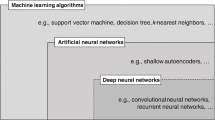
Abstract
Forecasting techniques have been widely used in automatic assessment in virtual teaching and learning environments, allowing educators to make decisions in both present and future planning. However, due to the element of uncertainty intrinsic to the forecasting methods, a number of studies have been carried out in order to find a more efficient model that allows for exploring and inferring the relation of a dependent variable with independent variables. In this context, we propose an alternative to solve the problem of automatic evaluation with the use of artificial neural networks that are adjusted, or trained, so that a certain input leads to a specific target output. Therefore, the research seeks to achieve the following: (1) review the state-of-the-art work published in this area, (2) propose a better forecasting model as compared to the existing model, (3) perform a comparative analysis with the previous experiments of multiple linear regression (MLR) and symbolic regression, (4) propose future research guidelines. To this end, a case study was applied to clarify the benefits of the artificial neural networks, emphasizing its efficiency and simplicity of implementation. With a margin of error of less than 2%, this proposal simulates a specialist, and automatically evaluates a student’s answer. As a result, the proposed model performance overcomes the methods of multiple linear regression and symbolic regression efficiently, eliminating the problem of randomness, reducing processing time and at the same time providing a model with higher accuracy and lower error rates.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
McCarthy, J., Minsky, M.L., Rochester, N., Shannon, C.E.: A proposal for the dartmouth summer research project on artificial intelligence, August 31, 1955. AI Mag. 27(4), 12 (2006)
Russell, S., Norvig, P.: Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, 3rd edn. Prentice Hall Press, Upper Saddle River, NJ (2009)
Rumelhart, D.E., Hinton, G.E., Williams, R.J.: Learning internal representations by error propagation. Parallel Distributed Processing: Explorations in the Microstructure of Cognition, vol. 1, pp. 318–362. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA (1986)
Sharda, R.: Neural networks for the MS/OR analyst: an application bibliography. Interfaces (Providence) 24(2), 116–130 (1994)
White, H.: Learning in artificial neural networks: a statistical perspective. Neural Comput. 1, 425–464 (1989)
Ripley, B.D.: Statistical aspects of neural networks. In: Barndorff-Nielsen, O.E., Jensen, J.L., Kendall, W.S. (eds.) Networks and Chaos-Statistical and Probabilistic Aspects, pp. 40–123. Chapman and Hall, London (1993)
Cheng, B., Titterington, D.: Neural networks: a review from a statistical perspective. Stat. Sci. 9(1), 2–54 (1994)
Hu, M.J.-C.: Application of the adaline system to weather forecasting. Doctoral dissertation, Department of Electrical Engineering, Stanford University (1964)
Zhang, G., Patuwo, B.E., Hu, M.Y.: Forecasting with artificial neural networks: the state of the art. Int. J. Forecast. 14(1), 35–62 (1998)
Wutsqa, D.U., Kusumawati, R., Subekti, R.: The application of Elman recurrent neural network model for forecasting consumer price index of education, recreation and sports in Yogyakarta. In: 2014 10th International Conference on Natural Computation (ICNC), pp. 192–196 (2014)
Leva, S., Dolara, A., Grimaccia, F., Mussetta, M., Ogliari, E.: Analysis and validation of 24 hours ahead neural network forecasting of photovoltaic output power. Math. Comput. Simul. 131, 88–100 (2017)
Kim, Y., Jang, H., Kim, J., Lee, J.: Prediction of storage efficiency on CO2 sequestration in deep saline aquifers using artificial neural network. Appl. Energy 185, 916–928 (2017)
Song, Q., Zheng, Y.-J., Xue, Y., Sheng, W.-G., Zhao, M.-R.: An evolutionary deep neural network for predicting morbidity of gastrointestinal infections by food contamination. Neurocomputing 226, 16–22 (2017)
Silva, C., Fonseca, J.: Educational data mining: a literature review. In: Rocha, Á., Serrhini, M., Felgueiras, C. (eds.) Europe and MENA Cooperation Advances in Information and Communication Technologies, pp. 87–94. Springer, Switzerland (2017)
Costa, E.B., Fonseca, B., Santana, M.A., de Araújo, F.F., Rego, J.: Evaluating the effectiveness of educational data mining techniques for early prediction of students’ academic failure in introductory programming courses. Comput. Human Behav. 73, 247–256 (2017)
Ajiboye, A.R., Abdullah-Arshah, R., Qin, H.: Using an enhanced feed-forward BP network for predictive model building from students’ data. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. 22(2), 169–175 (2016)
Wang, T., Mitrovic, A.: Using neural networks to predict student’s performance. Comput. Educ. 1, 969–973 (2002)
Fausett, L.V., Elwasif, W.: Predicting performance from test scores using backpropagation and counterpropagation. Neural Netw. 1994. IEEE World Congr. Comput. Intell. 5, 3398–3402 (1994)
