Abstract
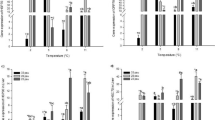
Caffeine, a biologically active drug with many known molecular targets, is recognized as a contaminant of marine systems. Although the concentrations of caffeine reported from aquatic systems are low (ng/l–μg/l), harmful ecological effects not detected by traditional toxicity tests could occur as a result of caffeine contamination. We used Hsp70, a molecular biomarker of cellular stress, to investigate the sub-lethal cellular toxicity of environmentally relevant concentrations of caffeine on the mussel Mytilus californianus, a dominant species in the rocky intertidal zone along the Oregon Coast. Hsp70 concentrations in the gill and mantle tissue of mussels exposed to 0.05, 0.2, and 0.5 μg/l of caffeine for 10, 20, and 30 days were compared to basal levels in control mussels. Hsp70 in the gill tissue of M. californianus had an initial attenuation of the stress protein followed by a significant up-regulation relative to controls in all but the 0.5 μg/l treatment. Hsp70 in the mantle tissue of mussels exposed to caffeine did not differ from control mussels. This study provides laboratory evidence that environmentally relevant concentrations of caffeine can exert an effect on M. californianus gill tissue at the molecular-level.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ait-Aissa S, Porcher JM, Arrigo AP, Lambre C (2000) Activation of the hsp70 promoter by environmental inorganic and organic chemicals: relationship with cytotoxicity and lipophilicity. Toxicology 145:147–157
Arts MJ, Schill RO, Knigge T, Eckwert H, Kammenga JE, Kohler HR (2004) Stress proteins (hsp70, hsp60) induced in isopods and nematodes by field exposure to metals in a gradient near Avonmouth, UK. Ecotoxicology 13:739–755
Barraco RA, Stefano GB (1990) Pharmacological evidence for the modulation of monoamine release by adenosine in the invertebrate nervous system. J Neurochem 54:2002–2006
Benowitz NL (1990) Clinical pharmacology of caffeine. Ann Rev Med 41:277–288
Berthou F, Flinois JP, Ratanasavanh D, Beaune P, Riche C, Guillouzo A (1991) Evidence for the involvement of several cytochromes P-450 in the first steps of caffeine metabolism by human liver microsomes. Drug Metab Dispos 19:561–567
Buckley BA, Owen ME, Hofmann GE (2001) Adjusting the thermostat: the threshold induction temperature for the heat-shock response in intertidal mussels (genus Mytilus) changes as a function of thermal history. J Exp Biol 204:3571–3579
Buerge IJ, Poiger T, Muller MD, Buser HR (2003) Caffeine, an anthropogenic marker for wastewater contamination of surface waters. Environ Sci Technol 37:691–700
Chapple JP, Smerdon GR, Hawkins JS (1997) Stress-70 Protein induction in Mytilus edulis: tissue-specific responses to elevated temperature reflect relative vulnerability and physiological function. J Exp Mar Bio 217:225–235
Cheney RH (1945) The effects of caffeine on oxygen consumption and cell division in the fertilized egg of the sea urchin, Arbacia punctulata. J Gen Physiol 29:63–72
Comeau F, Surette C, Brun GL, Losier R (2008) The occurrence of acidic drugs and caffeine in sewage effluents and receiving waters from three coastal watersheds in Atlantic Canada. Sci Total Environ 396:132–146
Daly JW (2007) Caffeine analogs: bioledical impacts. Cell Mol Life Sci 64:2153–2169
Depledge MH (1994) The rational basis for the use of biomarkers as ecotoxicological tools. In: Fossi MC, Leonzio C (eds) Nondestructive biomarkers in vertebrates. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, pp 261–285
Eckwert H, Alberti G, Koehler HR (1997) The induction of stress proteins (hsp) in Oniscus asellus (Isopoda) as a molecular marker of multiple heavy metal exposure: I. Principles and toxicological assessment. Ecotoxicology 6:249–262
Fabbri E, Valbonesi P, Franzellitti S (2008) HSP expression in bivalves. Invert Survival J 5:135–161
Feder ME, Hofmann GE (1999) Heat-shock proteins, molecular chaperones, and the stress response: evolutionary and ecological physiology. Ann Rev Physiol 61:243–282
Fraker SL, Smith GR (2004) Direct and interactive effects of ecologically relevant concentrations of organic wastewater contaminants on Rana pipiens tadpoles. Environ Toxicol 19:250–256
Fredholm BB, Battig K, Holmen J, Nehlig A, Zvarrtau EE (1999) Actions of caffeine in the brain with reference factors that contribute to its widespread use. Pharmacol Rev 51:83–133
Gagné F, Blaise C, André C (2006) Occurrence of pharmaceutical products in a municipal effluent and toxicity to rainbow trout (Oncorhyncus mykiss) hepatocytes. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 64:329–336
