Abstract
Background
Ethanol ingestion causes a variety of gastrointestinal disturbances including motility alterations. Slow wave propagation coordinates gastrointestinal motility, and abnormal slow wave activity is thought to contribute to motility disorders. To date, however, little is known about the effect of acute ethanol on motility disturbances associated with slow wave activity.
Aim
To investigate the effect of ethanol on small intestine slow wave activity.
Methods
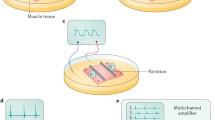
Segments (3–5 cm long) were isolated from the rat duodenum, jejunum, and ileum and mounted in an organ bath superfused with a normal Tyrode solution or with 1, 3, or 5 % ethanol containing Tyrode. The electrical activities were recorded using an array of 121 extracellular electrodes, and motility recordings were performed using a digital video camera.
Results
The frequency and amplitude of slow wave activity were not altered at 1, 3, or 5 % ethanol concentrations, but a significant drop in velocity was found at 3 and 5 % ethanol. Furthermore, inexcitable areas appeared in a dose-dependent manner. Slow wave was sometimes also seen to propagate in a circular fashion, thereby describing a reentrant loop. Finally, in all duodenal, jejunal, and ileal segments, ethanol inhibited contractions and became fully quiescent at 3–5 %.
Conclusions
These studies for the first time demonstrate that ethanol significantly inhibits slow wave and spike activity in a dose-dependent manner and could also initiate reentrant activities. Intestinal contractions were also inhibited in a dose-dependent manner. In conclusion, ethanol inhibits both slow wave activity and motor activity to cause ethanol-induced intestinal disturbances.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Horowitz M, Maddox A, Bochner M, et al. Relationships between gastric emptying of solid and caloric liquid meals and alcohol absorption. Am J Physiol. 1989;257:G291–G298.
Willson CA, Bushnell D, Keshavarzian A. The effect of acute and chronic ethanol administration on gastric-emptying in cats. Dig Dis Sci. 1990;35:444–448.
Lu G, Sarr MG, Szurszewski JH. Effects of ethyl alcohol on canine jejunal circular smooth muscle. Dig Dis Sci. 1997;42:2403–2410.
Huizinga JD, Thuneberg L, Kluppel M, Malysz J, Mikkelsen HB, Bernstein A. W/kit gene required for interstitial cells of Cajal and for intestinal pacemaker activity. Nature. 1995;373:347–349.
Lammers WJ. Spatial and temporal coupling between slow waves and pendular contractions. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2005;289:G898–G903.
He CL, Soffer EE, Ferris CD, Walsh RM, Szurszewski JH, Farrugia G. Loss of interstitial cells of Cajal and inhibitory innervation in insulin-dependent diabetes. Gastroenterology. 2001;121:427–434.
Huizinga JD, Lammers WJ. Gut peristalsis is governed by a multitude of cooperating mechanisms. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009;296:G1–G8.
Martin JL, Justus PG, Mathias JR. Altered motility of the small-intestine in response to ethanol (Etoh)—an explanation for the diarrhea associated with the consumption of alcohol. Gastroenterology. 1980;78:1218.
Robles EA, Mezey E, Halsted CH, Schuster MM. Effect of ethanol on motility of small-intestine. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1974;135:17–24.
Sanders KM, Bauer AJ. Ethyl-alcohol interferes with excitation-contraction mechanisms of canine antral muscle. Am J Physiol. 1982;242:G222–G230.
Dondas NY, Kaplan M, Kaya D, Singirik E. The impact of extracellular and intracellular Ca2+ on ethanol-induced smooth muscle contraction. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2009;30:1421–1427.
Fagundes DS, Grasa L, Arruebo MP, Plaza MA, Murillo MD. Ca2+-activated K+ channels involved in duodenal dismotility induced by ethanol. Alcohol Alcohol. 2007;42:291–295.
Malysz J, Afeli SA, Provence A, Petkov GV. Ethanol-mediated relaxation of guinea pig urinary bladder smooth muscle: involvement of BK and L-type Ca2+ channels. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014;306:C45–C58.
Lammers WJ, Al-Bloushi HM, Al-Eisaei SA, et al. Slow wave propagation and plasticity of interstitial cells of Cajal in the small intestine of diabetic rats. Exp Physiol. 2011;96:1039–1048.
