Abstract
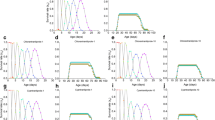
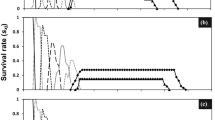
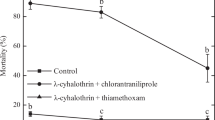
The seven-spot ladybird beetle, Coccinella septempunctata, is a major natural enemy of aphids in the field and in greenhouses in China and is part of integrated pest management (IPM). Imidacloprid, a highly efficient insecticide that not only kills aphids at lethal concentrations, but also can cause various sublethal effects in nontarget organisms. To strengthen IPM and its sustainability, it is important assessing possible side effects on natural enemies. When the effects of sublethal concentrations (LC5 and 10%LC5) of imidacloprid on C. septempunctata were evaluated, the adult longevity was shortened by 23.97 and 28.68 %, and the fecundity reduced by 52.81 and 56.09 % compared to control population. In the F1 generation (i.e., the progeny of the exposed individuals), the juvenile development was slower by 1.44 days and 0.66 days, and the oviposition period was shortened by 10 and 13 days, respectively. The fecundity of the F1 generation decreased by 17.88, 44.03 and 51.69 % when exposed to 1%LC5, 10%LC5, and LC5, respectively. The results of demographical growth estimates showed that the intrinsic rate of increase (r m ) and net reproductive rate (R 0 ) were lower in C. septempunctata populations that had been exposed to sublethal concentrations of imidacloprid. The results emphasize the importance of assessing side effects of low imidacloprid concentrations on such predator species, even at the transgenerational level.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbes K, Biondi A, Kurtulus A, Ricupero M, Russo A, Siscaro G, Chermiti B, Zappalà L (2015) Combined non-target effects of insecticide and high temperatures on the parasitoid Bracon nigricans. PLoS One 10(9):e0138411
Abbott WS (1925) A method for computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J Econ Entomol 18:265–267
Ali A, Ahmad F, Biondi A, Wang Y, Desneux N (2012) Potential for using Datura alba leaf extracts against two major stored grain pests, the khapra beetle Trogoderma granarium and the rice weevil Sitophillus oryzae. J Pest Sci 85:359–366
Ahmad M, Ossiewatsch HR, Basedow T (2003) Effects of neem treated aphids as food/hosts on their predators and parasitoids. J Appl Entomol 127:458–464
Baas J, Jager T, Kooijman B (2010) A review of DEB theory in assessing toxic effects of mixtures. Sci Total Environ 408:3740–3745
Bengochea P, Budia F, Viñuela E, Medina P (2014) Are kaolin and copper treatments safe to the olive fruit fly parasitoid Psyttalia concolor? J Pest Sci 87:351–359
Biondi A, Desneux N, Siscaro G, Zappalà L (2012a) Using organic-certified rather than synthetic pesticides may not be safer for biological control agents: selectivity and side effects of 14 pesticides on the predator Orius laevigatus. Chemosphere 87:803–812
Biondi A, Mommaerts V, Smagghe G, Vinuela E, Zappalà L, Desneux N (2012b) The non-target impact of spinosyns on beneficial arthropods. Pest Manag Sci 68:1523–1536
Biondi A, Zappalà L, Stark JD, Desneux N (2013) Do biopesticides affect the demographic traits of a parasitoid wasp and its biocontrol services through sublethal effects? PLoS One 8:e76548
Biondi A, Campolo O, Desneux N, Siscaro G, Palmeri V, Zappalà L (2015) Life stage-dependent susceptibility of Aphytis melinus DeBach (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae) to two pesticides commonly used in citrus orchards. Chemosphere 128:142–147
Biondi A, Zappalà L, Di Mauro A, Tropea Garzia G, Russo A, Desneux N, Siscaro G (2016) Can alternative host plant and prey affect phytophagy and biological control by the zoophytophagous mirid Nesidiocoris tenuis?. BioControl 61:79–90
Bompard A, Jaworski CC, Bearez P, Desneux N (2013) Sharing a predator: can an invasive alien pest affect the predation on a local pest? Pop Ecol 55:433–440
Blacquiere T, Smagghe G, Van Gestel CA, Mommaerts V (2012) Neonicotinoids in bees: a review on concentrations, side-effects and risk assessment. Ecotoxicology 21:973–992
Bozsik A (2006) Susceptibility of adult Coccinella septempunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) to insecticides with different modes of action. Pest Manag Sci 62:651–654
Cabral S, Soares AO, Garcia P (2011) Voracity of Coccinella undecimpunctata: effects of insecticides when foraging in a prey/plant system. J Pest Sci 84:373–379
