Abstract
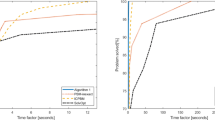
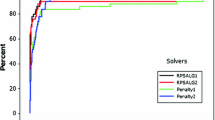
In this paper, we study a semi-infinite programming (SIP) problem with a convex set constraint. Using the value function of the lower level problem, we reformulate SIP problem as a nonsmooth optimization problem. Using the theory of nonsmooth Lagrange multiplier rules and Danskin’s theorem, we present constraint qualifications and necessary optimality conditions. We propose a new numerical method for solving the problem. The novelty of our numerical method is to use the integral entropy function to approximate the value function and then solve SIP by the smoothing projected gradient method. Moreover we study the relationships between the approximating problems and the original SIP problem. We derive error bounds between the integral entropy function and the value function, and between locally optimal solutions of the smoothing problem and those for the original problem. Using certain second order sufficient conditions, we derive some estimates for locally optimal solutions of problem. Numerical experiments show that the algorithm is efficient for solving SIP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, E.J., Nash, P.: Linear Programming in Infinite-Dimension over Topological Vector Space: Theory and Applications. Wiley, New York (1987)
Bhattacharjee, B., Lemonidis, P., Green Jr, W.H., Barton, P.I.: Global solution of semi-infinite programs. Math. Program. 103, 283–307 (2005)
Cánovas, M.J., Hantoute, A., López, M.A., Parra, J.: Stability of indices in the KKT conditions and metric regularity in convex semi-infinite optimization. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 139, 485–500 (2008)
Chen, X., Womersley, R.S., Ye, J.J.: Minimizing the condition number of a Gram matrix. SIAM J. Optim. 21, 127–148 (2011)
Clarke, F.H.: Optimization and Nonsmooth Analysis. Wiley-Interscience, New York (1983)
Clarke, F.H., Ledyaev, YuS, Stern, R.J., Wolenski, P.R.: Nonsmooth Analysis and Control Theory. Springer, New York (1998)
Coope, I.D., Watson, G.A.: A projected Lagrangian algorithm for semi-infinite programming. Math. Program. 32, 337–356 (1985)
Danskin, J.M.: The Theory of Max–Min and Its Applications to Weapons Allocation Problems. Springer, New York (1967)
Fang, S.C., Lin, C.J., Wu, S.-Y.: Solving quadratic semi-infinite programming problems by using relaxed cutting-plane scheme. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 129, 89–104 (2001)
Floudas, C.A.: Deterministic Global Optimization, Theory, Methods and Applications. Kluwer, Dordrecht (2000)
Floudas, C.A., Stein, O.: The adaptive convexification algorithm: a feasible point method for semi-infinite programming. SIAM J. Optim. 18, 1187–1208 (2007)
Goberna, M.A., López, M.A.: Linear Semi-infinite Optimization. Wiley, Chichester (1998)
Guerra, Vśzquez F., Rückmann, J.-J., Stein, O., Still, G.: Generalized semi-infinite programming: a tutorial. J. Compu. Appl. Math. 217, 394–419 (2008)
Gustafson, S.A., Kortanek, K.O.: Numerical treatment of a class of semi-infinite programming problems. Naval Res. Logis. Quart. 20, 477–504 (1973)
Hettich, R.P., Jongen, H.T.: Semi-infinite Programming: Conditions of Optimality and Applications. In: Stoer, J. (ed.) Optimization Techniques. Lecture Notes in Control and Information Sciences. Springer, Berlin (1978)
Hettich, R.P., Kortanek, K.O.: Semi-infinite programming: theory, methods, and applications. SIAM Rev. 35, 380–429 (1993)
Hu, H.: A one-phase algorithm for semi-infinite linear programming. Math. Program. 46, 85–103 (1990)
Jongen, H.T., Jonker, P., Twilt, F.: Critical sets in parametric optimization. Math. Program. 34, 333–353 (1989)
Jourani, A.: Constraint qualifications and Lagrange multipliers in nondifferentiable programming problems. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 81, 533–548 (1994)
Kortanek, K., No, H.: A central cutting plane algorithm for convex semi-infinite programming problems. SIAM J. Optim. 3, 901–918 (1993)
Lai, H.C., Wu, S.-Y.: On linear semi-infinite programming problems: an algorithm. Numer. Func. Anal. Optim. 13, 287–304 (1992)
