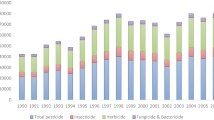
Abstract
Despite their environmental implications, ecotoxicological information regarding pesticide mixtures is relatively scarce. This study aimed to determine the ecotoxicity of individual pesticide formulations and their mixtures (insecticides and fungicides), which are applied during the production cycle of potato, according to agricultural practices from a Latin American region in Costa Rica. Two benchmark organisms were employed: Daphnia magna and Lactuca sativa. First, the evaluation of individual formulations (chlorothalonil, propineb, deltamethrin+imidacloprid, ziram, thiocyclam and chlorpyrifos) revealed differences between available EC50 for active ingredients (a.i.) and their respective formulations toward D. magna; on the contrary, no information could be retrieved from scientific literature for comparison in the case of L. sativa. In general, acute toxicity was higher toward D. magna than L. sativa. Moreover, interactions could not be determined on L. sativa, as the chlorothalonil formulation was not toxic at high levels and the concentration-response to propineb could not be fitted to obtain an IC50 value. The commercial formulation composed of deltamethrin+imidacloprid followed the concentration addition model (when compared with parameters retrieved from individual a.i.) and the other three mixtures evaluated (I: chlorothalonil-propineb-deltamethrin+imidacloprid; II: chlorothalonil-propineb-ziram-thiocyclam; III: chlorothalonil-propineb-chlorpyrifos) produced an antagonistic effect on D. magna, thus suggesting less acute toxicity than their individual components. Subsequent chronic studies showed that one of the most toxic mixtures (II) negatively affected D. magna reproduction at sublethal concentrations indicating that this mixture poses a risk to this species if these pesticides co-exist in freshwater systems. These findings provide useful data to better estimate the impact of real agricultural practices related to the use of agrochemicals.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar P (2014) Utilización del programa PIRI (Pesticide Impact Rating Index) como indicador de peligrosidad de la movilidad y toxicidad de los plaguicidas utilizados en dos fincas agrícolas cercanas a la quebrada Sanatorio, Cartago (Tesis de Licenciatura). Universidad de Costa Rica, San Pedro
Arias-Andrés MJ, Rämö R, Mena FT, Ugalde R, Grandas L, Ruepert C, Castillo LE, Van den Brink PJ, Gunnarsson JS (2018) Lower tier toxicity risk assessment of agriculture pesticides detected on the Río Madre de Dios watershed, Costa Rica. Environ Sci Poll Res 25:13312–13321
Belden JB, Gilliom RJ, Lydy MJ (2007) How well can wepredict the toxicity of pesticide mixtures to aquatic life? Integr Environ Assess Manag 3:364–372
Bostanian NJ, Larocque N, Chouinard G, Coderre D (2001) Baseline toxicity of several pesticides to Hyaliodes vitripennis (Say) (Hemiptera: Miridae). Pest Manage Sci 57:1007–1010
Bravo V, de la Cruz E, Herrera G, Ramírez F (2013) Uso de plaguicidas en cultivos agrícolas como herramienta para el monitoreo de peligros en salud. Uniciencia 27:351–376
Bravo V, de la Cruz E, Berrocal S, Ramírez F (2015) Importación de plaguicidas: peligros agudos en salud y efectos cancerígenos. Observatorio Ambiental, UNA http://www.observatorioambiental.una.ac.cr/index.php/indicadores-ambientales/84-plaguicidasysalud. Accessed November 11, 2021
Carazo-Rojas E, Pérez-Rojas G, Pérez-Villanueva M, Chinchilla-Soto C, Chin-Pampillo JS, Aguilar-Mora P, Alpízar-Marín M, Masís-Mora M, Rodríguez-Rodríguez CE, Vryzas Z (2018) Pesticide monitoring and ecotoxicological risk assessment in surface water bodies and sediments of a tropical agro-ecosystem. Environ Poll 241:800–809
Cedergreen N (2014) Quantifying synergy: a systematic review of mixture toxicity studies within environmental toxicology. PLOS ONE 9:e96580
Chin-Pampillo JS, Ruiz KH, Aguilar PM, Arias VM, Masis MM (2012) Caracterización de la calidad del agua de la Quebrada Sanatorio en Tierra Blanca ubicada en una zona agrícola de la provincia de Cartago y sus implicaciones para la salud pública. O Mundo da Saúde 36:548–555
Chiu MC, Hunt L, Resh VH (2016) Response of macroinvertebrate communities to temporal dynamics of pesticide mixtures: a case study from the Sacramento River watershed, California. Environ Poll 219:89–98
