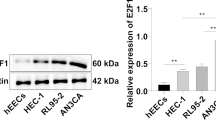
Abstract
Endometrial cancer is the most frequent malignancy of the female genital tract in western countries. Our group has previously characterized the upregulation of the transcription factor ETV5 in endometrial cancer with a specific and significant increase in those tumor stages associated with myometrial invasion. We have shown that ETV5 overexpression in Hec1A endometrial cancer cells induces epithelial to mesenchymal transition resulting in the acquisition of migratory and invasive capabilities. In the present work, we have identified Nidogen 1 (NID1) and Nuclear Protein 1 (NUPR1) as direct transcriptional targets of ETV5 in endometrial cancer cells. Inhibition of NID1 and NUPR1 in ETV5 overexpressing cells reduced cell migration and invasion in vitro and reduced tumor growth and dissemination in an orthotopic endometrial cancer model. Importantly, we confirmed a significant increase of NUPR1 and NID1 protein expression in the invasion front of the tumor compared to their paired superficial zone, concomitant to ETV5 overexpression. Altogether, we conclude that NID1 and NUPR1 are novel targets of ETV5 and are actively cooperating with ETV5 at the invasion front of the tumor in the acquisition of an invasive phenotype to jointly drive endometrial cancer invasion.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EMT:
-
Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition
- NID1:
-
Nidogen 1
- NUPR1:
-
Nuclear Protein 1
- H:
-
Hec1A cells
- HG:
-
Hec1A cells transfected with the pEGFP-C2 vector alone
- HGE:
-
Hec1A cells transfected with the pEGFP-hETV5
- HGEshNID1:
-
HGE with downregulation of NID1
- HGEshNUPR1:
-
HE with downregulation of NUPR1
- HGEshC:
-
HE with shControl
- ChIP:
-
Chromatin immunoprecipitation
- RTqPCR:
-
Real time quantitative PCR
References
Amant F, Moerman P, Neven P et al (2005) Endometrial cancer. Lancet 366:491–505. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67063-8
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A (2013) Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin 63:11–30. doi:10.3322/caac.21166
Colas E, Pedrola N, Devis L et al (2012) The EMT signaling pathways in endometrial carcinoma. Clin Transl Oncol Off Publ Fed Span Oncol Soc Natl Cancer Inst Mex 14:715–720. doi:10.1007/s12094-012-0866-3
Tanaka Y, Terai Y, Kawaguchi H et al (2013) Prognostic impact of EMT (epithelial-mesenchymal-transition)-related protein expression in endometrial cancer. Cancer Biol Ther 14:13–19. doi:10.4161/cbt.22625
Thiery JP (2002) Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer 2:442–454. doi:10.1038/nrc822
Yilmaz M, Christofori G (2009) EMT, the cytoskeleton, and cancer cell invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev 28:15–33. doi:10.1007/s10555-008-9169-0
Planagumà J, Gonzalez M, Doll A et al (2006) The up-regulation profiles of p21WAF1/CIP1 and RUNX1/AML1 correlate with myometrial infiltration in endometrioid endometrial carcinoma. Hum Pathol 37:1050–1057. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2006.03.007
Planagumà J, Abal M, Gil-Moreno A et al (2005) Up-regulation of ERM/ETV5 correlates with the degree of myometrial infiltration in endometrioid endometrial carcinoma. J Pathol 207:422–429. doi:10.1002/path.1853
Monge M, Colas E, Doll A et al (2007) ERM/ETV5 up-regulation plays a role during myometrial infiltration through matrix metalloproteinase-2 activation in endometrial cancer. Cancer Res 67:6753–6759. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-4487
Colas E, Muinelo-Romay L, Alonso-Alconada L et al (2012) ETV5 cooperates with LPP as a sensor of extracellular signals and promotes EMT in endometrial carcinomas. Oncogene 31:4778–4788. doi:10.1038/onc.2011.632
Creasman WT, Odicino F, Maisonneuve P et al (2006) Carcinoma of the corpus uteri. FIGO 26th annual report on the results of treatment in gynecological cancer. Int J Gynaecol Obstet Off Organ Int Fed Gynaecol Obstet 95(Suppl 1):S105–S143. doi:10.1016/S0020-7292(06)60031-3
Creasman W (2009) Revised FIGO staging for carcinoma of the endometrium. Int J Gynaecol Obstet Off Organ Int Fed Gynaecol Obstet 105:109. doi:10.1016/j.ijgo.2009.02.010
Llauradó M, Majem B, Castellví J et al (2012) Analysis of gene expression regulated by the ETV5 transcription factor in OV90 ovarian cancer cells identifies FOXM1 overexpression in ovarian cancer. Mol Cancer Res MCR 10:914–924. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-11-0449
