Abstract
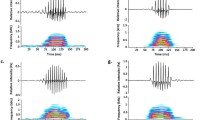
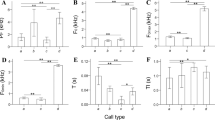
Divergence in acoustic traits between closely related species can be explained by phylogenetic history. In gobies, phylogenies reconstructed with acoustic signals primarily overlap with studies based on morphological or molecular data. Here, sound production of the two Ponto-Caspian gobies, Neogobius melanostomus and Ponticola kessleri, was recorded in controlled conditions and compared to determine the degree of interspecific acoustic variation across benthophilin gobies. Both species produced tonal-like sounds characterized by unique temporal and spectral properties during agonistic and reproductive intraspecific interactions, while the acoustic comparison revealed that the vocalizations of these two species differ in almost every acoustic property. N. melanostomus vocal structure was characterised by short (c. 100 ms), low-frequency (< 100 Hz) tonal sounds repeated at a relatively faster rate, while P. kessleri sounds appeared as a broadband, downward frequency modulated longer calls (c. 450 ms). Some acoustic features (sound rate and duration) proved to be stereotyped and could be considered a species-specific trait that could potentially be utilized to discriminate males or used by females for mate assessment. The tonal sounds appear to have a deeper origin within the Benthophilinae subfamily, as all acoustically investigated species to date have been able to produce this sound type. The recorded vocal repertoire represents a baseline for future comparative acoustic studies among the benthophilin gobies, aiming to gain additional information on the evolution of acoustic communication within Ponto-Caspian gobies and highlighting their importance in reconstructing phylogenetic relationships.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agorreta A, San Mauro D, Schliewen U, Van Tassell JL, Kovačić M, Zardoya R, Ruber L (2013) Molecular phylogenetics of Gobioidei and phylogenetic placement of European gobies. Mol Phylogenet Evol 69:619–633
Akamatsu A, Okumura T, Novarini N, Yan HY (2002) Empirical refinements applicable to the recording of fish sounds in small tanks. J Acoust Soc Am 112:3073–3082
Amorim MCP (2006) Diversity of sound production in fish. In: Ladich F, Collin SP, Moller P, Kapoor BG (eds) Communication in fishes, vol I. Science Publishers, Enfield, pp 71–105
Amorim MCP, Neves ASM (2007) Acoustic signalling during courtship in the painted goby, Pomatoschistus pictus. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 87:1017–1023
Amorim MCP, Simões JM, Almada VC, Fonseca PJ (2011) Stereotypy and variation of the mating call in the Lusitanian toadfish, Halobatrachus didactylus. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology 65(4):707–716
Amorim MCP, Pedroso SS, Bolgan M, Jordão JM, Caiano M, Fonseca PJ (2013) Painted gobies sing their quality out loud: acoustic rather than visual signals advertise male quality and contribute to mating success. Funct Ecol 27:289–298. https://doi.org/10.1111/13652435.12032
Bass AH, Mckibben JR (2003) Neural mechanisms and behaviors for acoustic communication in teleost fish. Neurobiology 605:1–26
Berg LS (1949) Ryby presnykh vod SSSR i sopredel’nykh stran. Ch. 3 (freshwater fishes of the USSR and adjacent countries. Part 3, Moscow: Akad. Nauk SSSR
Bianco PG, Miller PJ (1990) Yugoslavian and other records of the Italian freshwater goby Padogobius martensii, and a character polarization in gobioid fishes. J Nat Hist 24:1289–1302. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222939000770761
Bradbury JW, Vehrencamp SL (1998) Principles of animal communication. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland
Cap H, Deleporte P, Joachim J, Reby D (2008) Male vocal behavior and phylogeny in deer. Cladistics 24:917–931
Christie PJ, Mennill DJ, Ratcliffe LM (2004) Chickadee song structure is individually distinctive over long broadcast distances. Behav 141:101–124
Cocroft RB, Ryan MJ (1995) Patterns of advertisement call evolution in toads and chorus frogs. Animal Behav 49:283–303
Colleye O, Vandewalle P, Lanterbecq D, Lecchini D, Parmentier E (2011) Interspecific variation of calls in clownfishes: degree of similarity in closely related species. BMC Evol Biol 11:365
Crawford JD (1997) Hearing and acoustic communication in mormyrid electric fishes. Mar Freshw Behav Physiol 29:65–86
Gingras B, Mohandesan E, Boko D, Fitch WT (2013) Phylogenetic signal in the acoustic parameters of the advertisement calls of four clades of anurans. BMC Evol Biol 13:134. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-13-134