Commo F, Bot BM (2016) nplr: N-Parameter Logistic Regression. R package version 0.1–7. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=nplr
Decourtye A, Devillers J, Cluzeau S, Charreton M, Pham-Delegue MH (2004) Effects of imidacloprid and deltamethrin on associative learning in honeybees under semi-field and laboratory conditions. Ecotox Environ Safe 57:410–419
de Jong FMW, de Snoo GR, van de Zande JC (2008) Estimated nationwide effects of pesticide spray drift on terrestrial habitats in the Netherlands. J Environ Manage 86:721–730
Dewar AM, Westwood F, Bean KM, Haylock LA, Osborne R (1997) The relationship between pellet size and the quantity of imidacloprid applied to sugar beet pellets and the consequences for seedling emergence. Crop Prot 16:187–192
Diepens NJ, Pfennig S, Van den Brink PJ, Gunnarsson JS, Ruepert C, Castillo LE (2014) Effect of pesticides used in banana and pineapple plantations on aquatic ecosystems in Costa Rica. J Environ Biol 35:73–84
Ebel RC, Wallace B, Elkins CH (2000) Phytotoxicity of the systemic insecticide imidacloprid on tomato and cucumber in the greenhouse. Hort Technology 10:144–147
Echeverría-Sáenz S, Mena F, Pinnock M, Ruepert C, Solano K, de la Cruz E, Campos B, Sánchez-Avila J, Lacorte S, Barata C (2012) Environmental hazards of pesticides from pineapple crop production in the Río Jiménez watershed (Caribbean Coast, Costa Rica). Sci Total Environ 440:106–114
Echeverría-Sáenz S, Mena F, Arias-Andrés M, Vargas S, Ruepert C, Van den Brink PJ, Castillo LE, Gunnarsson JS (2018) In situ toxicity and ecological risk assessment of agro-pesticide runoff in the Madre de Dios River in Costa Rica. Environ Sci Poll Res 25:13270–13282
Escobar-Chávez C, Alvariño L, Iannacone J (2019) Evaluación del riesgo ambiental acuático de la mezcla de los plaguicidas imidacloprid (insecticida) y propineb (fungicida) en Daphnia magna Straus, 1820. PAIDEIA XXI 9:301–332
Escher B, Braun G, Zarfl C (2020) Exploring the Concepts of Concentration Addition and Independent Action Using a Linear Low‐Effect Mixture Model. Environ Toxicol Chem 39:2552–2559
EPA (2002) EPA-821-R-02-012 Methods for measuring the acute toxicity of effluents and receiving water to freshwater and marine organisms. Office of Water (4303T), Washington, DC
EPA (2002) Ziram: A Preliminary HED Risk Assessment for the Reregistration Eligibility Decision (RED) Document. U. S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
Faust M, Altenburger R, Grimme LH (2000) Predictive assessment of the aquatic toxicity of multiple chemical mixtures. J Environ Qual 29:1063
Fernández-Casalderrey A, Ferrando MD, Andreu-Moliner E (1993) Effects of endosulfan on survival, growth and reproduction of Daphnia magna. Comp Biochem Physiol Part - C: Pharmacol Toxicol Endocrinol 106:437–441
Fernández‐Casalderrey A, Ferrando MD, Andreu‐Moliner E (1995) Chronic toxicity of diazinon to Daphnia magna: Effects on survival, reproduction and growth. Toxicol Environ Chem 49:25–32
Ferrando MD, Sancho E, Andreu-Moliner E (1996) Chronic toxicity of fenitrothion to an algae (Nannochloris oculata), a rotifer (Brachionus calyciflorus), and the cladoceran (Daphnia magna). Ecotox Environ Safe 35:112–120
Fournier M, Ramírez F, Ruepert C, Vargas S, Echeverría S (2010) Diagnóstico sobre contaminación de aguas, suelos y productos hortícolas por el uso de agroquímicos en la microcuenca de las quebradas Plantón y Pacayas en Cartago, Costa Rica. INTA-UNA, Costa Rica, pp 1–85
Fungicide Resistance Action Committee (FRAC) (2021) FRAC code list: Fungal control agents sorted by cross resistance pattern and mode of action (including coding for FRAC Groupson product labels). FRAC https://www.frac.info/docs/default-source/publications/frac-code-list/frac-code-list-2022--final.pdf?sfvrsn=b6024e9a_2. Accessed 31 January 2022
Gharaei A, Karimi M, Mirdar HJ, Miri M, Faggio C (2020) Population growth of Brachionus calyciflorus affected by deltamethrin and imidacloprid insecticides. Iran J Fish Sci 19:588–601
Huete-Soto A, Castillo-González H, Masís-Mora M, Chin-Pampillo JS, Rodríguez-Rodríguez CE (2017) Effects of oxytetracycline on the performance and activity of biomixtures: removal of herbicides and mineralization of chlorpyrifos. J Hazard Mater 321:1–8
