Abstract
Nitric oxide (NO) plays an important role as a nonadrenergic, noncholinergic inhibitory neurotransmitter in the GI tract. Our study aims were to investigate the effect of a single intragastric L-arginine (L-Arg) administration, as a source of NO, on proximal stomach tone in basal and postintragastric administration of a polymeric diet in humans and to evaluate concomitantly the effect on antral area as an indirect assessment of gastric emptying. Eight healthy volunteers were studied in a randomized double-blind crossover study after, respectively, 15 g L-Arg, 30 g L-Arg, or placebo administered in the stomach through a gastric tube. The drug administration was followed by a polymeric diet infusion (500 ml/500 kcal) at a rate of 250 ml/hr. Gastric tone variations were recorded with an electronic barostat, gastric emptying was concomitantly estimated by repeated ultrasound measurements of antral area, and symptoms were recorded throughout the experiment.
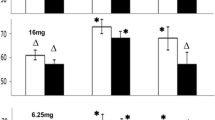
L-Arg administration was associated with significantly higher increases in barostat bag volumes at both dosages, 30 g (117±16 ml) and 15 g (67±15 ml), compared to placebo (46±11 ml; P < 0.05). In response to the polymeric diet the 30-g L-Arg challenge was associated with a smaller increase in intrabag volume, whereas postinfusion final volumes did not differ in the three treatment conditions. Antral areas were not different at any time of measurement among the three challenges. Bloating and diarrhea were observed after 30-g L-Arg administration in five subjects of eight. Short-term L-Arg administration was able to induce proximal stomach relaxation that allowed a secondary response to enteral feeding only at the 15-g dosage. This 15-g dosage was as well tolerated as the placebo and was associated with no significant changes in gastric emptying patterns.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jahnberg T (1977) Gastric adaptive relaxation. Effects of vagal activation and vagotomy. An experimental study in dogs and in man. Scand J Gastroenterol 12:5–32
Azpiroz F, Malagelada JR (1985) Intestinal control of gastric tone. Am J Gastroenterol 249:501–509
Azpiroz F, Malagelada JR (1987) Importance of vagal input in maintaining gastric tone in the dog. J Physiol 384:511–524
Azpiroz F, Malagelada JR (1986) Vagally mediated gastric relaxation induced by intestinal nutrients in the dog. Am J Physiol 251:G727–G735
Desai KMW, Sessa WC, Vane JR (1991) Involvement of nitric oxide in the reflex relaxation of the stomach to accommodate food or fluid. Nature 351:477–479
Paterson CA, Anvari M, Tougas G, Huizinga JD (2000) Nitrergic and cholinergic vagal pathways involved in the regulation of canine proximal gastric tone: a in vivo study. Neurogastroenterol Motil 12:301–306
Russo A, Fraser R, Adachi K, Horowitz M, Boeckxstaens G (1999) Evidence that nitric oxide mechanisms regulate small intestinal motility in humans. Gut 44:72–76
Kuiken SD, Vergeer M, Heisterkamp SH, Tytgat GN, Boeckxstaens GE (200) Role of nitric oxide in gastric motor and sensoy functions in healthy subjects. Gut 51:212–218
Tack J, Demedts I, Meulemans A, Schuurkes J, Janssens J (2002) Role of nitric oxide in the gastric accommodation reflex and in meal induced satiety in humans. Gut 51:219–224
Tack J, Coulie B, Wilmer A, Andrioli A, Janssens J (2000) Influence of sumatriptan on gastric fundus tone and on the perception of gastric distension in man. Gut 46:468–473
Meulemans AL, Helsen LF, Schuurkes JAJ (1993) The role of nitric oxide (NO) in 5-H-induced relaxations of the guinea pig stomach. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 348:424–430
Coulie B, Tack J, Sifrim D, Andriolli A, Janssens J (1999) Role of nitric oxide in fasting gastric fundus tone and 5-HT1 receptor-mediated relaxation of gastric fundus. Am J Physiol 276:G373–G377
Konturek JW, Thor P, Domschke W (1995) Effects of nitric oxide on antral motility and gastric emptying in humans. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 7:97–102
Fiorucci S, Distrutti E, Quintieri A, Sarpi L, Spirchez Z, Gulla N, Morelli A (1995) L-Arginine/nitric oxide pathway modulates gastric motility and gallbladder emptying induced by erythromycin and liquid meal in humans. Dig Dis Sci 40:1365–1371
Straathof JWA, Adamse M, Onkenhout W, Lamers CBHW, Masclee AAM (2000) Effects of L-arginine on lower oesophageal sphincter motility in man. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 12:419–424
Bruins MJ, Luiking YC, Soeters PB, Lamers WH, Akkermans LMA, Deutz NEP (2004) Effects of long-term intravenous and intragastric L-arginine intervention on jejunal motility and visceral nitric oxide production in the hyperdynamic compensated endotoxaemic pig. Neurogastroenterol Motil 16:819–828
Luiking YC, Weusten BLAM, Portincasa P, Van Der Meer R, Smout AJMP, Akkermans LMA (1998) Effects of long-term oral L-arginine on esophageal motility and gallbladder dynamics in healthy humans. Am J Physiol 274:G984–G991
