Abstract
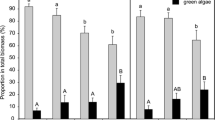
The biological response of periphyton chronically exposed to metals of urban origin (Cd, Ni and Zn) was investigated with a Pollution-Induced Community Tolerance (PICT) approach using a previously developed short-term toxicity test based on β-glucosidase (heterotrophic) activity. Periphyton was grown on plastic membranes immersed in indoor aquaria contaminated with metals at realistic contamination levels (0.3, 3 μg/l for Cd, 5, 50 μg/l for Ni, 20, 200 μg/l for Zn). After 3 weeks of exposure, biofilms’ parameters (dry-weight, chlorophyll a concentration, heterotrophic activity) were analyzed and tolerance acquisition of the heterotrophic communities was assessed using the toxicity test. Modifications of bacterial and eukaryotic community structure were assessed with Automated Ribosomal Intergenic Spacer Analysis (ARISA). Effects of metal exposure were observed on biofilms parameters in the Cd and Zn experiments. Tolerance levels increased for both Cd-exposed biofilms, and for the high metal treatment biofilms in the Ni and Zn experiments. Analysis of the ARISA profiles showed that metal exposure affected the structure of both bacterial and eukaryotic communities. Moreover, Cd tolerance of the Zn-exposed heterotrophic communities was evaluated, which showed that the Zn-tolerant community (high metal treatment in the Zn experiment) also became tolerant to Cd (co-tolerance). The study shows that tolerance acquisition can be detected after exposure to environmental metal concentrations using β-glucosidase activity as an endpoint in short-term toxicity tests.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Admiraal W, Tubbing DMJ (1991) Extracellular enzyme activity associated with suspended matter in the River Rhine. Freshw Biol 26:507–517
Admiraal W, Blanck H, Buckert-de Jong M, Guasch H, Ivorra N, Lehmann V, Nystrom BAH, Paulsson M, Sabater S (1999) Short-term toxicity of zinc to microbenthic algae and bacteria in a metal polluted stream. Water Res 33(9):1989–1996
Blanck H (2002) A critical review of procedures and approaches used for assessing pollution-induced community tolerance (PICT) in biotic communities. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 8:1003–1034
Blanck H, Dahl B (1996) Pollution-induced community tolerance (PICT) in marine periphyton in a gradient of tri-n-butyltin (TBT) contamination. Aquat Toxicol 35(1):59–77
Blanck H, Wängberg S-A, Molander S (1988) Pollution-Induced Community Tolerance—a new ecotoxicological tool. In: Cairns JJ, Pratt JR (eds) Functional testing of aquatic biota for estimating hazards of chemicals. American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, pp 219–230
Blanck H, Admiraal W, Cleven RFMJ, Guasch H, van den Hoop MAGT, Ivorra N, Nyström B, Paulsson M, Petterson RP, Sabater S et al (2003) Variability in zinc tolerance, measured as incorporation of radio-labeled carbon dioxide and thymidine, in periphyton communities sampled from 15 European river stretches. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 44(1):17–29
Blanck H, Eriksson KM, Grönvall F, Dahl B, Guijarro KM, Birgersson G, Kylin H (2009) A retrospective analysis of contamination and periphyton PICT patterns for the antifoulant irgarol 1051, around a small marina on the Swedish west coast. Mar Pollut Bull 58(2):230–237
Bourgeault A, Gourlay-Francé C, Vincent-Hubert F, Palais F, Geffard A, Biagianti-Risbourg S, Pain-Devin S, Tusseau-Vuillemin MH (2010) Lessons from a transplantation of zebra mussels into a small urban river: an integrated ecotoxicological assessment. Environ Toxicol 25(5):468–478
Burns A, Ryder DS (2001) Potential for biofilms as biological indicators in Australian riverine systems. Ecol Manag Restor 2(1):53–64
Cardinale M, Brusetti L, Quatrini P, Borin S, Puglia AM, Rizzi A, Zanardini E, Sorlini C, Corselli C, Daffonchio D (2004) Comparison of different primer sets for use in automated ribosomal intergenic spacer analysis of complex bacterial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(10):6147–6156
Chrost RJ (1991) Microbial enzymes in aquatic environments. Springer-Verlag, New York
Clements WH, Rohr JR (2009) Community responses to contaminants: using basic ecological principles to predict ecotoxicological effects. Environ Toxicol Chem 28(9):1789–1800
Dorigo U, Bérard A, Bouchez A, Rimet F, Montuelle B (2010) Transplantation of microbenthic algal assemblages to assess structural and functional recovery after diuron exposure. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 59:555–563
Fechner LC, Gourlay-Francé C, Uher E, Tusseau-Vuillemin MH (2010a) Adapting an enzymatic toxicity test to allow comparative evaluation of natural freshwater biofilms’ tolerance to metals. Ecotoxicology 19(7):1302–1311