Iannacone J, Alvariño L, Caballero C, Sánchez J (2000) Cuatro ensayos ecotoxicológicos para evaluar lindano y clorpirifos. Gayana 64:139–146
Joly P, Bonnemoy F, Charvy JCH, Bohatier J, Mallet C (2013) Toxicity assessment of the maize herbicides S-metolachlor, benoxacor, mesotrione and nicosulfuron, and their corresponding commercial formulations, alone and in mixtures, using the Microtox® test. Chemosphere 93:2444–2450
Lewis KA, Tzilivakis J, Warner D, Green A (2016) An international database for pesticide risk assessments and management. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 22:1050–1064
Li X, Zhao X, Yao Y, Guob M, Li S (2021) New insights into crosstalk between apoptosis and necroptosis co-induced by chlorothalonil and imidacloprid in Ctenopharyngodon idellus kidney cell. Sci Total Environ 780:146591
Loewy RM, Monza LB, Kirs VE, Savini MC (2011) Pesticide distribution in an agricultural environment in Argentina. J Environ Sci Health B 46:662–670
Marinovich M, Viviani B, Capra V, Corsini E, Anselmi L, D’Agostino G, Di Nucci A, Binaglia M, Tonini M, Galli CL (2002) Facilitation of acetylcholine signaling by the dithiocarbamate fungicide propineb. Chem Res Toxicol 15:26–32
Nagya K, Duca RC, Lovas S, Creta M, Scheepers PTJ, Godderis L, Ádám B (2020) Systematic review of comparative studies assessing the toxicity of pesticide active ingredients and their product formulations. Environ Res 181:108926
OECD (2012) Test No. 211: Daphnia magna Reproduction Test, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2. OECD Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264185203-en
Pereira JL, Antunes SC, Castro BB, Marques CR, Goncalves AMM, Goncalves F, Pereira R (2009) Toxicity evaluation of three pesticides on non-target aquatic and soil organisms: commercial formulation versus active ingredient. Ecotoxicology 18:455–463
Pérez-Villanueva M, Chin-Pampillo J, Aguilar-Mora P, Guzmán AP, Masís-Mora M, Arias-Mora V, Ramírez-Morales D (2021) An integrative water quality evaluation in two surface water bodies from a tropical agricultural region in Cartago, Costa Rica. Environ Sci Poll Res https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17283-y
Phyu YL, Palmer CG, Warne MSJ, Hose GC, Chapman JC, Lim RP (2011) A comparison of mixture toxicity assessment: Examining the chronic toxicity of atrazine, permethrin and chlorothalonil in mixtures to Ceriodaphnia cf. dubia. Chemosphere 85:1568–1573
R Core Team (2021) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. URL https://www.R-project.org/
Ramírez-Morales D, Perez-Villanueva ME, Chin-Pampillo JS, Aguilar-Mora P, Arias-Mora V, Masís-Mora M (2021) Pesticide occurrence and water quality assessment from an agriculturally influenced Latin-American tropical region. Chemosphere 262:127851
Ramírez-Muñoz F, Fournier-Leiva M, Ruepert C, Hidalgo-Ardón C (2014) Uso de agroquímicos en el cultivo de papa en Pacayas, Cartago Costa Rica. Agronomía Mesoamericana 25:337–345
Rämö RA, van den Brink PJ, Ruepert C, Castillo LE, Gunnarsson JS (2018) Environmental risk assessment of pesticides in the River Madre de Dios, Costa Rica using PERPEST, SSD, and msPAF models. Environ Sci Pollu Res 25:13254–13269
Ritz C, Baty F, Streibig JC, Gerhard D (2015) Dose-Response Analysis Using R. PLoS ONE 10:146021. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0146021
Rizo-Patrón FV, Kumar A, McCoy MBC, Springer M, Trama FA (2013) Macroinvertebrate communities as bioindicators of water quality in conventional and organic irrigated rice fields in Guanacaste, Costa Rica. Ecol Indic 29:68–78
Rizzati V, Briand O, Guillou H, Gamet-Payrastre L (2016) Effects of pesticide mixtures in human and animal models: An update of the recent literature. Chem Biol Interact 254:231–246
Rodríguez-Rodríguez CE, Matarrita J, Herrero-Nogareda L, Pérez-Rojas G, Alpízar-Marín M, Chinchilla-Soto C, Pérez-Villanueva M, Vega-Méndez D, Masís-Mora M, Cedergreen N, Carazo-Rojas E (2021) Environmental monitoring and risk assessment in a tropical Costa Rican catchment under the influence of melon and watermelon crop pesticides. Environ Poll 284:117498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117498
Ruíz-Hidalgo K, Masís-Mora M, Barbieri E, Carazo-Rojas E, Rodríguez-Rodríguez CE (2016) Ecotoxicological analysis during the removal of carbofuran in fungal bioaugmented matrices. Chemosphere 144:864–871