Günther AC (1861) Catalogue of Fishes in the British Museum 3:409–467
Hamao S, Sugit N, Nishiumi I (2015) Geographic variation in bird songs: examination of the effects of sympatric related species on the acoustic structure of songs. Acta Ethol 19:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10211-015-0228-6
Horvatić S, Cavraro F, Zanella D, Malavasi S (2015) Sound production in the Ponto-Caspian goby Neogobius fluviatilis and acoustic affinities within the Gobius lineage: implications for phylogeny. Biol J Linn Soc 117:564–573
Huyse T, Van Houdt J, Volckaert FAM (2004) Paleoclimatic history and vicariant speciation in the ‘sand goby’ group (Gobiidae, Teleostei). Mol Phylogenet Evol 32:324–336
Kottelat M, Freyhof J (2007) Handbook of European freshwater fishes. Kouelat, Comol, Switzerland and Freyhof. Berlin, Gennany
Kovačić M, Patzner RA (2011) North-Eastern Atlantic and Mediterranean gobius. In: Patzner RA, Van Tassell JL, Kovačić M, Kapoor BG (eds) The biology of gobies. Science Publishers, CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, New York, pp 177–206
Kovačić M, Šanda R (2016) A new species of Gobius (Perciformes: Gobiidae) from the Mediterranean Sea and the redescription of Gobius bucchichi. J Fish Biol 88:1104–1124
Ladich F, Kratochvil H (1989) Sound production in the marmoreal goby Proterorhinus marmoratus (Pallas) (Gobiidae: Teleostei). Zool Jahrb Abt allg Zool Physiol Tiere 93:501–504
Laiolo P, Rolando A (2003) The evolution of vocalisations in the genus Corvus: effects of phylogeny, morphology and habitat. Evol Ecol 17:111–123
Lobel PS (1998) Possible species specific courtship sounds by two sympatric cichlids fishes in Lake Malati, Africa. Environ Biol Fish 52:443–452
Lugli M (2010) Sounds of shallow water fishes pitch within the quiet window of the habitat ambient noise. J Comp Physiol A 196:439–451. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-010-0528-2
Lugli M, Torricelli P (1999) Prespawning sound production in mediterranean sand gobies. J Fish Biol 54:691–694
Lugli M, Pavan G, Torricelli P, Bobbio L (1995) Spawning vocalisations in male freshwater gobiids (Pisces, Gobiidae). Environ Biol Fish 43:219–231
Lugli M, Torricelli P, Pavan G, Miller PJ (1996) Breeding sounds of male Padogobius nigricans with suggestions for further evolutionary study of vocal behaviour in gobioid fishes. J Fish Biol 49:648–657
Lugli M, Torricelli P, Pavan G, Mainardi D (1997) Sound production during courtship and spawning among freshwater gobiids (Pisces, Gobiidae). Mar Fresh Behav Physiol 29:109–126
Lugli M, Yan HY, Fine ML (2003) Acoustic communication in two freshwater gobies: the relationship between ambient noise, hearing thresholds and sound spectrum. J Comp Physiol 189:309–320
Malavasi S, Torricelli P, Lugli M, Pravoni F, Mainardi D (2003) Male courtship sounds in a teleost with alternative reproductive tactics, the grass goby, Zosterisessor ophiocephalus. Environ Biol Fish 66:231–236. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023923403180
Malavasi S, Collatuzzo S, Torricelli P (2008) Interspecific variation of acoustic signals in Mediterranean gobies (Perciformes, Gobiidae): comparative analysis and evolutionary outlook. Biol J Linn Soc 93:763–778. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8312.2008.00947.x
Malavasi S, Valerio C, Torricelli P (2009) Courtship sounds and associated behaviours in the Canestrini’s goby Pomatoschistus canestrinii. J Fish Biol 75:1883–1887
Mann DA, Lobel PS (1995) Passive acoustic detection of sounds produced by the damselfish Dascyllus albisella (Pomacentridae). Bioacoustics 6:199–213
Medvedev DA, Sorokin PA, Vasil’ev VP, Chernova NV, Vasil’eva ED (2013) Reconstruction of phylogenetic relations of Ponto-Caspian gobies (Gobiidae, Perciformes) based on mitochondrial genome variation and some problems of their taxonomy. J Ichthyol 53:702–712
Mélotte G, Vigouroux R, Michel C, Parmentier E (2016) Interspecific variation of warning calls in piranhas: a comparative analysis. Sci Rep 6:36127. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep36127
Miller PJ (1984) The tokology of gobioid fishes. In: Potts GW, Wotton RJ (eds) Fish reproduction: strategies and tactics. Academic Press, London, pp 119–153
Miller PJ (2003) The freshwater fishes of Europe. Mugilidae, Atherinidae, Atherinopsidae, Blenniidae, Odontobutidae, Gobiidae 1, Wiebelsheim: AULA Verlag, vol. 8/I, pp 157-345
Miller PJ (2004) The freshwater fishes of Europe. Gobiidae 2, Wiebelsheim: AULA Verlag, vol. 8/II, pp 33-93
Mitchell S, Poland J, Fine ML (2008) Does muscle fatigue limit advertisement calling in the oyster toadfish Opsanus tau? Animal Behav 76:1011–1016
