Abstract
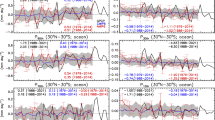
On 21–22 July 2012, torrential rains hit North China, with the daily precipitation record at Beijing station reaching 160.6 mm; this event is named the Beijing 7–21 case. This paper assesses the likelihood of the occurrence of local torrential rains, such as the Beijing 7–21 case, from the perspective of climate variability. In particular, the influence of the Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO) is assessed. There were five extreme events, with daily precipitation records equal to or larger than 160.6 mm, at Beijing station during the period 1951–2012; all of these events happened during negative phases of the PDO. The present analysis indicates that precipitation events more extreme than the Beijing 7–21 case should happen more than once per decade during negative phases of the PDO, but only about once every four decades during positive PDO phases. The negative phase of the PDO is found to be associated with a much greater probability of daily records of southerly winds in North China during summer. Strong southerly summer monsoons are deemed favorable for increasing the occurrence of local extreme rainfall over North China.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
CMA (2013) China climate bulletin 2012. China Meteorological Administration pp 54
Chung C, Ramanathan V (2007) Relationship between trends in land precipitation and tropical SST gradient. Geophys Res Lett 34. doi:10.1029/2007GL030491
Coles S, Bawa J, Trenner L, et al. (2001) An introduction to statistical modeling of extreme values. Springer, London, pp. 54–57
Dai AG (2012) The influence of the inter-decadal Pacific oscillation on US precipitation during 1923–2010. Clim Dyn 41:633–646. doi:10.1007/s00382-012-1446-5
Deser C, Phillips AS, Hurrell JW (2004) Pacific interdecadal climate variability: Linkages between the tropics and the North Pacific during boreal winter since 1900. J Clim 17(16):3109–3124. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(2004)017 < 3109:PICVLB > 2.0.CO;2
Dole R, Hoerling M, Perlwitz J, Eischeid J, Pegion P, Zhang T, Quan XW, Xu TY, Murray D (2011) Was there a basis for anticipating the 2010 Russian heat wave? Geophys Res Lett 38:L06702. doi:10.1029/2010GL046582
Dong B, Dai A (2015) The influence of the interdecadal Pacific oscillation on temperature and precipitation over the globe. Clim Dyn. doi:10.1007/s00382-015-2500-x
Harris I, Jones PD, Osborn TJ, et al. (2014) Updated high-resolution grids of monthly climatic observations–the CRU TS3. 10 dataset. Int J Climatol 34(3):623–642. doi:10.1002/joc.3711
Hoerling M, Hurrell J, Eischeid J (2006) Detection and attribution of 20th century northern and southern African rainfall change. J Clim 19:3989–4008. doi:10.1175/J CLI384 2.1
Huang NE, Shen Z, Long SR, et al. (1998) The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and nonstationary time series analysis. Proc Roy Soc London Series A 454:903–995
Huang NE, Wu ZH (2008) A review on Hilbert-Huang transform: method and its applications to geophysical studies. Rev Geophys 46:RG2006. doi:10.1029/2007RG000228
Huang G, Yan ZW (1999) The east Asia summer monsoon circulation anomaly index and its interannual variations. Chin Sci Bull 44:421–424. doi:10.1007/BF02885855
Kalnay E, Kanamitsu M, Kistler R, et al. (1996) The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 77:437–470. doi:10.1175/1520-0477(1996)077<0437:TNYRP>2.0.CO;2
Katz RW, Parlange MB, Naveau P (2002) Statistics of extremes in hydrology. Adv Water Resour 25:1287–1304. doi:10.1016/S0309-1708(02)00056-8
Li N, Ran LK, Zhou YS, Gao ST (2013) Diagnosis of the frontogenesis and slantwise vorticity development caused by the deformation in the Beijing “7–21” torrential rainfallevent. Acta Metall Sin 71:593–605 in Chinese. doi:10.1167/qxxb2013.065
Liu HW, Zhou TJ, Zhu YX, Lin YH (2012) The strengthening east Asia summer monsoon since the early 1990s. Chin Sci Bull 57:1553–1558. doi:10.1007/s11434-012-4991-8