Savoye G, Bouin M, Hervé S, Denis P, Ducrotte P (2005) Gastric tone variations during gastric infusion of fiber-supplemented formulas. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 20:409–414
Savoye G, Bouin M, Denis P, Ducrotté P (2005) Delayed postprandial fundic relaxation: a new abnormal finding in functional dyspepsia. Scand J Gastroenterol 40:354–355
Le Blanc-Louvry I, Savoye G, Maillot C, Denis P, Ducrotté P (2003) An impaired accommodation of the proximal stomach to a meal is associated with symptoms after distal gastrectomy. Am J Gastroenterol 98:2642–2647
Ropert A, Bruley des Varannes S, Bizais Y, Roze C, Galmiche JP (1993) Simultaneous assessment of liquid emptying and proximal gastric tone in humans. Gastroenterology 105:667–674
Ropert A, Cherbut C, Roze C, Le Quellec A, Holst JJ, Fu-Cheng X, Bruley des Varannes S, Galmiche JP (1996) Colonic fermentation and proximal gastric tone in humans. Gastroenterology 111:289–296
Azpiroz F, Malagelada JR (1990) Isobaric intestinal distension in humans: sensorial relay and reflex gastric relaxation. Am J Physiol 258:G202–G207
Bouin M, Savoye G, Hervé S, Hellot MF, Denis P, Ducrotté P (2001) Does the supplementation of the formula with fibre increase the risk of gastro-oesophageal reflux during enteral nutrition? A human study. Clin Nutr 20:307–312
Savoye-Collet C, Savoye G, Smout A (2003) Determinants of transpyloric fluid transport: a combined study usingreal time ultrasound, manometry and impedance recording. Am J Physiol 285:G1147–G1152
American Gastroenterological Association (1995) Technical review on tube feeding for enteral nutrition. Gastroenterology 108(4):1282–1301
Castillo L, DeRojas TC, Chapman TE, Vogt J, Burke JF, Tannenbaum SR, Young VR (1993) Splanchnic metabolism of dietary arginine in relation to nitric oxide synthesis in normal adult man. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:193–197
Leaf CD, Wishnok JS, Tannenbaum SR (1989) L-Arginine is a precursor for nitrate biosyntheis inhumans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 163:1032–1037
Weir GC, Samols E, Loo S, Patel YC, Gabbey KH (1979) Somatostatin and pancreatic polypeptide secretion. Effects of glucagons, insulin and arginine. Diabetes 28:35–40
Haruma K, Wiste JA, Camilleri M (1997) Effect of octreotide on gastrointestinal pressure profiles in health, functional and organic gastrointestinal disorders. Gut 35:1064–1069
Horowitz M, Harding PE, Maddox A, Maddern GJ, Collins PJ, Chatterton BE (1986) Gastric and esophageal emptying and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1:97–113
Bourgeois S, Coulie B, Tack J, Andrioli A, Janssens J (1996) The somatostatin-analogue octreotide inhibits tone and phasic contractile activity of the gastric fundus in man. Gastroenterology 110:A639 [abstract]
Savoye G, Bouin M, Labbé L, Mosni G, Morcamp P, Denis P, Ducrotté P (2005) Concomitant variations of gastric tone and duodenal motility in humans. Results of a placebo-controlled study assessing octreotide and sumatriptan. Scand J Gastroenterol 41:536–543
Taylor IL, Byrne WJ, Christies DL, Ament ME, Walsh JH (1982) Effect of individual L-amino acids on gastric acid secretion and gastric serum gastrin and pancreatic polypeptide release in humans. Gastroenterology 83:273–278
Bode-Boger SM, Boger RH, Creutzig A, Tsikas D, Gutzki FM, Alexander K, Frolich JC (1994) L-Arginine infusion decrease peripheral arterial resistance and inhibits platelet aggregation in healthy subjects. Clin Sci 87:303–310
Sarnelli G, Sifrim D, Janssens J, Tack J (2004) Influence of sidenafil on gastric sensorimotor function in humans. Am J Physiol 287:G988–G992
Mundt MW, Hausken T, Samsom M (2002) Effect of intragastric barostat bag on proximal and distal gastric accommodation in response to liquid meal. Am J Physiol 283:G681–G686
Indireshkumar K, Brasseur JG, Faas H, Hebbard GS, Kunz P, Dent J, Feinle C, Li M, Boesiger P, Fried M, Schwizer W (2000) Relative contributions of pressure pump and peristaltic pump to gastric emptying. Am J Physiol 278:G604–G616
Hausken T, Mundt M, Samsom M (2002) Low antroduodenal pressure gradients are responsible for gastric emptying of a low caloric liquid meal in humans. Neurogastroenterol Motil 14:97–105
Savoye G, Oors J, Smout A (2003) Interdigestive transpyloric fluid transport assessed by intraluminal impedance recording. Am J Physiol 284:G663–G669
Savoye G, Oors J, Smout A (2005) Duodenal acid clearance in humans: observations made with intraluminal impedance recordings. Dig Dis Sci 50:1553–1560
Rao ASC, Lu R, Schulze-Delrieu K (1996) Duodenum as an immediate brake to gastric outflow: a videofluoroscopic and manometric assessment. Gastroenterology 110:740–747
Acknowledgment
This work was supported in part by a grant from Nutricia-France.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Savoye, G., Jemaa, Y., Mosni, G. et al. Effects of Intragastric L-Arginine Administration on Proximal Stomach Tone Under Basal Conditions and After an Intragastric Diet. Dig Dis Sci 51, 2147–2153 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-9393-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-9393-9