Lammers WJ, Stephen B, Karam SM. Functional reentry and circus movement arrhythmias in the small intestine of normal and diabetic rats. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012;302:G684–G689.
Lammers WJ, Dhanasekaran S, Slack JR, Stephen B. Two-dimensional high-resolution motility mapping in the isolated feline duodenum: methodology and initial results. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2001;13:309–323.
Moore JG, Christian PE, Datz FL, Coleman RE. Effect of wine on gastric-emptying in humans. Gastroenterology. 1981;81:1072–1075.
Palasciano G, Portincasa P, Diciaula A, Palmieri V. Prolonged consumption of moderate doses of alcohol and in-vitro gastroduodenal and ileal contractility in the rat. Eur J Clin Invest. 1995;25:171–175.
Pirola RC, Davis AE. Effects of intravenous alcohol on motility of duodenum and of sphincter of Oddi. Australas Ann Med. 1970;19:24.
Krishnamra N, Limlomwongse L. The in vivo effect of ethanol on gastrointestinal motility and gastrointestinal handling of calcium in rats. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 1987;33:89–98.
Cortot A, Jobin G, Ducrot F, Aymes C, Giraudeaux V, Modigliani R. Gastric emptying and gastrointestinal absorption of alcohol ingested with a meal. Dig Dis Sci. 1986;31:343–348.
Halsted CH, Robles EA, Mezey E. Distribution of ethanol in the human gastrointestinal tract. Am J Clin Nutr. 1973;26:831–834.
Persson J. Alcohol and the small-intestine. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1991;26:3–15.
Israel Y, Valenzuela JE, Salazar I, Ugarte G. Alcohol and amino acid transport in the human small intestine. J Nutr. 1969;98:222–224.
Spach MS, Kootsey JM. The Nature of Electrical Propagation in Cardiac-Muscle. Am J Physiol. 1983;244:H3–H22.
Lammers WJ, Ver Donck L, Stephen B, Smets D, Schuurkes JA. Focal activities and re-entrant propagations as mechanisms of gastric tachyarrhythmias. Gastroenterology. 2008;135:1601–1611.
O’Grady G, Egbuji JU, Du P, et al. High-resolution spatial analysis of slow wave initiation and conduction in porcine gastric dysrhythmia. Neurogastroent Motil. 2011;23:E345–E355.
Lammers WJ, Hamid R. The initiation, continuation, and termination of spontaneous episodes of circus movements in the pregnant myometrium of the rat. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1998;179:1515–1526.
Allessie MA, Bonke FI, Schopman FJ. Circus movement in rabbit atrial muscle as a mechanism of tachycardia. III. The “leading circle” concept: a new model of circus movement in cardiac tissue without the involvement of an anatomical obstacle. Circ Res. 1977;41:9–18.
Schotten U, Verheule S, Kirchhof P, Goette A. Pathophysiological mechanisms of atrial fibrillation: a translational appraisal. Physiol Rev. 2011;91:265–325.
Nattel S. New ideas about atrial fibrillation 50 years. Nature. 2002;415:219–226.
Rensma PL, Allessie MA, Lammers WJEP, Bonke FIM, Schalij MJ. Length of excitation wave and susceptibility to reentrant atrial arrhythmias in normal conscious dogs. Circ Res. 1988;62:395–410.
Smeets JLRM, Allessie MA, Lammers WJEP, Bonke FIM, Hollen J. The wavelength of the cardiac impulse and reentrant arrhythmias in isolated rabbit atrium—the role of heart-rate, autonomic transmitters, temperature, and potassium. Circ Res. 1986;58:96–108.
Charles F, Phillips SF. Effects of ethanol, xylose, and glucose on canine jejunal motility. Am J Physiol. 1995;269:G363–G369.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Mr. M. Shafiullah and Mr. M. ElWasila for taking care of the animals.
Author Contributions
SBS, BS and WJ designed and performed the experiments; SBS, BS, SSN, and WJ analyzed the data and SBS, KHS and WJL wrote the paper.
Grant Support
This work was supported by Grants from the College of Medicine and Health Sciences, UAE University, Al Ain, UAE.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests or financial obligations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Subramanya, S.B., Stephen, B., Nair, S.S. et al. Effect of Ethanol Exposure on Slow Wave Activity and Smooth Muscle Contraction in the Rat Small Intestine. Dig Dis Sci 60, 3579–3589 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-015-3813-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-015-3813-7