Ling, C., Ni, Q., Qi, L., Wu, S.-Y.: A new smoothing Newton-type algorithm for semi-infinite programming. J. Global Optim. 47, 133–159 (2010)
Li, D.H., Qi, L., Tam, J., Wu, S.-Y.: A smoothing Newton method for semi-infinite programming. J. Global Optim. 30, 169–194 (2004)
Lin, G.H., Xu, M., Ye, J.J.: On solving simple bilevel programs with a nonconvex lower level program. Math. Program. Ser. A. doi:10.1007/s10107-013-0633-4
López, M., Still, G.: Semi-infinite programming. Eur. J. Opera. Res. 180, 491–518 (2007)
Ni, Q., Ling, C., Qi, L., Teo, K.L.: A truncated projected Newton-type algorithm for large-scale semi-infinite programming. SIAM J. Optim. 16, 1137–1154 (2006)
Polak, E.: Optimization: Algorithms and Consistent Approximations. Springer, Berlin (2006)
Polak, E.: On the mathematical foundations of nondifferentiable optimization in engineering design. SIAM Rev. 29, 21–89 (1987)
Qi, L., Ling, C., Tong, X.J., Zhou, G.: A smoothing projected Newton-type algorithm for semi-infinite programming. Comput. Optim. Appl. 42, 1–30 (2009)
Qi, L., Wu, S.-Y., Zhou, G.: Semismooth Newton methods for solving semi-infinite programming problems. J. Global Optim. 27, 215–232 (2003)
Reemtsen, R., Görner, S.: Numerical methods for semi-infinite programming: a survey. In: Reemtsen, R., Rückmann, J.-J. (eds.) Semi-Infinite Programming, pp. 195–275. Kluwer, Boston (1998)
Roleff, K.: A stable multiple exchange algorithm for linear SIP. In: Hettich, R. (ed.) Semi-Infinite Programming. Lecture Notes in Control and Information Sciences, vol. 15, pp. 83–96. Springer, Berlin (1978)
Shapiro, A.: Semi-infinite programming, duality, discretization and optimality conditions. Optimization 58, 133–161 (2009)
Shiu, T.-J., Wu, S.-Y.: Relaxed cutting plane method with convexification for solving nonlinear semi-infinite programming problems. Comput. Optim. Appl. 53, 91–113 (2012)
Stein, O.: Bilevel-Strategies on Semi-infinite Programming. Kluwer, Boston (2003)
Stein, O.: How to solve a semi-infinite optimization problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 223, 312–320 (2012)
Stein, O., Still, G.: Solving semi-infinite optimization problems with interior point techniques. SIAM J. Control Optim. 42, 769–788 (2003)
Still, G.: Discretization in semi-infinite programming: the rate of convergence. Math. Program. 91, 53–69 (2001)
Tanaka, Y., Fukushima, M., Ibaraki, T.: A globally convergent SQP method for semi-infinite nonlinear optimization. J. Comput. Appl. Math 23, 141–153 (1988)
Teo, K.L., Yang, X.Q., Jennings, L.S.: Computational discretization algorithms for functional inequality constrained optimization. Ann. Oper. Res 28, 215–234 (2000)
Wu, S.-Y., Fang, S.C.: Solving convex programs with infinitely many linear constraints by a relaxed cutting plane method. Comput. Math. Appl. 38, 23–33 (1999)
Wu, S.-Y., Fang, S.C., Lin, C.J.: Relaxed cutting plane method for solving linear semi-infinite programming problems. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 99, 759–779 (1998)
Wu, S.-Y., Li, D.H., Qi, L., Zhou, G.: An iterative method for solving KKT system of the semi-infinite programming. Optim. Methods Soft. 20, 629–643 (2005)
Ye, J.J., Wu, S.-Y.: First order optimality conditions for generalized semi-infinite programming problems. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 137, 419–434 (2008)
Zhang, L.P., Wu, S.-Y., López, M.A.: A new exchange method for convex semi-infinite programming. SIAM J. Optim. 20, 2959–2977 (2010)
Acknowledgments
The research of this author was partially supported by NSERC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, M., Wu, SY. & Ye, J.J. Solving semi-infinite programs by smoothing projected gradient method. Comput Optim Appl 59, 591–616 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10589-014-9654-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10589-014-9654-z
Keywords
- Nonlinear semi-infinite programming problem
- Value function
- Integral entropy function
- Smoothing projected gradient algorithm
- Locally optimal solution