Abstract
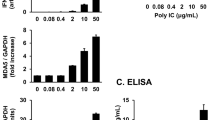
Studies conducted using murine arthritis models have indicated that the use of in vitro-transcribed messenger RNA (IVT mRNA) is an effective therapeutic approach for joint diseases. However, the use of IVT mRNA in human synovial cells has not been widely studied. Recently, the outbreak of the novel coronavirus disease has accelerated the development of innovative mRNA vaccines, such as those containing a modified nucleic acid, N1-methylpseudouridine-5′-triphosphate (m1ψ). IVT mRNA is an attractive tool for biological experiments and drug discovery. To verify the protein expression from IVT mRNA in vitro, primary cultured fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) and MH7A human synovial fibroblast cells were transfected with enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) mRNA with or without m1ψ incorporation. EGFP was detected using western blotting and fluorescence microscopy. A multiplex assay was performed to comprehensively understand IVT mRNA-induced immunogenicity. Gene expression levels were measured using reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. In both MH7A cells and FLS, cells transfected with EGFP mRNA containing m1ψ generated higher levels of EGFP than those transfected with unmodified EGFP or control mRNAs. The multiplex assay of the FLS culture supernatant and reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction for FLS revealed that both concentration and expression of IL-6, TNF-α, and CXCL10 were upregulated by unmodified EGFP mRNA, whereas they were suppressed by EGFP mRNA with m1ψ. Overall, m1ψ incorporation enhanced protein expression and decreased the expression of cytokines. These findings may contribute to arthritis research.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The source data for most of the figures are available from the authors.
References
Aini H, Itaka K, Fujisawa A et al (2016) Messenger RNA delivery of a cartilage-anabolic transcription factor as a disease-modifying strategy for osteoarthritis treatment. Sci Rep 6:18743. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep18743
Alexopoulou L, Holt AC, Medzhitov R, Flavell RA (2001) Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptor 3. Nature 413:732–738. https://doi.org/10.1038/35099560
Anderson BR, Muramatsu H, Jha BK et al (2011) Nucleoside modifications in RNA limit activation of 2′-5′-oligoadenylate synthetase and increase resistance to cleavage by RNase L. Nucleic Acids Res 39:9329–9338. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr586
Anderson BR, Muramatsu H, Nallagatla SR et al (2010) Incorporation of pseudouridine into mRNA enhances translation by diminishing PKR activation. Nucleic Acids Res 38:5884–5892. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkq347
Andries O, Mc Cafferty S, De Smedt SC et al (2015) N(1)-methylpseudouridine-incorporated mRNA outperforms pseudouridine-incorporated mRNA by providing enhanced protein expression and reduced immunogenicity in mammalian cell lines and mice. J Control Release 217:337–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCONREL.2015.08.051
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA et al (1988) The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31:315–324. https://doi.org/10.1002/ART.1780310302
Baden LR, El-Sahly HM, Essink B et al (2021) Efficacy and safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. N Engl J Med 384:403–416. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMOA2035389
Bartok B, Firestein GS (2010) Fibroblast-like synoviocytes: key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Rev 233:233–255. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.0105-2896.2009.00859.X
Boczkowski D, Nair SK, Snyder D, Gilboa E (1996) Dendritic cells pulsed with RNA are potent antigen-presenting cells in vitro and in vivo. J Exp Med 184:465–472. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.184.2.465
Conry RM, LoBuglio AF, Wright M et al (1995) Characterization of a messenger RNA polynucleotide vaccine vector. Cancer Res 55:1397–1400