Hyne RV, Maher WA (2003) Invertebrate biomarkers: links to toxicosis that predict population decline. Ecotoxiol Environ Saf 54:366–374
Johnson JD, Campisi J, Sharkey CM, Kennedy SL, Nickerson M, Fleshner M (2005) Adrenergic receptors mediate stress-induced elevations in extracellular Hsp72. J Appl Physiol 99:1789–1795
Kiang JG, Tsokos GC (1998) Heat shock protein 70 kDa: molecular biology, biochemistry, and physiology. Pharmacol Ther 80:183–201
Lacoste A, De Cian MC, Cueff A, Poulet SA (2001a) Noradrenaline and a-adrenergic signaling induce the hsp70 gene promoter in mollusc immune cells. J Cell Sci 114:3557–3564
Lacoste A, Malham SKMC, Cueff A, Poulet SA (2001b) Stress-induced catecholamine changes in the hemolymph of the oyster Crassostrea gigas. Gen Comp Endocr 122:181–188
Laporte PF (2005) Mytilus trossulus hsp70 as a biomarker for arsenic exposure in the marine environment: Laboratory and real-world results. Biomarkers 10:417–428
Lewis R, Handy RD, Cordi Z, Billinghurst Z, Depledge MH (1999) Stress proteins (HSP’s): Methods of detection and their use as an environmental biomarker. Ecotoxicology 8:351–368
Moore MT, Greenway SL, Farris JL, Guerra B (2008) Assessing caffeine as an emerging environmental concern using conventional approaches. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 54:31–35
Mukhopadhyay I, Nazir A, Saxena DK, Kar Chowdhuri D (2003) Heat shock response: hsp70 in environmental monitoring. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 17:249–254
Nath J, Rebhun LI (1976) Effects of caffeine and other methylxanthines on the development and metabolism of sea urchin eggs: involvement of NADP and glutathione. J Cell Biol 68:440–450
Peeler KA, Opsahl SP, Chanton JP (2006) Tracking anthropogenic inputs using caffeine, indicator bacteria, and nutrients in rural freshwater and urban marine systems. Environ Sci Technol 40:7616
Pollack K, Balazs K, Oginseitan O (2009) Proteomic assessment of caffeine effects on coral symbionts. Environ Sci Technol 43:2085–2091
Quinn B, Gagne F, Blaise C (2008) An investigation into the acute and chronic toxicity of eleven pharmaceuticals (and their solvents) found in wastewater effluent on the cnidarian, Hydra attenuata. Sci Total Environ 389:306–314
Sanders BM (1990) Stress proteins: potential as multi-tiered biomarkers. In: Shugart L, McCarthy J (eds) Environmental biomarkers. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, pp 165–191
Sawyer SJ, Muscatine L (2001) Cellular mechanisms underlying temperature-induced bleaching in the tropical sea anemone Aiptasia pulchella. J Exp Biol 204:3443–3456
Siegener R, Chen RF (2002) Caffeine in Boston harbor sea water. Mar Poll Bull 44:383–387
Smith GR, Burgett AA (2005) Effects of three organic wastewater contaminants on American toad, Bufo americanus. Ecotoxicology 14:477–482
Staempfli C, Becker-Van Slooten K, Tarradellas J (2002) Hsp70 instability and induction by a pesticide in Folsomia candida. Biomarkers 7:68–79
Stefano GB, Cadet P, Zhu W, Rialas CM, Mantione K, Benz D, Fuentes R, Caseres F, Fricchione GL, Fulop Z, Slingsby B (2002) The blueprint for stress can be found in invertebrates. Neuroendocrinol Lett 23:85–93
Vilaboa NE, Calle C, Pérez C, De Blas E, García-Bermejo L, Aller P (1995) cAMP increasing agents prevent the stimulation of heat-shock protein 70 (HSP70) gene expression by cadmium chloride in human myeloid cells. J Cell Sci 108:2877–2883
Weigel S, Berger U, Jensen E, Kallenborn R, Thoresen H, Huhnerfuss H (2004) Determination of selected pharmaceuticals and caffeine in sewage and seawater from Tromso/Norway with emphasis on ibuprofen and its metabolites. Chemosphere 56:583–592
Wheelock CE, Wolfe MF, Olsen H, Tjeerdema RS, Sowby ML (1999) Hsp60-induced tolerance in the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis exposed to multiple environmental contaminants. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 36:281–287
Acknowledgments
This project was funded in part by a Portland State University Faculty Enhancement Grant to E. F. Granek and B. A. Buckley and by an Oregon Sea Grant Program Development Grant to E. F. Granek. NOAA’s National Marine Fisheries Service and the NOAA Portland, Oregon Office provided additional funding for supplies. Malcolm Staudinger, Caitlyn Peake, Paul Pettus, Amanda Kelly, Ben Prital, provided help in the field and laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
del Rey, Z.R., Granek, E.F. & Buckley, B.A. Expression of HSP70 in Mytilus californianus following exposure to caffeine. Ecotoxicology 20, 855–861 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-011-0649-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-011-0649-6