Summary
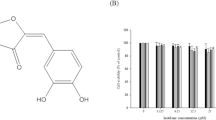
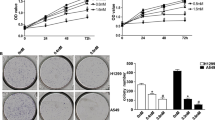
The nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), tolfenamic acid (TA) is emerging as a new anti-cancer agent. TA induces the degradation of specific Specificity protein (Sp) transcription factors, Sp1, Sp3 and Sp4 which are associated with tumor growth and metastasis. In this study we have evaluated the effect of TA on lung cancer using both in vitro and in vivo models. TA in a dose dependent manner inhibited proliferation and cell viability of two different lung cancer cells, A549 and CRL5803. TA treatment for 48 h significantly decreased the expression of Sp1, Sp3 and Sp4. The hepatocyte growth factor receptor, c-Met is overexpressed in a variety of cancers including lung cancer and Sp proteins mediate the regulation of c-Met. TA diminished the expression of c-Met protein and modulates its downstream signaling pathway. Furthermore, TA treatment significantly increased the number of apoptotic cells and pro-apoptotic markers c-PARP and Bax confirming the activation of apoptotic pathways. In vivo studies using the orthotopic mice model for lung cancer showed that TA (25 mg/kg/2 days and 50 mg/kg/2 days) resulted in a dose dependent decrease in tumor formation. The immunohistochemical staining of lung tissue showed high expression of Sp1, Sp3, Sp4, c-Met and phospho Met in control group and a dose dependent decrease in TA treated groups. The crucial findings of this study support that targeting c-Met with a potent inhibitor of Sp proteins is a robust strategy for the implications in lung cancer treatment and TA can serve as a therapeutic agent for this devastating disease.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Smigal C, Thun MJ (2006) Cancer statistics, 2006. CA Cancer J Clin 56:106–130
Bey EA, Bentle MS, Reinicke KE, Dong Y, Yang CR, Girard L, Minna JD, Bornmann WG, Gao J, Boothman DA (2007) An NQO1- and PARP-1-mediated cell death pathway induced in non-small-cell lung cancer cells by beta-lapachone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:11832–11837
Albert JM, Cao C, Kim KW, Willey CD, Geng L, Xiao D, Wang H, Sandler A, Johnson DH, Colevas AD, Low J, Rothenberg ML, Lu B (2007) Inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase enhances cell death and improves tumor growth delay in irradiated lung cancer models. Clin Cancer Res 13:3033–3042
Fong KM, Sekido Y, Gazdar AF, Minna JD (2003) Lung cancer. 9: molecular biology of lung cancer: clinical implications. Thorax 58:892–900
Devereux TR, Taylor JA, Barrett JC (1996) Molecular mechanisms of lung cancer. Interaction of environmental and genetic factors. Giles F. Filley Lecture. Chest 109:14S–19S
Herbst RS, Heymach JV, Lippman SM (2008) Lung cancer. N Engl J Med 359:1367–1380
Aviel-Ronen S, Blackhall FH, Shepherd FA, Tsao MS (2006) K-ras mutations in non-small-cell lung carcinoma: a review. Clin Lung Cancer 8:30–38
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, Harris PL, Haserlat SM, Supko JG, Haluska FG, Louis DN, Christiani DC, Settleman J, Haber DA (2004) Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med 350:2129–2139
Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S, Herman P, Kaye FJ, Lindeman N, Boggon TJ, Naoki K, Sasaki H, Fujii Y, Eck MJ, Sellers WR, Johnson BE, Meyerson M (2004) EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 304:1497–1500
Ma PC, Jagadeeswaran R, Jagadeesh S, Tretiakova MS, Nallasura V, Fox EA, Hansen M, Schaefer E, Naoki K, Lader A, Richards W, Sugarbaker D, Husain AN, Christensen JG, Salgia R (2005) Functional expression and mutations of c-Met and its therapeutic inhibition with SU11274 and small interfering RNA in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res 65:1479–1488
Hahn O, Salgia R (2005) Novel therapies in lung cancer. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 19:343–367 vii
Natali PG, Prat M, Nicotra MR, Bigotti A, Olivero M, Comoglio PM, Di Renzo MF (1996) Overexpression of the met/HGF receptor in renal cell carcinomas. Int J Cancer 69:212–217
Olivero M, Rizzo M, Madeddu R, Casadio C, Pennacchietti S, Nicotra MR, Prat M, Maggi G, Arena N, Natali PG, Comoglio PM, Di Renzo MF (1996) Overexpression and activation of hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor in human non-small-cell lung carcinomas. Br J Cancer 74:1862–1868
Hellman A, Zlotorynski E, Scherer SW, Cheung J, Vincent JB, Smith DI, Trakhtenbrot L, Kerem B (2002) A role for common fragile site induction in amplification of human oncogenes. Cancer Cell 1:89–97
