haihe River, China. Environmental Geology, 50, 431–438.
Ministry of Environmental Protection of China. (2011). Emission standard of air pollutants for thermal power plants (GB 13223–2011). Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. (In Chinese).
Nordberg, G. F. (2009). Historical perspectives on cadmium toxicology. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 238, 192–200.
Pacyna, J. M. (1987). Atmospheric emissions of arsenic, cadmium, lead and mercury from high temperature processes in power generation and industry. In T. C. Hutchinson & K. M. Meema (Eds.), Lead, mercury, cadmium and arsenic in the environment (pp. 69–87). New York: Wiley.
Pan, J. L., Plant, J. A., Voulvoulis, N., Oates, C. J., & Ihlenfeld, C. (2010). Cadmium levels in Europe: Implications for human health. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 32, 1–12.
Perez-Santana, S., Pomares, A. M., Villanueva, T. M., Pena, I. M., Brunori, C., & Morabito, R. (2007). Total and partial digestion of sediments for the evaluation of trace element environmental pollution. Chemosphere, 66, 1545–1553.
Qiu, H., Vijver, M. G., & Peijnenburg, W. J. G. M. (2011). Interactions of cadmium and zinc impact their toxicity to the earthworm Aporrectodea caliginosa. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 30, 2084–2093.
Ren, D. Y., Zhao, F. H., Wang, Y. Q., & Yang, S. J. (1999). Distributions of minor and trace elements in Chinese coals. International Journal of Coal Geology, 40, 109–118.
Sammut, M. L., Noack, Y., Rose, J., Hazemann, J. L., Proux, O., Depoux, M., et al. (2010). Speciation of Cd and Pb in dust emitted from sinter plant. Chemosphere, 78, 445–450.
Shi, R. G., Lv, J. G., Cai, Y. M., Liu, Y., Wang, Z. H., Feng, J. M., et al. (2010). Levels, spatial distribution and possible sources of heavy metals contamination of suburban soils in Tianjin, China. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 85, 287–290.
Shikazono, N., Tatewaki, K., Mohiuddin, K. M., Nakano, T., & Zakir, H. M. (2012). Sources, spatial variation, and speciation of heavy metals in sediments of the Tamagawa River in Central Japan. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 34, 13–26.
Song, D. Y., Qin, Y., Zhang, J. Y., Wang, W. F., & Zheng, C. G. (2007). Concentration and distribution of trace elements in some coals from Northern China. International Journal of Coal Geology, 69, 179–191.
Tao, S., Cui, Y. H., Xu, F., Li, B. G., Cao, J., Liu, W., et al. (2004). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in agricultural soil and vegetables from Tianjin. Science of the Total Environment, 320, 11–24.
The Standardization Administration of China. (2005). Fly ash used for cement and concrete (GB/T1596-2005). Beijing: China Standard Press. (In Chinese).
Tianjin Environmental Protection Bureau. (1999). Environmental quality report of Tianjin in 1998. Tianjin: Tianjin Environmental Protection Bureau. (In Chinese).
Tianjin Environmental Protection Bureau. (2000). Environmental quality report of Tianjin in 1999. Tianjin: Tianjin Environmental Protection Bureau. (In Chinese).
Tianjin Environmental Protection Bureau. (2009). Environmental quality report of Tianjin in 2008. Tianjin: Tianjin Environmental Protection Bureau. (In Chinese).
Tianjin Statistics Bureau. (2009). Tianjin statistical yearbook 2008. Beijing: China Statistics Press. (In Chinese).
US EPA. (1996). Method 3052 microwave assisted acid digestion of siliceous and organically based matrices. http://www.epa.gov/osw/hazard/testmethods/sw846/pdfs/3052.pdf. Accessed June 2011.
Wang, X. L., Sato, T., Xing, B. S., & Tao, S. (2005a). Health risks of heavy metals to the general public in Tianjin, China via consumption of vegetables and fish. Science of the Total Environment, 350, 28–37.
Wang, M. S., Zheng, B. S., Hu, J., Li, S. H., & Wang, B. B. (2005b). Distribution of arsenic in southwest coals. Journal of China Coal Society, 30(3), 344–348. (In Chinese).
Wei, Z., Wu, G. H., Su, R. X., Li, C. W., & Liang, P. Y. (2011). Mobility and contamination assessment of mercury in coal fly ash, atmospheric deposition, and soil collected from Tianjin, China. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 30, 1997–2003.
Wu, G. H., Wei, Z., & Su, R. X. (2011). Distribution, accumulation and mobility of mercury in superficial sediment samples from Tianjin, northern China. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 13, 2488–2495.
Wu, G. H., Zu, Z. Z., Liu, E. B., Li, W. Q., & Zheng, H. Q. (2008). Concentration and distribution of heavy metals in urban sewage discharge channel of Tianjin. Huan Jing Ke Xue, 29(6), 413–420. (In Chinese).
Wu, S. P., Zuo, Q., & Lan, T. (2004). PAHs in airborne particles from Tianjin in winter season. Huan Jing Ke Xue, 25(4), 13–17. (In Chinese).
Xu, J. L., & Yang, J. R. (1996). Heavy metals in land ecosystem. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. (In Chinese).
Xu, K., Deng, T., Liu, J. T., & Peng, W. G. (2012). Phosphate removal from digested sludge supernatant using modified fly ash. Water Environment Research, 84, 411–416.
Yabe, J., Nakayama, S. M. M., Ikenaka, Y., Muzandu, K., Ishizuka, M., & Umemura, T. (2011). Uptake of lead, cadmium and other metals in the liver and kidneys of cattle near a lead-zinc mine in Kabwe, Zambia. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 30, 1892–1897.
Zandi, M., & Russell, N. V. (2007). Design of a leaching test framework for coal fly ash accounting for environmental conditions. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 131, 509–526.
Zhang, S. N., Liu, W., & Wang, D. L. (2008). Heavy metal pollution and their history trend in the surface sediment of the Haihe River. Arid Environmental Monitoring, 22(3), 130–133. (In Chinese).
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the 973 Program (2010CB434806), the Tianjin Natural Science Foundation (2010JCZDJC24500 and 10SYSYJC27400) and the Key Laboratory for Ecological Environment in Coastal Areas, State Oceanic Administration of China (201111).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, G., Yang, C., Guo, L. et al. Cadmium contamination in Tianjin agricultural soils and sediments: relative importance of atmospheric deposition from coal combustion. Environ Geochem Health 35, 405–416 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-012-9503-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-012-9503-x