Llauradó M, Abal M, Castellví J et al (2012) ETV5 transcription factor is overexpressed in ovarian cancer and regulates cell adhesion in ovarian cancer cells. Int J Cancer J Int Cancer 130:1532–1543. doi:10.1002/ijc.26148
Sandi MJ, Hamidi T, Malicet C et al (2011) p8 expression controls pancreatic cancer cell migration, invasion, adhesion, and tumorigenesis. J Cell Physiol 226:3442–3451. doi:10.1002/jcp.22702
Muinelo-Romay L, Colas E, Barbazan J et al (2011) High-risk endometrial carcinoma profiling identifies TGF-β1 as a key factor in the initiation of tumor invasion. Mol Cancer Ther 10:1357–1366. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-1019
Cabrera S, Llauradó M, Castellví J et al (2012) Generation and characterization of orthotopic murine models for endometrial cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis 29:217–227. doi:10.1007/s10585-011-9444-2
Chung AE, Dong LJ, Wu C, Durkin ME (1993) Biological functions of entactin. Kidney Int 43:13–19
Kopfstein L, Christofori G (2006) Metastasis: cell-autonomous mechanisms versus contributions by the tumor microenvironment. Cell Mol Life Sci CMLS 63:449–468. doi:10.1007/s00018-005-5296-8
De Wever O, Mareel M (2003) Role of tissue stroma in cancer cell invasion. J Pathol 200:429–447. doi:10.1002/path.1398
Talbot LJ, Bhattacharya SD, Kuo PC (2012) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition, the tumor microenvironment, and metastatic behavior of epithelial malignancies. Int J Biochem Mol Biol 3:117–136
Friedl P, Alexander S (2011) Cancer invasion and the microenvironment: plasticity and reciprocity. Cell 147:992–1009. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.11.016
Brannon KM, Million Passe CM, White CR et al (2007) Expression of the high mobility group A family member p8 is essential to maintaining tumorigenic potential by promoting cell cycle dysregulation in LbetaT2 cells. Cancer Lett 254:146–155. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2007.03.011
Hamidi T, Cano CE, Grasso D et al (2012) Nupr1-aurora kinase A pathway provides protection against metabolic stress-mediated autophagic-associated cell death. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 18:5234–5246. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0026
Goruppi S, Iovanna JL (2010) Stress-inducible protein p8 is involved in several physiological and pathological processes. J Biol Chem 285:1577–1581. doi:10.1074/jbc.R109.080887
Jiang WG, Davies G, Martin TA et al (2006) Com-1/p8 acts as a putative tumour suppressor in prostate cancer. Int J Mol Med 18:981–986
Du P, Ye L, Yang Y, Jiang WG (2013) Candidate of metastasis 1 regulates in vitro growth and invasion of bladder cancer cells. Int J Oncol 42:1249–1256. doi:10.3892/ijo.2013.1802
Aumailley M, Battaglia C, Mayer U et al (1993) Nidogen mediates the formation of ternary complexes of basement membrane components. Kidney Int 43:7–12
Hopf M, Göhring W, Kohfeldt E et al (1999) Recombinant domain IV of perlecan binds to nidogens, laminin-nidogen complex, fibronectin, fibulin-2 and heparin. Eur J Biochem FEBS 259:917–925
Joyce JA, Pollard JW (2009) Microenvironmental regulation of metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer 9:239–252. doi:10.1038/nrc2618
Vasseur S, Hoffmeister A, Garcia-Montero A et al (2002) p8-deficient fibroblasts grow more rapidly and are more resistant to adriamycin-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 21:1685–1694. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205222
Acknowledgments
We thank Marie-Noé Lavaut for technical assistance. This work has been supported by the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation (SAF2011-26548), the Spanish Ministry of Health (RD12/0036/0035), the AECC (Grupos Estables de Investigacion 2011—AECC- GCB 110333 REVE), the Fundació La Marató TV3 (2/C/2013), the CIRIT Generalitat de Catalunya (2014 SGR 1330) and the European Commission EU FP7-PEOPLE-2010-IRSES (PROTBIOFLUID-269285). La Ligue Contre le Cancer, INCa, Canceropole PACA, DGOS (labellisation SIRIC) and INSERM to JLI. EM is recipient of a fellowship from the Ministry of Education, Culture and Sport (Spain) (FPU12/05571).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Jaume Reventós and Anna Ruiz have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pedrola, N., Devis, L., Llauradó, M. et al. Nidogen 1 and Nuclear Protein 1: novel targets of ETV5 transcription factor involved in endometrial cancer invasion. Clin Exp Metastasis 32, 467–478 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-015-9720-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-015-9720-7