Ma ZG, Shao LJ (2006) Relationship between dry/wet variation and the Pacific decade oscillation (PDO) in northern China during the last 100 years. Chinese J Atmos Sci 30(3):464–474(in Chinese). doi:10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2006.03.10
Ma ZG (2007) The interdecadal dry/wet trend and shift of north China and their relationship to the Pacific decadal oscillation (PDO). Chin Sci Bull 52(15):2130–2139(in Chinese)
Mantua NJ, Hare SR, Zhang Y, Wallace JM, Francis RC (1997) A Pacific interdecadal climate oscillation with impacts on salmon production. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 78:1069–1079. doi:10.1175/15200477(1997)078<1069:APICOW>2.0.CO;2
Mantua NJ, Hare SR (2002) The Pacific decadal oscillation. J Oceanogr 58:35–44. doi:10.1023/A:1015820616384
Pall P, Aina T, Stone DA, Stott PA, Nozawa T, Hilberts AGJ, Lohmann D, Allen MR (2011) Anthropogenic greenhouse gas contribution to flood risk in England and Wales in autumn 2000. Nature 470:382–385. doi:10.1038/nature09762
Pei L, Yan ZW, Yang H (2015) Multidecadal variability of dry/wet patterns in eastern China and their relationship with the Pacific decadal oscillation in the last 413 years. Chin Sci Bull 60(1):97–108(in Chinese). doi:10.1360/N972014-00790
Perlwitz J, Hoerling M, Eischeid J, Xu TY, Kumar A (2009) A strong bout of natural cooling in 2008. Geophys Res Lett 36:L23706. doi:10.1029/2009GL041188
Peterson TC, Stott PA, Herring S (2012) Explaining extreme events of 2011 from a climate perspective. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 93(7):1041–1067. doi:10.1175/BAMS-D-12-00021.1
Peterson TC, Hoerling MP, Stott PA, Gerring SC (2013) Explaining extreme events of 2012 from a climate perspective. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 94(9):S1–S74. doi:10.1175/BAMS-D-13-00085.1
Power ST, Casey T, Folland CK, Colman MV (1999) Inter-decadal modulation of the impact of ENSO on Australia. Clim Dyn 15:319–324. doi:10.1007/s003820050284
Qian C (2009) A new method for the formation of climate anomaly reference frame and its validation and application (in Chinese). Doctoral Dissertation. Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Science, Beijing, pp. 13–24
Qian C, Wu ZH, Fu ZB, Wang DX (2011) On changing El Nino: a view from time-varying annual cycle, interannual variability, and mean state. J Clim 24:6486–6500. doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-10-05012.1
Qian C, Zhou TJ (2014) Multidecadal variability of north China aridity and its relationship to PDO during 1900–2010. J Clim 27(3):1210–1222. doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-13-00235.1
Quan ML, Liu HW, Zhu YX, Cheng L (2013) Study of the dynamic effects of the upper-level jet stream on the Beijing rainstorm of 21 July 2012. Acta Metall Sin 71(6):1012–1019 in Chinese. doi:10.1167/qxxb2013.092
Rotstayn LD, Lohmann U (2002) Tropical rainfall trends and the indirect aerosol effect. J Clim 15:2103–2116. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(2002)015 < 2103:TRTATI > 2.0.CO;2
Schneider UB, Andreas B, Peter F, Anja MC, Bruno R, Markus Z (2011) GPCC Full Data Reanalysis Version 6.0 at 0.5°: Monthly land-surface precipitation from rain-gauges built on GTS-based and historic data. doi:10.5676/DWD_GPCC/FD_M_V6_050
Si D, Ding YH, Liu YJ (2009) Decadal northward shift of the meiyu belt and the possible cause. Chin Sci Bull 54:4742–4748. doi:10.1007/s11434-009-0385-y
Sun JS, He N, Wang GR, Chen MX, Liao XN, Wang H (2012) Preliminary analysis on synoptic configuration evolvement and mechanism of a torrential rain occurring in Beijing on 21 July 2012. Torrential Rain Disaster 31(3):218–225(in Chinese)
Solomon S et al. (2007) Climate change 2007-the physical science basis: Working group I contribution to the fourth assessment report of the IPCC (Vol. 4). Cambridge University Press