Fechner LC, Vincent-Hubert F, Gaubert P, Bouchez T, Gourlay-Francé C, Tusseau-Vuillemin MH (2010b) Combined eukaryotic and bacterial community fingerprinting of natural freshwater biofilms using Automated Ribosomal Intergenic Spacer Analysis. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 74(3):542–553
Gustavson K, Wängberg S-A (1995) Tolerance induction and succession in microalgae communities exposed to copper and atrazine. Aquat Toxicol 32(4):283–302
Gustavson K, Petersen S, Pedersen B, Stuer-Lauridsen F, Wängberg S-A (1999) Pollution-Induced Community Tolerance (PICT) in coastal phytoplankton communities exposure to copper. Hydrobiologia 416:125–138
Hill AV (1910) The possible effects of the aggregation of the molecules of haemoglobin on its dissociation curves. J Physiol 40:iv–vii
Ivorra N, Bremer S, Guasch H, Kraak MHS, Admiraal W (2000) Differences in the sensitivity of benthic microalgae to Zn and Cd regarding biofilm development and exposure history. Environ Toxicol Chem 19(5):1332–1339
Ivorra N, Hettelaar J, Kraak MHS, Sabater S, Admiraal W (2002) Responses of biofilms to combined nutrient and metal exposure. Environ Toxicol Chem 21(3):626–632
Legendre P, Legendre L (1998) Numerical ecology. Elsevier Science B.V, Amsterdam
Lehmann V, Tubbing GMJ, Admiraal W (1999) Induced metal tolerance in microbenthic communities from three lowland rivers with different metal loads. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 36(4):384–391
Maksymiec W (1997) Effect of copper on cellular processes in higher plants. Photosynthetica 34(3):321–342
Meylan S, Behra R, Sigg L (2004) Influence of metal speciation in natural freshwater on bioaccumulation of copper and zinc in periphyton: a microcosm study. Environ Sci Technol 38(11):3104–3111
Michelland RJ, Dejean S, Combes S, Fortun-Lamothe L, Cauquil L (2009) StatFingerprints: a friendly graphical interface program for processing and analysis of microbial fingerprint profiles. Mol Ecol Resour 9(5):1359–1363
Morin S, Duong T, Herlory O, Feurtet-Mazel A, Coste M (2008) Cadmium toxicity and bioaccumulation in freshwater biofilms. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 54(2):173–186
Paulsson M, Nystrom B, Blanck H (2000) Long-term toxicity of zinc to bacteria and algae in periphyton communities from the river Gota Alv, based on a microcosm study. Aquat Toxicol 47(3–4):243–257
Ranjard L, Poly F, Lata JC, Mougel C, Thioulouse J, Nazaret S (2001) Characterization of bacterial and fungal soil communities by automated ribosomal intergenic spacer analysis fingerprints: biological and methodological variability. Appl Environ Microbiol 67(10):4479–4487
Romaní A, Fund K, Artigas J, Schwartz T, Sabater S, Obst U (2008) Relevance of polymeric matrix enzymes during biofilm formation. Microb Ecol 56(3):427–436
Sabater S, Guasch H, Ricart M, Romaní A, Vidal G, Klünder C, Schmitt-Jansen M (2007) Monitoring the effect of chemicals on biological communities. The biofilm as an interface. Anal Bioanal Chem 387(4):1425–1434
Serra A, Corcoll N, Guasch H (2009) Copper accumulation and toxicity in fluvial periphyton: the influence of exposure history. Chemosphere 74(5):633–641
Serra A, Guasch H, Admiraal W, Van Der Geest HG, Van Beusekom SAM (2010) Influence of phosphorus on copper sensitivity of fluvial periphyton: the role of chemical, physiological and community-related factors. Ecotoxicology 19(4):770–780
Soldo D, Behra R (2000) Long-term effects of copper on the structure of freshwater periphyton communities and their tolerance to copper, zinc, nickel and silver. Aquat Toxicol 47(3–4):181–189
Thévenot DR, Moilleron R, Lestel L, Gromaire M-C, Rocher V, Cambier P, Bonté P, Colin J-L, de Pontevès C, Meybeck M (2007) Critical budget of metal sources and pathways in the Seine River basin (1994–2003) for Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Ni, Pb and Zn. Sci Total Environ 375(1–3):180–203
Tusseau-Vuillemin M-H, Gourlay C, Lorgeoux C, Mouchel J-M, Buzier R, Gilbin R, Seidel J-L, Elbaz-Poulichet F (2007) Dissolved and bioavailable contaminants in the Seine river basin. Sci Total Environ 375(1–3):244–256
Vindimian E (2001) REGTOX: The solution for dose-response modeling with Exel. http://eric.vindimian.9online.fr/
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Office National de l’Eau et des Milieux Aquatiques (ONEMA). We are grateful to Aurélie Germain for her valuable help in the laboratory and to Julien Guieu for editing the English version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fechner, L.C., Gourlay-Francé, C. & Tusseau-Vuillemin, MH. Low exposure levels of urban metals induce heterotrophic community tolerance: a microcosm validation. Ecotoxicology 20, 793–802 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-011-0630-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-011-0630-4