Myrberg AA, Lugli M (2006) Reproductive behavior and acoustical interations. In: Ladich F, Collin SP, Moller P, Kaapor BG (eds) Communication in fishes, vol 1. Science Publishers, Enfield, pp 146–176
Myrberg AA, Spanier E, Ha SJ (1978) Temporal patterning in acoustical communication. Contrasts in Behavior, Wiley, New York
Neilson ME, Stepien CA (2009) Escape from the Ponto Caspian: evolution and biogeography of an endemic goby species flock (Benthophilinae: Gobiidae: Teleostei). Mol Phylogenet Evol 52:84–102
Parmentier E, Kever L, Boyle K, Corbisier Y, Sawelew L, Malavasi S (2013) Sound production mechanism in Gobius paganellus (Gobiidae). J Exp Biol 216:3189–3199
Penzo E, Gandolfi G, Bargelloni L, Colombo L, Patarnello T (1998) Messinian salinity crisis and the origin of freshwater lifestyle in western Mediterranean gobies. Mol Biol Evol 15:1472–1480
Remage-Healey L, Bass AH (2006) A rapid, neuromodulatory role for steroid hormones in the control of reproductive behavior. Brain Res 1126:27–35
Rice AN, Bass AH (2009) Novel vocal repertoire and paired swimbladders of the three-spined toadfish, Batrachomoeus trispinosus: insights into the diversity of the Batrachoididae. J Exp Biol 212:1377–1391
Robillard T, Desutter-Grandcolas L (2004) High frequency calling in Eneopterinae crickets (Orthoptera, Grylloidea, Eneopteridae): adaptive radiation revealed by phylogenetic analysis. Biol J Linn Soc 83:577–584
Robillard T, Legendre F, Desutter-Grandcolas L, Grandcolas P (2006) Phylogenetic analysis and alignment of behavioral sequences by direct optimization. Cladistics 22:602–633
Rollo A, Andraso G, Janssen J, Higgs D (2007) Attraction and localization of round goby (Neogobius melanostomus) to conspecific calls. Behaviour 144:1–21
Sebastianutto L, Picciulin M, Costantini M, Rocca M, Ferrero E (2008) Four types of sounds from one winner: vocalizations during territorial behaviour in the red-mouthed goby Gobius cruentatus (Pisces, Gobiidae). Acta Ethol 11:115–121
Simonovic PD, Nikolić VP, Skora KE (1996) Vertebral number in Ponto-Caspian gobies: phylogenetic relevance. J Fish Biol 49:1027–1029
Spanier E (1979) Aspects of species recognition by sound in four species of damselfishes, genus Eupomacentrus (Pisces: Pomacentridae). Z Tierpsychol 51:301–316. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0310.1979.tb00691.x
Thacker CE (2011) Systematics of Gobiidae. In: Patzner RA, Van Tassell JL, Kovačić M, Kapoor BG (eds) The Biology of Gobies. Enfield, NH: Science Publishers, p 129–136
Thacker CE (2015) Biogeography of goby lineages (Gobiiformes: Gobioidei): origin, invasions, and extinction through the Cenozoic. J Biogeogr 42:1615–1625. https://doi.org/10.1111/jbi.12545
Thacker CE, Roje DM (2011) Phylogeny of Gobiidae and identification of gobiid lineages. Syst Biodivers 9:229–347
Thorson RF, Fine ML (2002) Crepuscular changes in emission rate and parameters of the boatwhistle advertisement call of the gulf toadfish, Opsanus beta. Environ Biol Fish 63:321–331. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014334425821
Torricelli P, Parmigiani S, Lugli M, Gandolfi G (1988) Intermale aggression in Padogobius martensi (günther) (pisces Gobiidae): effect of size and prior residence. Monit Zoolog Ital – Ital J Zool 22:121–131. https://doi.org/10.1080/00269786.1988.10736547
Torricelli P, Lugli M, Pavan G (1990) Analysis of sound produced by male Padogobius martensi (Pisces: Gobiidae) and factors affecting their structural properties. Bioacoustics 2:261–175
Zeyl JN, Malavasi S, Holt DE, Noel P, Lugli M, Johnston CE (2016) Convergent aspects of acoustic communication in darters, sculpins and gobies. In: Sisneros AJ (ed) Fish hearing and bioacoustics: an anthology in honor of Arthur N. Popper and Richard R. Fay. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 93–120
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to Linda Zanella for proofreading the manuscript and two anonymous referees for their comments that improved the overall quality of the manuscript. All methods and procedures were approved by the Ethics Committee of Biology Division (Faculty of Science, approval no: 251-58-10617-18-14).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horvatić, S., Bem, L., Malavasi, S. et al. Comparative analysis of sound production between the bighead goby Ponticola kessleri and the round goby Neogobius melanostomus: Implications for phylogeny and systematics. Environ Biol Fish 102, 727–739 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-019-00866-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-019-00866-7