Chen Z, Qu Y, Xiao D, Song L, Zhang S, Gao X, Desneux N, Song D (2015) Lethal and social-mediated effects of ten insecticides on the subterranean termite Reticulitermes speratus. J Pest Sci 88:741–751
Chi H (1988) Life-table analysis incorporating both sexes and variable development rates among individuals. Environ Entomol 17:26–31
Chi H (2012) TWOSEX-MS Chart: a computer program for the age-stage, two-sex life table analysis. National Chung Hsing University, Taichung Taiwan
Chi H, Liu H (1985) Two new methods for the study of insect population ecology. Bull Inst Zool 24:225–240
Chi H, Su HY (2006) Age-stage, two-sex life tables of Aphidius gifuensis (Ashmead) (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) and its host Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Homoptera: Aphididae) with mathematical proof of the relationship between female fecundity and the net reproductive rate. Environ Entomol 35:10–21
Cresswell JE, Desneux N, vanEngelsdorp D (2012) Dietary traces of neonicotinoid pesticides as a cause of population declines in honey bees: an evaluation by Hill’s epidemiological criteria. Pest Manag Sci 68:819–827
Desneux N, Wajnberg E, Fauvergue X, Privet S, Kaiser L (2004) Oviposition behaviour and patch‐time allocation in two aphid parasitoids exposed to deltamethrin residues. Entomol Exp Appl 112:227–235
Desneux N, Ramirez‐Romero R, Kaiser L (2006) Multistep bioassay to predict recolonization potential of emerging parasitoids after a pesticide treatment. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:2675–2682
Desneux N, Decourtye A, Delpuech JM (2007) The sublethal effects of pesticides on beneficial arthropods. Annu Rev Entomol 52:81–106
Decourtye A, Henry M, Desneux N (2013) Environment: overhaul pesticide testing on bees. Nature 497:188
Eisenback BM, Salom SM, Kok LT, Lagalante AF (2010) Lethal and sublethal effects of imidacloprid on Hemlock woolly Adelgid (Hemiptera: Adelgidae) and two introduced predator species. J Econ Entomol 103:1222–1234
Finney DJ (1971) Probit analysis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Fogel MN, Schneider MI, Desneux N, Gonzalez B, Ronco AE (2013) Impact of the neonicotinoid acetamiprid on immature stages of the predator Eriopis connexa (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Ecotoxicology 22:1063–1071
Gao SK, Yang ZQ (2015) Application of life table in pest biological control. Chinese. J Biol Control 31:256–263
Grafton-Cardwell EE, Gu P (2003) Conserving vedalia beetle, Rodolia cardinalis (Mulsant) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae), in citrus: a continuing challenge as new insecticides gain registration. J Econ Entomol 96:1388–1398
Gerami S, Jahromi KT, Ashouri A, Rasoulian G, Heidari A (2005) Sublethal effects of imidacloprid and pymetrozine on the life table parameters of Aphis gossypii Glover (Homoptera: Aphididae). Comm Appl Biol Sci 70:779–785
Gontijo PC, Moscardini VF, Michaud JP, Carvalho GA (2014) Non-target effects of chlorantraniliprole and thiamethoxam on Chrysoperla carnea when employed as sunflower seed treatments. J Pest Sci 87:711–719
Guedes RNC, Smagghe G, Stark JD, Desneux N (2016) Pesticide-induced stress in arthropod pests for optimized integrated pest management programs. Annu Rev Entomol 61:43–62
Han P, Niu CY, Lei CL, Cui JJ, Desneux N (2010) Quantification of toxins in a Cry1Ac+CpTI cotton cultivar and its potential effects on the honey bee Apis mellifera L. Ecotoxicology 19:1452–1459
Han P, Niu CY, Biondi A, Desneux N (2012) Does transgenic Cry1Ac+CpTI cotton pollen affect hypopharyngeal gland development and midgut proteolytic enzyme activity in the honey bee Apis mellifera L. (Hymenoptera, Apidae)? Ecotoxicology 21:2214–2221
He YX, Zhao J, Zheng Y, Zhan Z, Desneux N, Wu KM (2012) Lethal effect of imidacloprid on the coccinellid predator Serangium japonicum and sublethal effects on predator voracity and on functional response to the whitefly Bemisia tabaci. Ecotoxicology 21:1291–1300
He YX, Zhao JW, Zheng Y, Weng QY, Biondi A, Desneux N, Wu KM (2013) Assessment of potential sublethal effects of various insecticides on key biological traits of the tobacco whitefly, Bemisia tabaci. Int J Biol Sci 9:246–255
Jager T, Zimmer EI (2012) Simplified dynamic energy budget model for analysing ecotoxicity data. Ecol Model 225:74–81
Ji LL, Dong YK, Li ZH (2011) The indoor toxicity effect of four pesticides to the adult of Coccinella septempunctata. Shangdong Agric Sci 5:74–75. (in Chinese)