Tu K, Yan Z, Wang Y (2011) A spatial cluster analysis of heavy rains in China. Atmos Oceanic Sci Lett 4:36–40
Wang YF, Wang B, Oh JH (2001) Impacts of the preceding El Nino on the East Asian summer atmospheric circulation. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 79:575–588. doi:10.2151/jmsj.79.575
Wu AM, Ni YQ (1997) The influence of Tibetan plateau on the interannual variability of Asian monsoon. Adv Atmos Sci 14:491–504
Wu Z, Huang NE, Long SR, et al. (2007) On the trend, detrending, and variability of nonlinear and nonstationary time series. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(38):14889–14894. doi:10.1073/pnas.0701020104
Wu Z, Huang NE (2009) Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: a noise-assisted data analysis method. Adv Adapt Data Anal 1:1–41. doi:10.1142/S1793536909 000047
Xia JJ, Tu K, Yan ZW, Qi YJ (2015) The super-heat wave in eastern China during July–August 2013: a perspective of climate change. Int J Climatol. doi:10.1002/joc.4424
Yu L, Tore F, Odd HO, et al. (2014) Modulation of the Pacific decadal oscillation on the summer precipitation over east China: a comparisonof observations to 600-years control run of Bergen climate model. Clim Dyn. doi:10.1007/s00382-014-2141-5
Zhao LN, Yang XD, Qi D, Liu RH (2007) The analysis of precipitation and flooding features in the huaihe river basin during the summer of 2007. Clim Environ Res 12:728–737(in Chinese). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1006-9585.2007.06.003
Zhao YY, QH Z, Du Y, Jiang M, Zhang JP (2013) Objective analysis of circulation extremes during the 21 July 2012 torrential rain in Beijing. Acta Metall Sin 27(5):626–635. doi:10.1007/s13351-013-0507-y
Zhang J, Wang DY, Tian H, Zhu HF, Chen XH (2008) Comparative analysis of atmospheric circulation characteristic over huaihe river during the severe precipitation between 2003 and 2005. Sci Meteorol Sin 28:402–408(in Chinese). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1009-0827.2008.04.008
Zhang X, Zwiers FW, Hegerl GC, et al. (2007) Detection of human influence on twentieth-century precipitation trends. Nature 448(7152):461–465. doi:10.1038/nature06025
Zhang Y, Wallace JM, Battisti DS (1997) ENSO-like interdecadal variability: 1900–1993. J Clim 10:1004–1020. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(1997)010 < 1004:ELIV > 2.0.CO;2
Zhou TJ, Gong DY, Li J, Li B (2009) Detecting and understanding the multi-decadal variability of the east Asian summer monsoon - recent progress and state of affairs. Meteorol Z 18:455–467. doi:10.1127/0941-2948/2009/0396
Zhou TJ, Song FF, Lin RP, et al. (2013) The 2012 north China floods: explaining an extreme rainfall event in the context of a long-term drying tendency [in “explaining extreme event of 2012 from a climate perspective”]. Bull Amer Meteor Sci 94:S49–S51
Zhu KZ (1934) Southeast monsoon and precipitation over China. Acta Geograph Sin 1:1–28(in Chinese)
Zhu YL, Wang HJ, Zhou W, Ma JH (2011) Recent changes in the summer precipitation pattern in east China and the background circulation. Clim Dyn 36:1463–1473. doi:10.1007/s00382-010-0852-9
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (Grant No.2012CB956200), the Special Fund for Public Welfare Industry (meteorology) (Grant No.GYHY201306026), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.41405082 and 51339004) and Beijing Natural Science Foundation (No.8144055).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of a Special Issue on “Decadal Scale Drought in Arid Regions” edited by Zong-Liang Yang and Zhuguo Ma
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pei, L., Xia, J., Yan, Z. et al. Assessment of the Pacific decadal oscillation’s contribution to the occurrence of local torrential rainfall in north China. Climatic Change 144, 391–403 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-016-1610-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-016-1610-8