Di Renzo MF, Olivero M, Katsaros D, Crepaldi T, Gaglia P, Zola P, Sismondi P, Comoglio PM (1994) Overexpression of the Met/HGF receptor in ovarian cancer. Int J Cancer 58:658–662
Maulik G, Kijima T, Ma PC, Ghosh SK, Lin J, Shapiro GI, Schaefer E, Tibaldi E, Johnson BE, Salgia R (2002) Modulation of the c-Met/hepatocyte growth factor pathway in small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 8:620–627
Ma PC, Maulik G, Christensen J, Salgia R (2003) c-Met: structure, functions and potential for therapeutic inhibition. Cancer Metastasis Rev 22:309–325
Siegfried JM, Weissfeld LA, Luketich JD, Weyant RJ, Gubish CT, Landreneau RJ (1998) The clinical significance of hepatocyte growth factor for non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg 66:1915–1918
Bharti A, Ma PC, Maulik G, Singh R, Khan E, Skarin AT, Salgia R (2004) Haptoglobin alpha-subunit and hepatocyte growth factor can potentially serve as serum tumor biomarkers in small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res 24:1031–1038
Zhang X, Li Y, Dai C, Yang J, Mundel P, Liu Y (2003) Sp1 and Sp3 transcription factors synergistically regulate HGF receptor gene expression in kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 284:F82–94
Zhang X, Liu Y (2003) Suppression of HGF receptor gene expression by oxidative stress is mediated through the interplay between Sp1 and Egr-1. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 284:F1216–1225
Papineni S, Chintharlapalli S, Abdelrahim M, Lee SO, Burghardt R, Abudayyeh A, Baker C, Herrera L, Safe S (2009) Tolfenamic acid inhibits esophageal cancer through repression of specificity proteins and c-Met. Carcinogenesis 30:1193–1201
Abdelrahim M, Safe S (2005) Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors decrease vascular endothelial growth factor expression in colon cancer cells by enhanced degradation of Sp1 and Sp4 proteins. Mol Pharmacol 68:317–329
Abdelrahim M, Smith R 3rd, Burghardt R, Safe S (2004) Role of Sp proteins in regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression and proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res 64:6740–6749
Abdelrahim M, Samudio I, Smith R 3rd, Burghardt R, Safe S (2002) Small inhibitory RNA duplexes for Sp1 mRNA block basal and estrogen-induced gene expression and cell cycle progression in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 277:28815–28822
Hong J, Samudio I, Liu S, Abdelrahim M, Safe S (2004) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-dependent activation of p21 in Panc-28 pancreatic cancer cells involves Sp1 and Sp4 proteins. Endocrinology 145:5774–5785
Khan S, Abdelrahim M, Samudio I, Safe S (2003) Estrogen receptor/Sp1 complexes are required for induction of cad gene expression by 17beta-estradiol in breast cancer cells. Endocrinology 144:2325–2335
Abdelrahim M, Baker CH, Abbruzzese JL, Safe S (2006) Tolfenamic acid and pancreatic cancer growth, angiogenesis, and Sp protein degradation. J Natl Cancer Inst 98:855–868
Abdelrahim M, Baker CH, Abbruzzese JL, Sheikh-Hamad D, Liu S, Cho SD, Yoon K, Safe S (2007) Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 expression by specificity proteins 1, 3, and 4 in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res 67:3286–3294
Abdelrahim M, Liu S, Safe S (2005) Induction of endoplasmic reticulum-induced stress genes in Panc-1 pancreatic cancer cells is dependent on Sp proteins. J Biol Chem 280:16508–16513
Konduri S, Colon J, Baker CH, Safe S, Abbruzzese JL, Abudayyeh A, Basha MR, Abdelrahim M (2009) Tolfenamic acid enhances pancreatic cancer cell and tumor response to radiation therapy by inhibiting survivin protein expression. Mol Cancer Ther 8:533–542
Lee JC, Krochak R, Blouin A, Kanterakis S, Chatterjee S, Arguiri E, Vachani A, Solomides CC, Cengel KA, Christofidou-Solomidou M (2009) Dietary flaxseed prevents radiation-induced oxidative lung damage, inflammation and fibrosis in a mouse model of thoracic radiation injury. Cancer Biol Ther 8:47–53
Gidoni D, Dynan WS, Tjian R (1984) Multiple specific contacts between a mammalian transcription factor and its cognate promoters. Nature 312:409–413
Suske G (1999) The Sp-family of transcription factors. Gene 238:291–300
Cui J, Meng X, Gao X, Tan G (2009) Curcumin decreases the expression of Pokemon by suppressing the binding activity of the Sp1 protein in human lung cancer cells. Mol Biol Rep [Epub ahead of print].