Liang P, Tian YA, Biondi A, Desneux N, Gao XW (2012) Short-term and transgenerational effects of the neonicotinoid nitenpyram on susceptibility to insecticides in two whitefly species. Ecotoxicology 21:1889–1898
Lu YH, Wu KM, Jiang YY, Guo YY, Desneux N (2012) Widespread adoption of Bt cotton and insecticide decrease promotes biocontrol services. Nature 487:362–365
Lucas E, Giroux S, Demougeo S, Duchesne RM, Coderre D (2004) Compatibility of a natural enemy, Coleomegilla maculata lengi (Col.,Coccinellidae) and four insecticides used against the Colorado potato beetle (Col.,Chrysomelidae). J Appl Entomol 128:233–239
Malaquias JB, Ramalho FS, Omoto C, Godoy WAC, Silveira RF (2013) Imidacloprid affects the functional response of predator Podisus nigrispinus (Dallas) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) to strains of Spodoptera frugiperda (JE Smith) on Bt cotton. Ecotoxicology 23:192–200
Mirande L, Desneux N, Haramboure M, Schneider MI (2015) Intraguild predation between an exotic and a native coccinellid in Argentina: the role of prey density. J Pest Sci 88:155–162
Moscardini VF, Gontijo PC, Michaud JP, Carvalho GA (2015) Sublethal effects of insecticide seed treatments on two nearctic lady beetles (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Ecotoxicology 5:1152–1161
Moser SE, Obrycki JJ (2009) Non-target effects of neonicotinoid seed treatments: mortality of coccinellid larvae related to zoophytophagy. Biol Control 51:487–492
Nauen R, Koob B, Elbert A (1998) Antifeedant effects of sublethal dosages of imidacloprid on Bemisia tabaci. Entomol Exp Appl 88:287–293
Palumbo JC, Horowitz AR, Prabhaker N (2001) Insecticidal control and resistance management for Bemisia tabaci. Crop Prot 20:739–765
Pan H, Liu Y, Liu B, Lu Y, Xu X, Qian X et al. (2014) Lethal and sublethal effects of cycloxaprid, a novel cis-nitromethylene neonicotinoid insecticide, on the mirid bug Apolygus lucorum. J Pest Sci 87:731–738
Papachristos DP, Milonas PG (2008) Adverse effects of soil applied insecticides on the predatory coccinellid Hippodamia undecimnotata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Biol Control 47:77–81
Pérez-Hedo M, Urbaneja A (2015) Prospects for predatory mirid bugs as biocontrol agents of aphids in sweet peppers. J Pest Sci 88:65–73
Qu YY, Xiao D, Li JY, Chen Z, Biondi A, Desneux N, Gao XW, Song DL (2015) Sublethal and hornesis effects of imidacloprid on the soybean aphid Aphis glycines. Ecotoxicology 24:479–487
Ragsdale DW, Landis DA, Brodeur J, Heimpel GE, Desneux N (2011) Ecology and management of the soybean aphid in North America. Annu Rev Entomol 56:375–399
Ramirez-Romero R, Desneux N, Decourtye A, Chaffiol A, Pham-Delègue MH (2008) Does Cry1Ab protein affect learning performances of the honeybee Apis mellifera L. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 70:327–333
Saeed R, Razaq M, Hardy IC (2015) The importance of alternative host plants as reservoirs of the cotton leaf hopper, Amrasca devastans, and its natural enemies. J Pest Sci 88:517–531
Sanchez-Bayo F (2014) The trouble with neonicotinoids. Science 6211:806–807
Sanchez-Bayo F, Goulson D, Pennacchio F, Nazzi F, Goka K, Desneux N (2016) Are bee diseases linked to pesticides? – A brief review. Environ Int 89-90:7–11
Schneider MI, Sanchez N, Pineda S, Chi H, Ronco A (2009) Impact of glyphosate on the development, fertility and demography of Chrysoperla externa (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae): ecological approach. Chemosphere 76:1451–1455
Singh SR, Walters KFA, Port GR, Northing P (2004) Consumption rates and predatory activity of adult and forth instar larvae of the seven spot ladybird, Coccinella septempunctata (L.), following contact with dimethoate residue and contaminated prey in laboratory arenas. Biol Control 30:127–133
Smith SF, Krischik VA (1999) Effects of systemic imidacloprid on Coleomegilla maculata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Biol control 28:1189–1195
Sohrabi F, Shishehbor P, Saber M, Mosaddegh MS (2012) Lethal and sublethal effects of buprofezin and imidacloprid on the whitefly parasitoid Encarsia inaron (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae). Crop Prot 32:83–89
Sohrabi F, Shishehbor P, Saber M, Mosaddegh MS (2013) Lethal and sublethal effects of imidcaloprid and buprofezin on the sweetpotato white parasitoid Eretmocerus mundus (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae). Crop Prot 45:98–103
Stark JD, Banks JE (2003) Population-level effects of pesticides and other toxicants on arthropods. Annu Rev Entomol 48:505–519
