Summary
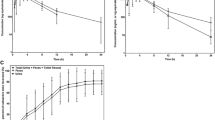
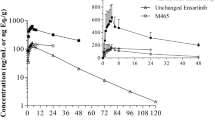
Lenvatinib is an orally available multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor with anti-angiogenic and antitumor activity. To get more insight into the disposition of lenvatinib, a mass balance study was performed in patients with advanced solid tumors. A single oral 24 mg (100 μCi) dose of 14C-lenvatinib was administered to six patients, followed by collection of blood, plasma, urine and feces for 7 to 10 days. The collected material was analyzed for total radioactivity, unchanged lenvatinib and selected metabolites. The safety and antitumor effect of a daily oral dose of 24 mg non-labeled lenvatinib were assessed in the extension phase of the study. Peak plasma concentrations of lenvatinib and total radioactivity were reached 1.6 and 1.4 h after administration, respectively, and their terminal phase half-lifes were 34.5 and 17.8 h, respectively. Unchanged lenvatinib systemic exposure accounted for 60 % of the total radioactivity in plasma. Peak concentrations of the analyzed metabolite were over 700-fold lower than the peak plasma concentration of lenvatinib. Ten days after the initial dose, the geometric mean (± CV) recovery of administered dose was 89 % ±10 %, with 64 % ±11 % recovered in feces and 25 % ±18 % in urine. Unchanged lenvatinib in urine and feces accounted for 2.5 % ±68 % of the administered dose, indicating a major role of metabolism in the elimination of lenvatinib. In conclusion, lenvatinib is rapidly absorbed and extensively metabolized, with subsequent excretion in urine and, more predominantly, in feces. Additionally, lenvatinib showed acceptable safety and preliminary antitumor activity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergers G, Benjamin LE (2003) Tumorigenesis and the angiogenic switch. Nat Rev Cancer 3(6):401–410
Mazitschek R, Giannis A (2004) Inhibitors of angiogenesis and cancer-related receptor tyrosine kinases. Curr Opin Chem Biol 8(4):432–441
Hartmann JT, Haap M, Kopp HG, Lipp HP (2009) Tyrosine kinase inhibitors—a review on pharmacology, metabolism and side effects. Curr Drug Metab 10:470–481
Matsui J, Yamamoto Y, Funahashi Y, Tsuruoka A, Watanabe T, Wakabayashi T, Uenaka T, Asada M (2008) E7080, a novel inhibitor that targets multiple kinases, has potent antitumor activities against stem cell factor producing human small cell lung cancer H146, based on angiogenesis inhibition. Int J Cancer 122(3):664–671
Bruheim S, Kristian A, Uenaka T, Suo Z, Tsuruoka A, Nesland JM, Fodstad Ø (2011) Antitumour activity of oral E7080, a novel inhibitor of multiple tyrosine kinases, in human sarcoma xenografts. Int J Cancer 129(3):742–750
Ikuta K, Yano S, Trung VT, Hanibuchi M, Goto H, Li Q, Wang W, Yamada T, Ogino H, Kakiuchi S, Uehara H, Sekido Y, Uenaka T, Nishioka Y, Sone S (2009) E7080, a multi-tyrosine kinase inhibitor, suppresses the progression of malignant pleural mesothelioma with different proangiogenic cytokine production profiles. Clin Cancer Res 15(23):7229–7237
Matsui J, Funahashi Y, Uenaka T, Watanabe T, Tsuruoka A, Asada M (2008) Multi-kinase inhibitor E7080 suppresses lymph node and lung metastases of human mammary breast tumor MDA-MB-231 via inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor-receptor (VEGF-R) 2 and VEGF-R3 kinase. Clin Cancer Res 14(17):5459–5465
Glen H, Mason S, Patel H, Macleod K, Brunton VG (2011) E7080, a multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor suppresses tumor cell migration and invasion. BMC Cancer 11(1):309
Yamada K, Yamamoto N, Yamada Y, Nokihara H, Fujiwara Y, Hirata T, Koizumi F, Nishio K, Koyama N, Tamura T (2011) Phase I dose-escalation study and biomarker analysis of E7080 in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 17(8):2528–2537
Boss DS, Glen H, Beijnen JH, Keesen M, Morrison R, Tait B, Copalu W, Mazur A, Wanders J, O’Brien JP, Schellens JHM, Evans TRJ (2012) A phase I study of E7080, a multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumours. Br J Cancer 106(10):1598–1604
Dubbelman A, Rosing H, Thijssen B, Gebretensae A, Lucas L, Chen H, Shumaker R, Schellens JHM, Beijnen JH (2012) Development and validation of LC-MS/MS assays for the quantification of E7080 and metabolites in various human biological matrices. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 887–888:25–34
Dubbelman A, Rosing H, Jansen RS, Mergui-roelvink M, Huitema ADR, Koetz B, Lymboura M, Reyderman L, Lopez-anaya A, Schellens JHM, Beijnen JH (2012) Mass Balance Study of [ 14 C ] Eribulin in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Drug Metab Dispos 40(2):313–321
Zhu M, Zhao W, Vazquez N, Mitroka JG (2005) Analysis of low level radioactive metabolites in biological fluids using high-performance liquid chromatography with microplate scintillation counting: method validation and application. J Pharm Biomed Anal 39(1–2):233–245
F. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (2001) Guidance for industry, bioanalytical method validation [Online]. Available: http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/Guidances/ucm070107.pdf. Accessed 05 July 2014
Keizer RJ, Gupta A, Mac Gillavry MR, Jansen M, Wanders J, Beijnen JH, Schellens JHM, Karlsson MO, Huitema ADR (2010) A model of hypertension and proteinuria in cancer patients treated with the anti-angiogenic drug E7080. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 37(4):347–363
van Erp NP, Gelderblom H, Guchelaar H-J (2009) Clinical pharmacokinetics of tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Cancer Treat Rev 35(8):692–706
Shumaker R, Aluri J, Fan J, Martinez G, Pentikis H, Ren M (2014) Influence of hepatic impairment on lenvatinib pharmacokinetics following single-dose oral administration. J Clin Pharmacol. doi:10.1002/jcph.398
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the patients that participated in this study and acknowledge Abadi Gebretensae for his bioanalytical support.
This study was supported by Eisai Inc. Part of this work was previously presented as follows: Dubbelman AC, Rosing Hilde, Mergui-Roelvink M, Gupta A, Verbel D, Sellecchia R, Fan J, Thompson GA, Shumaker R, Huitema ADR, Beijnen JH, Schellens JHM. (2013) A mass balance study of 14C-lenvatinib (E7080) in patients with advanced solid tumours or lymphomas. Scientific Spring Meeting of the Dutch Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Biopharmacy, March 30, 2012; abstract published in British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 76 (5): pp. 831–831.
Conflict of interest
A.C. Dubbelman, H. Rosing, C. Nijenhuis, A.D.R. Huitema, M. Mergui-Roelvink, J. H.M. Schellens and J.H. Beijnen declare they have no conflict of interest. A. Gupta is employee of Eisai Ltd., D. Verbel and R. Shumaker are employees of Eisai Inc. G.A. Thompson is a paid consultant to Eisai Inc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dubbelman, AC., Rosing, H., Nijenhuis, C. et al. Pharmacokinetics and excretion of 14C-lenvatinib in patients with advanced solid tumors or lymphomas. Invest New Drugs 33, 233–240 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-014-0181-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-014-0181-7