Diebold SS, Kaisho T, Hemmi H et al (2004) Innate Antiviral responses by means of TLR7-mediated recognition of single-stranded RNA. Science 303:1529–1531. https://doi.org/10.1126/SCIENCE.1093616
Foster JB, Choudhari N, Perazzelli J et al (2019) Purification of mRNA encoding chimeric antigen receptor is critical for generation of a robust T-Cell response. Hum Gene Ther 30:168–178. https://doi.org/10.1089/HUM.2018.145
Georgakopoulou EA, Tsimaratou K, Evangelou K et al (2013) Specific lipofuscin staining as a novel biomarker to detect replicative and stress-induced senescence. A method applicable in cryo-preserved and archival tissues. Aging 5:37–50
Hadas Y, Sultana N, Youssef E et al (2019) Optimizing modified mRNA in vitro synthesis protocol for heart gene therapy. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev 14:300–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.OMTM.2019.07.006
Heil F, Hemmi H, Hochrein H et al (2004) Species-specific recognition of single-stranded RNA via toll-like receptor 7 and 8. Science 303:1526–1529. https://doi.org/10.1126/SCIENCE.1093620
Holtkamp S, Kreiter S, Selmi A et al (2006) Modification of antigen-encoding RNA increases stability, translational efficacy, and T-cell stimulatory capacity of dendritic cells. Blood 108:4009–4017. https://doi.org/10.1182/BLOOD-2006-04-015024
Hornung V, Ellegast J, Kim S et al (2006) 5’-Triphosphate RNA is the ligand for RIG-I. Science 314:994–997. https://doi.org/10.1126/SCIENCE.1132505
Karikó K, Buckstein M, Ni H, Weissman D (2005) Suppression of RNA recognition by toll-like receptors: the impact of nucleoside modification and the evolutionary origin of RNA. Immunity 23:165–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IMMUNI.2005.06.008
Karikó K, Muramatsu H, Welsh FA et al (2008) Incorporation of pseudouridine into mRNA yields superior nonimmunogenic vector with increased translational capacity and biological stability. Mol Ther 16:1833–1840. https://doi.org/10.1038/MT.2008.200
Kato H, Takeuchi O, Mikamo-Satoh E et al (2008) Length-dependent recognition of double-stranded ribonucleic acids by retinoic acid-inducible gene-I and melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5. J Exp Med 205:1601–1610. https://doi.org/10.1084/JEM.20080091
Kato H, Takeuchi O, Sato S et al (2006) Differential roles of MDA5 and RIG-I helicases in the recognition of RNA viruses. Nature 441:101–105. https://doi.org/10.1038/NATURE04734
Koido S, Kashiwaba M, Chen D et al (2000) Induction of antitumor immunity by vaccination of dendritic cells transfected with MUC1 RNA. J Immunol 165:5713–5719. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.165.10.5713
Kormann MSD, Hasenpusch G, Aneja MK et al (2011) expression of therapeutic proteins after delivery of chemically modified mrNA in mice. Nat Biotechnol 29:154–157. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1733
Kuranobu T, Mokuda S, Oi K et al (2020) Activin A expressed in rheumatoid synovial cells downregulates TNFα-induced CXCL10 expression and osteoclastogenesis. Pathobiology 87:198–207. https://doi.org/10.1159/000506260
Li X, Lu C, Stewart M et al (2009) Structural basis of double-stranded RNA recognition by the RIG-I like receptor MDA5. Arch Biochem Biophys 488:23–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ABB.2009.06.008
Lund JM, Alexopoulou L, Sato A et al (2004) Recognition of single-stranded RNA viruses by Toll-like receptor 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:5598–5603. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0400937101
Mandl CW, Aberle JH, Aberle SW et al (1998) In vitro-synthesized infectious RNA as an attenuated live vaccine in a flavivirus model. Nat Med 4:1438–1440. https://doi.org/10.1038/4031
Martinon F, Krishnan S, Lenzen G et al (1993) Induction of virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in vivo by liposome-entrapped mRNA. Eur J Immunol 23:1719–1722. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.1830230749
Mokuda S, Miyazaki T, Ito Y et al (2015) The proto-oncogene survivin splice variant 2B is induced by PDGF and leads to cell proliferation in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Sci Rep 5:9795. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep09795