Herrera LJ, El-Hefnawy T, Queiroz de Oliveira PE, Raja S, Finkelstein S, Gooding W, Luketich JD, Godfrey TE, Hughes SJ (2005) The HGF receptor c-Met is overexpressed in esophageal adenocarcinoma. Neoplasia 7:75–84
Wong BS, Hsiao YC, Lin TW, Chen KS, Chen PN, Kuo WH, Chu SC, Hsieh YS (2009) The in vitro and in vivo apoptotic effects of Mahonia oiwakensis on human lung cancer cells. Chem Biol Interact 180:165–174
Daniel PT, Wieder T, Sturm I, Schulze-Osthoff K (2001) The kiss of death: promises and failures of death receptors and ligands in cancer therapy. Leukemia 15:1022–1032
Gogvadze V, Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B (2006) Multiple pathways of cytochrome c release from mitochondria in apoptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1757:639–647
Lee HJ, Lee HJ, Lee EO, Ko SG, Bae HS, Kim CH, Ahn KS, Lu J, Kim SH (2008) Mitochondria-cytochrome C-caspase-9 cascade mediates isorhamnetin-induced apoptosis. Cancer Lett 270:342–353
Lee JH, Lee YH, Lee HJ, Lee HJ, Lee EO, Ahn KS, Shim BS, Bae H, Choi SH, Ahn KS, Baek NI, Kim DK, Kim SH (2009) Caspase and mitogen activated protein kinase pathways are involved in Solanum lyratum herba induced apoptosis. J Ethnopharmacol 123:121–127
Lee KB, Kim KR, Huh TL, Lee YM (2008) Proton induces apoptosis of hypoxic tumor cells by the p53-dependent and p38/JNK MAPK signaling pathways. Int J Oncol 33:1247–1256
Safe S, Abdelrahim M (2005) Sp transcription factor family and its role in cancer. Eur J Cancer 41:2438–2448
Kang Y, Hong JA, Chen GA, Nguyen DM, Schrump DS (2007) Dynamic transcriptional regulatory complexes including BORIS, CTCF and Sp1 modulate NY-ESO-1 expression in lung cancer cells. Oncogene 26:4394–4403
Zheng Y, Ritzenthaler JD, Sun X, Roman J, Han S (2009) Prostaglandin E2 stimulates human lung carcinoma cell growth through induction of integrin-linked kinase: the involvement of EP4 and Sp1. Cancer Res 69:896–904
Tsou JH, Chang KY, Wang WC, Tseng JT, Su WC, Hung LY, Chang WC, Chen BK (2008) Nucleolin regulates c-Jun/Sp1-dependent transcriptional activation of cPLA2alpha in phorbol ester-treated non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. Nucleic Acids Res 36:217–227
Sun X, Ritzenthaler JD, Zhong X, Zheng Y, Roman J, Han S (2009) Nicotine stimulates PPARbeta/delta expression in human lung carcinoma cells through activation of PI3K/mTOR and suppression of AP-2alpha. Cancer Res 69:6445–6453
Acknowledgements
Authors thank M. D. Anderson Cancer Center Orlando’s Cancer Research Institute for providing necessary financial and technical assistance. The assistance of Donna Schade and Beth Isley is greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jimmie Colon and Md. Riyaz Basha have equal contributions.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PPT 609 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Colon, J., Basha, M.R., Madero-Visbal, R. et al. Tolfenamic acid decreases c-Met expression through Sp proteins degradation and inhibits lung cancer cells growth and tumor formation in orthotopic mice. Invest New Drugs 29, 41–51 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-009-9331-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-009-9331-8