Calvo-Flores, M.D., Galindo, E.G., Jiménez, M.C.P., Pérez, O.: Predicting students’ marks from Moodle logs using neural network models. In: Proceedings of IV International Conference Multimedia Information and Communication Technology Education, vol. 1, pp. 586–590, (2006)
Oladokun, V., Adebanjo, A.T., Charles-Owaba, O.: Predicting students’ academic performance using artificial neural network: a case study of an engineering course. Pac. J. Sci. Technol. 9(1), 72–79 (2009)
Sikder, M.F., Uddin, M.J., Halder, S.: Predicting students’ yearly performance using neural network: a case study of BSMRSTU. In: 2016 5th International Conference on Informatics, Electronics and Vision (ICIEV), pp. 524–529 (2016)
Sebastian, S.: Evaluating students performance by artificial neural network using WEKA. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 119(23), 975–8887 (2015)
Kardan, A.A., Sadeghi, H., Ghidary, S.S., Sani, M.R.F.: Prediction of student course selection in online higher education institutes using neural network. Comput. Educ. 65, 1–11 (2013)
Tang, S., Peterson, J.C., Pardos, Z.A.: Deep neural networks and how they apply to sequential education data. In: Proceedings of the Third (2016) ACM Conference on Learning @ Scale, pp. 321–324 (2016)
Piech, C., Spencer, J., Huang, J., Ganguli, S., Sahami, M., Guibas, L., Sohl-Dickstein, J., Academy, K.: Deep Knowledge Tracing. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 1–13 (2015)
Ognjanovic, I., Gasevic, D., Dawson, S.: Using institutional data to predict student course selections in higher education. Internet High. Educ. 29, 49–62 (2016)
Nakhkob, B., Khademi, M.: Predicted increase enrollment in higher education using neural networks and data mining techniques. J. Adv. Comput. Res. Q. 7(4), 2345–606 (2016)
Lino, A.D.P.: LABSQL: laboratório de ensino de SQL. Master’s Thesis, Programa de Pós-Graduação em Engenharia Elétrica, Universidade Federal do Pará (2007)
Ahadi, A., Behbood, V., Vihavainen, A., Prior, J., Lister, R.: Students syntactic mistakes in writing seven different types of SQL queries and its application to predicting students success. In: Proceedings of the 47th ACM Technical Symposium on Computing Science Education - SIGCSE ’16
Lino, A., Rocha, A., Sizo, A.: Virtual teaching and learning environments: automatic evaluation with symbolic regression. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 31(4), 2061–2072 (2016)
The Mathworks Inc., MATLAB - MathWorks, www.mathworks.com/products/matlab, http://www.mathworks.com/products/matlab/ (2016)
Basili, V.R., Rombach, H.D.: The TAME project: towards improvement-oriented software environments. Softw. Eng. IEEE Trans. 14(6), 758–773 (1988)
Halstead, M.H.: Elements of Software Science (Operating and Programming Systems Series), 7th edn. Elsevier, New York (1977)
McCabe, T.J.: A complexity measure. IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng. 2(4), 308–320 (1976)
Pressman, R.S.: Software Engineering: A Practitioner’s Approach. Palgrave Macmillan, Basingstoke (2005)
Calero, C., Piattini, M., Genero, M.: A case study with relational database metrics. In: Computer Systems and Applications, ACS/IEEE International Conference on 2001, pp. 485–487 (2001)
Piattini, M., Martínez, A.: Measuring for database programs maintainability. In: Piattini, M., Martínez, A. (eds.) Database and Expert Systems Applications, pp. 65–78. Springer, New York (2000)
Lino, A.D.P., Silva, A.S., Harb, M.P.A.A., Favero, E.L., Brito, S.R.: Avaliação automática de consultas SQL em ambiente virtual de ensino aprendizagem, \(2^{a}\) Conferência Ibérica de Sistemas e Tecnologias de Informação, pp. 89–100. CISTI, Porto, Portugal (2007)
Welty, C., Stemple, D.W.: Human factors comparison of a procedural and a nonprocedural query language. ACM Trans. Database Syst. 6(4), 626–649 (1981)
Kroenke, D.M.: Banco de dados: fundamentos, projeto e implementação, 6th ed. Livros Técnicos e Científicos (1999)
Dunlop, P., Smith, S.: Estimating key characteristics of the concrete delivery and placement process using linear regression analysis. Civ. Eng. Environ. Syst. 20(4), 273–290 (2003)
Fávero, L.P.L.: Análise de Dados: Modelos de Regressão com Excel®, Stata® e SPSS®.In: Rio de Janeiro (ed.):, vol. 1. (2015)
Møller, M.F.: A scaled conjugate gradient algorithm for fast supervised learning. Neural Netw. 6(4), 525–533 (1993)
Hagan, M.T., Menhaj, M.B.: Training feedforward networks with the Marquardt algorithm. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 5(6), 989–993 (1994)
Foresee, F.D., Hagan, M.T.: Gauss-Newton approximation to Bayesian learning in neural networks, 1997. In: International Conference on, 1997 vol. 3, pp. 1930–1935 (1997)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was conducted with CNPq support, National Council for Scientific and Technological Development - Brazil. We also appreciate the financial support of AISTI (Iberian Association for Information Systems and Technologies).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lino, A., Rocha, Á. & Sizo, A. Virtual teaching and learning environments: automatic evaluation with artificial neural networks. Cluster Comput 22 (Suppl 3), 7217–7227 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-017-1122-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-017-1122-y