Mokuda S, Nakamichi R, Matsuzaki T et al (2019) Wwp2 maintains cartilage homeostasis through regulation of Adamts5. Nat Commun 10:2429. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10177-1
Nance KD, Meier JL (2021) Modifications in an emergency: the role of N1-methylpseudouridine in COVID-19 vaccines. ACS Cent Sci 7:748–756. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSCENTSCI.1C00197
Nelson J, Sorensen EW, Mintri S et al (2020) Impact of mRNA chemistry and manufacturing process on innate immune activation. Sci Adv 6:eaaz6893. https://doi.org/10.1126/SCIADV.AAZ6893
Parr CJC, Wada S, Kotake K et al (2020) N 1-Methylpseudouridine substitution enhances the performance of synthetic mRNA switches in cells. Nucleic Acids Res 48:E35. https://doi.org/10.1093/NAR/GKAA070
Pichlmair A, Schulz O, Tan CP et al (2006) RIG-I-mediated antiviral responses to single-stranded RNA bearing 5ʹ-phosphates. Science 314:997–1001. https://doi.org/10.1126/SCIENCE.1132998
Polack FP, Thomas SJ, Kitchin N et al (2020) Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine. N Engl J Med 383:2603–2615. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMOA2034577
Sahin U, Karikó K, Türeci Ö (2014) MRNA-based therapeutics-developing a new class of drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discov 13:759–780. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd4278
Sander LE, Davis MJ, Boekschoten MV et al (2011) Detection of prokaryotic mRNA signifies microbial viability and promotes immunity. Nature 474:385–392. https://doi.org/10.1038/NATURE10072
Schirrmacher V, Förg P, Dalemans W et al (2000) Intra-pinna anti-tumor vaccination with self-replicating infectious RNA or with DNA encoding a model tumor antigen and a cytokine. Gene Ther 7:1137–1147. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301220
Sullenger BA, Nair S (2016) From the RNA world to the clinic. Science 352:1417–1420. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aad8709
Svitkin YV, Cheng YM, Chakraborty T et al (2017) N1-methyl-pseudouridine in mRNA enhances translation through eIF2α-dependent and independent mechanisms by increasing ribosome density. Nucleic Acids Res 45:6023–6036. https://doi.org/10.1093/NAR/GKX135
Van der Jeught K, De KS, Bialkowski L et al (2018) Dendritic cell targeting mRNA lipopolyplexes combine strong antitumor T-cell immunity with improved inflammatory safety. ACS Nano 12:9815–9829. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSNANO.8B00966
Yoneyama M, Kikuchi M, Natsukawa T et al (2004) The RNA helicase RIG-I has an essential function in double-stranded RNA-induced innate antiviral responses. Nat Immunol 5:730–737. https://doi.org/10.1038/NI1087
Yukawa K, Mokuda S, Kohno H et al (2020) Serum CXCL10 levels are associated with better responses to abatacept treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 38:956–963
Acknowledgements
We used MH7A cells with the MTA from KISSEI Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.. We would like to thank Shigeru Miyaki (Hiroshima University) for the preparation of experimental devices.
Funding
This research was funded by JSPS KAKENHI (Grant Number 19K18499), Mitsubishi Foundation, Takeda Science Foundation, Mochida Memorial Foundation for Medical and Pharmaceutical Research, Japanese Respiratory Foundation Grant, Japan Rheumatism Foundation, The Japan College of Rheumatology Grant for Promoting Research for Early RA, and The Nakatomi Foundation to S.M.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SM, HW, HK, MI, and KA performed the experiments and analyzed the data. SM, HW, SH, and ES planned the experiments and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest associated with the manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mokuda, S., Watanabe, H., Kohno, H. et al. N1-methylpseudouridine-incorporated mRNA enhances exogenous protein expression and suppresses immunogenicity in primary human fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Cytotechnology 74, 503–514 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-022-00540-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-022-00540-4