Summary
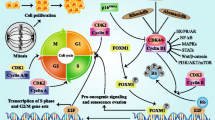
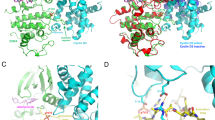
CDK4/6 inhibitors plus endocrine therapy is a standard therapy for HR+/HER2- breast cancer. Herein, using structure-based drug design strategy, a novel series of palbociclib derivatives were designed and synthesized as CDK4/6 inhibitors, among which compound 17m exhibited more potent CDK4/6 inhibitory activity and in vitro antiproliferative activity against the phosphorylated Rb-positive cell line MDA-MB-453 than the approved drug palbociclib. Moreover, compound 17m possessed remarkable CDK4/6 selectivity over other CDK family members including CDK1, CDK2, CDK3, CDK5, CDK7 and CDK9. The potent and selective CDK4/6 inhibitory activity endowed compound 17m with robust G1 cell cycle arrest ability in MDA-MB-453 cells. The intracellular inhibition of CDK4/6 by 17m was confirmed by western blot analysis of the levels of phosphorylated Rb in MDA-MB-453 cells. With respect to the metabolic stability, compound 17m possessed longer half-life (t1/2) in mouse liver microsome than palbociclib.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Douglas H, Robert AW (2000) The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100(1):57–70
Asghar U, Witkiewicz AK, Turner NC, Knudsen ES (2015) The history and future of targeting cyclin-dependent kinases in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 14(2):130–146
Malumbres M, Barbacid M (2009) Cell cycle, CDKs and cancer: a changing paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer 9(3):153–166
Yuan K, Wang X, Dong H, Min W, Hao H, Yang P (2020) Selective inhibition of CDK4/6: A safe and effective strategy for developing anticancer drugs. Acta Pharm Sin B 11(1):30–54
Sherr CJ, Beach D, Shapiro GI (2016) Targeting CDK4 and CDK6: From Discovery to Therapy. Cancer Discov 6(4):353–367
Kwapisz D (2017) Cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer: palbociclib, ribociclib, and abemaciclib. Breast Cancer Res Treat 166(1):41–54
Corona SP, Ravelli A, Cretella D, Cappelletti MR, Zanotti L, Dester M et al (2017) CDK4/6 inhibitors in HER2-positive breast cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 112:208–214
Toogood PL, Harvey PJ, Repine JT, Sheehan DJ, VanderWel SN, Zhou H et al (2005) Discovery of a potent and selective inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6. J Med Chem 48(7):2388–2406
Sohita D (2015) Palbociclib: first global approval. Drugs 75:543–551
Shi C, Wang Q, Liao X, Ge H, Huo G, Zhang L et al (2020) Discovery of a novel series of imidazo[1’,2’:1,6]pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin derivatives as potent cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 193:112239
Sunshine lake pharma (2016) Compounds as CDK small-molecule inhibitors and uses thereof. WOCN15084983
Shanghai hengrui pharmaceutical (2014) Thiophene miazines derivate, preparation method thereof and medical application thereof. WOCN14075387
Sunshine lake pharma (2016) 2-amino-pyrido[2,3-D]pyrimidin-7(8H)-one derivatives as CDK inhibitors and uses thereof. WOCN15084984
Wang P, Huang J, Wang K, Gu Y (2016) New palbociclib analogues modified at the terminal piperazine ring and their anticancer activities. Eur J Med Chem 122:546–556
Chen P, Lee NV, Hu W, Xu M, Ferre RA, Lam H et al (2016) Murray 4 Spectrum and Degree of CDK Drug Interactions Predicts Clinical Performance. Mol Cancer Ther 15(10):2273–2281
Tvorogov D, Thomas D, Liau NPD, Dottore M, Barry EF, Lathi M et al (2018) Accumulation of JAK activation loop phosphorylation is linked to type I JAK inhibitor withdrawal syndrome in myelofibrosis. Sci Adv 4:eaat3834
Meyer SC, Keller MD, Chiu S, Koppikar P, Guryanova OA, Rapaport F et al (2015) CHZ868, a Type II JAK2 inhibitor, reverses type I JAK inhibitor persistence and demonstrates efficacy in myeloproliferative neoplasms. Cancer Cell 28:15–28
Liu CY, Lau KY, Hsu CC, Chen JL, Lee CH, Huang TT et al (2017) Combination of palbociclib with enzalutamide shows in vitro activity in RB proficient and androgen receptor positive triple negative breast cancer cells. PLoS One 12(12):e0189007
Funding
This study was funded by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82073872).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XX and LLN designed the project. LMZ and JW performed the enzymatic screening; LYX and CFQ synthesized the molecules; WYJ and LY performed the in vitro experiments. XX analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
For this type of study, informed consent is not required.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Chen, F., Li, M. et al. Development of novel palbociclib-based CDK4/6 inhibitors exploring the back pocket behind the gatekeeper. Invest New Drugs 41, 638–651 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-023-01385-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-023-01385-0