Summary
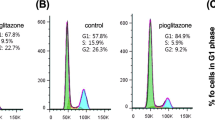
The anticancer activity of a novel pure 1,4-Diaryl-2-azetidinone (1), endowed with a higher solubility than the well known Combretastatin A4, is tested in mice. We previously reported that Compound (1) showed specific antiproliferative activity against duodenal and colon cancer cells, inducing activation of AMP-activated protein kinase and apoptosis. Here we estimate that the maximum tolerated dose in a mouse model is 40 mg/kg; the drug is well tolerated both in single dose and in repeated administration schedules. The drug displays a significant antitumor activity and a tumor growth delay when administered at the MTD both in single and fractionated i.v. administration in a mouse xenograft model of colorectal cancer. Arrest of tumor growth and relapse after drug suspension are parallel to modification in glucose demand as shown by PET studies with [18 F] FDG. These data strongly support Compound (1) as a promising molecule for in vivo treatment of colorectal cancer.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boyle P, Zaridze DG, Smans M (1985) Descriptive epidemiology of colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer 36:9–18
G.T.W. W, David. Day, Jeremy R. Jass, Ashley B. Price, Neil A. Shepherd, James M. Sloan, Ian C. Talbot, Bryan F. Warren, Morson and Dawson’s Gastrointestinal Pathology, Fourth Edition - Day - Wiley Online Library, (n.d.).
Venook A (2005) Critical evaluation of current treatments in metastatic colorectal cancer. Oncologist 10:250–61
Houlston RS (2001) What we could do now: molecular pathology of colorectal cancer. Mol Pathol 54:206–14
Ilyas M, Straub J, Tomlinson IP, Bodmer WF (1999) Genetic pathways in colorectal and other cancers. Eur J Cancer 35:1986–2002
Fearon ER, Vogelstein B (1990) A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell 61:759–67
Laurent-Puig P, Blons H, Cugnenc PH (1999) Sequence of molecular genetic events in colorectal tumorigenesis. Eur J Cancer Prev 8(Suppl 1):S39–47
Bardelli A, Siena S (2010) Molecular mechanisms of resistance to cetuximab and panitumumab in colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 28:1254–61
Frattini M, Saletti P, Romagnani E, Martin V, Molinari F, Ghisletta M et al (2007) PTEN loss of expression predicts cetuximab efficacy in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Br J Cancer 97:1139–45
Nam N-H (2003) Combretastatin A-4 analogues as antimitotic antitumor agents. Curr Med Chem 10:1697–722
G.R. Pettit, C. Temple, V.L. Narayanan, R. Varma, M.J. Simpson, M.R. Boyd, et al., Antineoplastic agents 322. synthesis of combretastatin A-4 prodrugs., Anticancer. Drug Des. 10 (1995) 299–309.
Simoni D, Romagnoli R, Baruchello R, Rondanin R, Rizzi M, Pavani MG et al (2006) Novel combretastatin analogues endowed with antitumor activity. J Med Chem 49:3143–52
Grosios K, Holwell SE, McGown AT, Pettit GR, Bibby MC (1999) In vivo and in vitro evaluation of combretastatin A-4 and its sodium phosphate prodrug. Br J Cancer 81:1318–27
West CML, Price P (2004) Combretastatin A4 phosphate. Anticancer Drugs 15:179–87
www.clinicaltrials.gov, (n.d.).