Stark JD, Banks JE, Vargas R (2004) How risky is risk assessment: the role that life history strategies play in susceptibility of species to stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:732–736
Stark JD, Vargas RI, Banks JE (2007) Incorporating ecologically relevant measures of pesticide effect for estimating the compatibility of pesticides and biocontrol agents. J Econ Entomol 100:1027–1032
Tan XL, Zhao J, Zhang F, Wang S (2014) Light dependency of life trails, reproduction, locomotion, and predaion in the polyphagous ladybird Hippodamia variegata. Entomol Exp Appl 152:200–208
Tan Y, Biondi A, Desneux N, Gao XW (2012) Assessment of physiological sublethal effects of imidacloprid on the mirid bug Apolygus lucorum (Meyer-Dür). Ecotoxicology 21:1989–1997
Tomizawa M, Casida JE (2001) Structure and diversity of insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Pest Manag Sci 57:914–922
Torres JB, Ruberson JR (2004) Toxicity of thiamethoxam and imidacloprid to Podisus nigrispinus (Dallas) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) nymphs associated to aphid and whitefly control in cotton. Neotrop Entomol 33:99–106
van Herk WG, Vernon RS, Vojtko B, Snow S, Fortier J, Fortin C (2015) Contact behaviour and mortality of wireworms exposed to six classes of insecticide applied to wheat seed. J Pest Sci 88:717–739
Vincent C, Ferran A, Guige L, Gambier J, Brun J (2000) Effects of imidacloprid on Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) larval biological and locomotorybehavior. Eur J Entomol 97:501–506
Wang S, Qi Y, Desneux N, Shi X, Biondi A, Gao X (2017) Sublethal and transgenerational effects of short-term and chronic exposures to the neonicotinoid nitenpyram in Aphis gossypii. J Pest Sci. doi: 10.1007/s10340-016-0770-7
Youn YN, Seo MJ, Shin JG, Jang C, Yub YM (2003) Toxicity of greenhouse pesticides to multicolored Asian ladybeetles, Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Biol Control 28:164–170
Yu CH, Fu, MR, LinRH, ZhangY, LiuYQ, JiangH, Brock, T.CM (2014a) Toxic effects of hexaflumuron on the development of Coccinella septempunctata. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 21:1418–1424
Yu CH, Lin RH, Fu MR, Zhou YM, Zong FL, Jiang H, Lv N, Piao XY, Zhang J, Liu YQ, Brock TCM (2014b) Impact of imidacloprid on life-cycle development of Coccinella septempunctata in laboratory microcosms. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 110:168–173
Zotti MJ, Grutzmacher AD, Lopes IH, Smagghe G (2013) Comparative effects of insecticides with different mechanisms of action on Chrysoperla externa (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae): Lethal, sublethal and dose-response effects. Insect Sci 20:743–752
Zhang DW, Dong M, Du XG (2011) Effects of organic management on predator densities of Myzus persicae (Sulzer) during transition to organic agriculture in peach fields in China. J Sustain Agri 35:826–839
Zhang X, Xu Q, Lu W, Liu F (2015) Sublethal effects of four synthetic insecticides on the generalist predator Cyrtorhinus lividipennis. J Pest Sci 88:383–392
Zhao J, Li S, Gao XW, Zhang F, Wang S (2015) Comparison of life tables of Cheilomenes sexmaculata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) under laboratory and greenhouse conditions. J Econ Entomol 108:1700–1707
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Key Basic Research and Development Program (973 program 2013CB127605), the Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest (201303108), and the Beijing Novo Program (z121105002512039). The authors are grateful to Professor Hsin Chi (Laboratory of Theoretical and Applied Ecology, Department of Entomology, National Chung Hsing University, Taiwan) for providing the age-stage two-sex life table software.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Statement of Human and Animal Rights
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted.
Informed consent
There were no human subjects, thus informed consent is not applicable for this study.
Additional information
Da Xiao and Jing Zhao contributed equally to the study
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, D., Zhao, J., Guo, X. et al. Sublethal effects of imidacloprid on the predatory seven-spot ladybird beetle Coccinella septempunctata . Ecotoxicology 25, 1782–1793 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-016-1721-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-016-1721-z