Sancho E, Sánchez M, Ferrando MD, Andreu-Moliner E (2001) Effects of thiobencarb herbicide to an alga (Nannochloris oculata) and the cladoceran (Daphnia magna). J Environ Sci Health B 36:55–65
Schreiner VC, Szöcs E, Bhowmik AK, Vijver MG, Schäfer RB (2016) Pesticide mixtures in streams of several European countries and the USA. Sci Total Environ 573:680–689
SEPSA (2016) Boletín Estadístico Agropecuario N° 26. Área de Estadísticas Económicas e Información, San José, Costa Rica
Servicio Fitosanitario del Estado (SFE) (2020) Uso aparente de plaguicidas en Costa Rica, período 2017–2019. MAG, Costa Rica, https://www.sfe.go.cr/Transparencia/Estimacion_de_uso_de_plaguicidas_en_Costa_Rica_2017_2019.pdf#search=uso%20aparente accessed 15 January 2021
Sharma A, Kumar V, Shahzad B, Tanveer M, Singh GP, Handa N, Kohli SK, Yadav P, Bali AS, Parihar RD, Dar OI, Singh K, Jasrotia S, Bakshi P, Ramakrishnan M, Kumar S, Bhardwaj R, Thukral AK (2019) Worldwide pesticide usage and its impacts on ecosystem. SN Appl Sci 1:1446
Sobrero MC, Ronco A (2004) Ensayo de toxicidad aguda con semillas de lechuga (Lactuca sativa L). In: Castillo MG (ed.) Ensayos toxicológicos y métodos de evaluación de calidad de aguas. IMTA, México, p 179
Song Y, Chen M, Zhou J (2017) Effects of three pesticides on superoxide dismutase and glutathione-S-transferase activities and reproduction of Daphnia magna. Arch Environ Prot 43:80–86
Tomé HVV, Ramos GS, Araújo MF, Santana WC, Santos GR, Guedes RNC, Maciel CD, Newland PL, Oliveira EE (2017) Agrochemical synergism imposes higher risk to Neotropical bees than to honeybees. R Soc Open Sci 4:160866
USEPA (1996) Ecological Effects Test Guidelines OPPTS 850.4200 Seed Germination/Root Elongation Toxicity Test. U.S. Environmnetal Protection Agency Washington D.C.
van Scoy AR, Tjeerdema RS (2014) Environmental fate and toxicology of chlorothalonil. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 232:89–105
Villarroel MJ, Sancho E, Ferrando MD, Andreu E (2003) Acute, chronic and sublethal effects of the herbicide propanil on Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 53:857–864
Walter NT, Adeleye VO, Muthomi PK, Ortiz RJR, Strzyzewski I, Funderburk J, Martini X (2018) Toxicity of different insecticides against two thrips (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) pests of concern in Central America. Florida Entomologist 101(4):627–633
Walter NT, Ortiz RJR, Strzyzewski I, Funderburk J, Martini X (2020) Toxicity of different insecticides against Franklinellia invasor (Thysanoptera: Thripidae), a mango pest in Central America. Fla Entomol 103:296–298
Xiaoqiang C, Hua F, Xuedong P, Xiao W, Min S, Bo F, Yunlong Y (2008) Degradation of chlorpyrifos alone and in combination with chlorothalonil and their effects on soil microbial populations. J Environ Sci 20:464–469
Xu L, Luo G, Sun Y, Huang S, Xu D, Xu G, Han Z, Gu Z, Zhang Y (2020) Multiple down-regulated cytochrome P450 monooxygenase genes contributed to synergistic interaction between chlorpyrifos and imidacloprid against Nilaparvata lugens. J Asia Pac Entomol 23:44–50
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Marta Pérez Villanueva for the technical support at initial stages of the implementation of the chronic toxicity assay; Paula Aguilar Mora for the description of the pesticide application cycle for potato crops in Costa Rica; and Marianella Castro Esquivel and José David Umaña Monge for the collaboration in the performance and data analysis of the chronic test.
Funding
This work was supported by Vicerrectoría de Investigación at Universidad de Costa Rica (project 908-B8-122).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by MM-R, DR-M and JRM-M. The first draft of the paper was written by MM-M and CE. R-R and all authors commented on previous versions of the paper. All authors read and approved the final paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Méndez-Rivera, M., Ramírez-Morales, D., Montiel-Mora, J.R. et al. Ecotoxicity of pesticide formulations and their mixtures: the case of potato crops in Costa Rica. Ecotoxicology 32, 383–393 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-023-02648-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-023-02648-5