Dark GG, Hill SA, Prise VE, Tozer GM, Pettit GR, Chaplin DJ (1997) Combretastatin A-4, an agent that displays potent and selective toxicity toward tumor vasculature. Cancer Res 57:1829–34
Vincent L, Kermani P, Young LM, Cheng J, Zhang F, Shido K et al (2005) Combretastatin A4 phosphate induces rapid regression of tumor neovessels and growth through interference with vascular endothelial-cadherin signaling. J Clin Invest 115:2992–3006
Mousset C, Giraud A, Provot O, Hamze A, Bignon J, Liu J-M et al (2008) Synthesis and antitumor activity of benzils related to combretastatin A-4. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18:3266–71
F. Orsini, G. Sello, Bioactive Natural Products (Part N), Elsevier, 2008
Aprile S, Del Grosso E, Tron GC, Grosa G (2007) In vitro metabolism study of combretastatin A-4 in rat and human liver microsomes. Drug Metab Dispos 35:2252–61
Tripodi F, Pagliarin R, Fumagalli G, Bigi A, Fusi P, Orsini F et al (2012) Synthesis and biological evaluation of 1,4-diaryl-2-azetidinones as specific anticancer agents: activation of adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase and induction of apoptosis. J Med Chem 55:2112–24
Hardie DG, Alessi DR (2013) LKB1 and AMPK and the cancer-metabolism link - ten years after. BMC Biol 11:36
Canta A, Chiorazzi A, Carozzi V, Meregalli C, Oggioni N, Sala B et al (2011) In vivo comparative study of the cytotoxicity of a liposomal formulation of cisplatin (lipoplatinTM). Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 68:1001–8
Meregalli C, Canta A, Carozzi VA, Chiorazzi A, Oggioni N, Gilardini A et al (2010) Bortezomib-induced painful neuropathy in rats: a behavioral, neurophysiological and pathological study in rats. Eur J Pain 14:343–50
Motta A, Damiani C, Del Guerra A, Di Domenico G, Zavattini G (2002) Use of a fast EM algorithm for 3D image reconstruction with the YAP-PET tomograph. Comput Med Imaging Graph 26:293–302
Cavaletti G, Nicolini G, Marmiroli P (2008) Neurotoxic effects of antineoplastic drugs: the lesson of pre-clinical studies. Front Biosci 13:3506–24
Nabha SM, Mohammad RM, Wall NR, Dutcher JA, Salkini BM, Pettit GR et al (2001) Evaluation of combretastatin A-4 prodrug in a non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma xenograft model: preclinical efficacy. Anticancer Drugs 12:57–63
Shen C-H, Shee J-J, Wu J-Y, Lin Y-W, Wu J-D, Liu Y-W (2010) Combretastatin A-4 inhibits cell growth and metastasis in bladder cancer cells and retards tumour growth in a murine orthotopic bladder tumour model. Br J Pharmacol 160:2008–27
Thoeny HC, De Keyzer F, Chen F, Vandecaveye V, Verbeken EK, Ahmed B et al (2005) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging allows noninvasive in vivo monitoring of the effects of combretastatin a-4 phosphate after repeated administration. Neoplasia 7:779–87
Mur Blanch N, Chabot GG, Quentin L, Scherman D, Bourg S, Dauzonne D (2012) In vitro and in vivo biological evaluation of new 4,5-disubstituted 1,2,3-triazoles as cis-constrained analogs of combretastatin A4. Eur J Med Chem 54:22–32
Buzzai M, Jones RG, Amaravadi RK, Lum JJ, DeBerardinis RJ, Zhao F et al (2007) Systemic treatment with the antidiabetic drug metformin selectively impairs p53-deficient tumor cell growth. Cancer Res 67:6745–52
M. Zakikhani, R.J.O. Dowling, N. Sonenberg, M.N. Pollak, The effects of adiponectin and metformin on prostate and colon neoplasia involve activation of AMP-activated protein kinase., Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila). 1 (2008) 369–75.
J.R. Fay, V. Steele, J.A. Crowell, Energy homeostasis and cancer prevention: the AMP-activated protein kinase., Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila). 2 (2009) 301–9.
Warburg O (1956) On the origin of cancer cells. Science 123:309–14
Chiaradonna F, Moresco RM, Airoldi C, Gaglio D, Palorini R, Nicotra F et al (2012) From cancer metabolism to new biomarkers and drug targets. Biotechnol Adv 30:30–51
Zhao S (1999) J. V Moore, M.L. Waller, A.T. McGown, J.A. Hadfield, G.R. Pettit, et al., Positron emission tomography of murine liver metastases and the effects of treatment by combretastatin A-4. Eur J Nucl Med 26:231–8
Lankester KJ, Maxwell RJ, Pedley RB, Dearling JL, Qureshi UA, El-Emir E et al (2007) Combretastatin A-4-phosphate effectively increases tumor retention of the therapeutic antibody, 131I-A5B7, even at doses that are sub-optimal for vascular shut-down. Int J Oncol 30:453–60
Acknowledgments
We thank Neil Campbell for language editing. We thank Anna Innocenzi and Martina Rocchi of the Mouse Histo-Pathological Unit of San Raffaele Scientific Institute for histological preparation. This work was supported by a grant to P.C. (FAR 2010) and by a grant from the MIUR-funded “SysBioNet” project of the Italian Roadmap for ESFRI Research Infrastructures.
Conflicts of interest
The authors state no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Valtorta, S., Nicolini, G., Tripodi, F. et al. A novel AMPK activator reduces glucose uptake and inhibits tumor progression in a mouse xenograft model of colorectal cancer. Invest New Drugs 32, 1123–1133 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-014-0148-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-014-0148-8