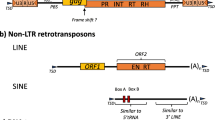
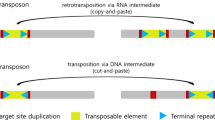
Abstract
Transposable elements are mobile genetic elements that have successfully populated eukaryotic genomes and show diversity in their structure and transposition mechanisms. Although first viewed solely as selfish, transposable elements are now known as important vectors to drive the adaptation and evolution of their host genome. Transposable elements can affect host gene structures, gene copy number, gene expression, and even as a source for novel genes. For example, a number of transposable element sequences have been co-opted to contribute to evolutionary innovation, such as the mammalian placenta and the vertebrate immune system. In plants, the need to adapt rapidly to changing environmental conditions is essential and is reflected, as will be discussed, by genome plasticity and an abundance of diverse, active transposon families. This review focuses on transposable elements in plants, particularly those that have beneficial effects on the host. We also emphasize the importance of having proper tools to annotate and classify transposons to better understand their biology.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Ac/Spm :
-
Activator/suppressor-mutator
- Bs1 :
-
Barren sterile1
- cDNA:
-
Complementary DNA
- CNE:
-
Conserved non-coding element
- DBD:
-
DNA-binding domain
- dsRNA:
-
Double-stranded RNA
- DTE:
-
Domesticated transposable element
- FAR1:
-
Far-red impaired response 1
- FHL:
-
FHY1-like
- FHY1:
-
Far-red elongated hypocotyl 1
- FHY3:
-
Far-red elongated hypocotyl 3
- hAT :
-
hobo/Ac/Tam
- HY5:
-
Elongated hypocotyl 5
- IN:
-
Integrase
- KI :
-
KAONASHI
- LINE:
-
Long interspersed element
- LTR:
-
Long terminal repeats
- MITE:
-
Miniature inverted transposable element
- MULE:
-
Mutator-like element
- MUG:
-
MUSTANG
- ORF:
-
Open reading frame
- PB1:
-
Phox and Bem1
- RdDM:
-
RNA-directed DNA methylation
- RH:
-
Ribonuclease H
- RT:
-
Reverse transcriptase
- SINE:
-
Short interspersed element
- TE:
-
Transposable element
- TIR:
-
Terminal inverted repeat
- TRIM:
-
Terminal-repeat retrotransposon in miniature
- ULP:
-
Ubiquitin-like protease
References
Agrawal A, Eastman QM, Schatz DG (1998) Transposition mediated by RAG1 and RAG2 and its implications for the evolution of the immune system. Nature 394:744–751
Agren JA, Wright SI (2011) Co-evolution between transposable elements and their hosts: a major factor in genome size evolution? Chromosom Res 19:777–786
Arabidopsis Genome I (2000) Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 408:796–815
Bennett MDAIJL (2011) Nuclear DNA amounts in angiosperms: targets, trends and tomorrow. Ann Bot 107:467–590
Bourque G, Leong B, Vega VB, Chen X, Lee YL, Srinivasan KG, Chew JL, Ruan Y, Wei CL, Ng HH, Liu ET (2008) Evolution of the mammalian transcription factor binding repertoire via transposable elements. Genome Res 18:1752–1762
Bundock P, Hooykaas P (2005) An Arabidopsis hAT-like transposase is essential for plant development. Nature 436:282–284
Bureau TE, White SE, Wessler SR (1994) Transduction of a cellular gene by a plant retroelement. Cell 77:479–480
Cao J, Schneeberger K, Ossowski S, Gunther T, Bender S, Fitz J, Koenig D, Lanz C, Stegle O, Lippert C, Wang X, Ott F, Muller J, Alonso-Blanco C, Borgwardt K, Schmid KJ, Weigel D (2011) Whole-genome sequencing of multiple Arabidopsis thaliana populations. Nat Genet 43:956–963
Castel SE, Martienssen RA (2013) RNA interference in the nucleus: roles for small RNAs in transcription, epigenetics and beyond. Nat Rev Genet 14:100–112
Cordaux R, Batzer MA (2009) The impact of retrotransposons on human genome evolution. Nat Rev Genet 10:691–703
Cornelis G, Heidmann O, Bernard-Stoecklin S, Reynaud K, Veron G, Mulot B, Dupressoir A, Heidmann T (2012) Ancestral capture of syncytin-Car1, a fusogenic endogenous retroviral envelope gene involved in placentation and conserved in Carnivora. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:E432–E441
Cowan RK, Hoen DR, Schoen DJ, Bureau TE (2005) MUSTANG is a novel family of domesticated transposase genes found in diverse angiosperms. Mol Biol Evol 22:2084–2089
de la Chaux N, Tsuchimatsu T, Shimizu KK, Wagner A (2012) The predominantly selfing plant Arabidopsis thaliana experienced a recent reduction in transposable element abundance compared to its outcrossing relative Arabidopsis lyrata. Mob DNA 3:2
Doolittle WF, Sapienza C (1980) Selfish genes, the phenotype paradigm and genome evolution. Nature 284:601–603
Dooner HK, Weil CF (2007) Give-and-take: interactions between DNA transposons and their host plant genomes. Curr Opin Genet Dev 17:486–492
El Baidouri M, Panaud O (2013) Comparative genomic paleontology across plant kingdom reveals the dynamics of TE-driven genome evolution. Genome Biol Evol 5:954–965
Elrouby N, Bureau TE (2010) Bs1, a new chimeric gene formed by retrotransposon-mediated exon shuffling in maize. Plant Physiol 153:1413–1424
Feschotte C, Pritham EJ (2007) DNA transposons and the evolution of eukaryotic genomes. Annu Rev Genet 41:331–368
Flagel LE, Wendel JF (2009) Gene duplication and evolutionary novelty in plants. New Phytol 183:557–564
Fu Y, Kawabe A, Etcheverry M, Ito T, Toyoda A, Fujiyama A, Colot V, Tarutani Y, Kakutani T (2013) Mobilization of a plant transposon by expression of the transposon-encoded anti-silencing factor. EMBO J 32:2407–2417
Fugmann SD (2010) The origins of the Rag genes–from transposition to V(D)J recombination. Semin Immunol 22:10–16
Gaut BS, Wright SI, Rizzon C, Dvorak J, Anderson LK (2007) Recombination: an underappreciated factor in the evolution of plant genomes. Nat Rev Genet 8:77–84
Gould SJ, Lloyd EA (1999) Individuality and adaptation across levels of selection: how shall we name and generalize the unit of Darwinism? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:11904–11909
Haudry A, Platts AE, Vello E, Hoen DR, Leclercq M, Williamson RJ, Forczek E, Joly-Lopez Z, Steffen JG, Hazzouri KM, Dewar K, Stinchcombe JR, Schoen DJ, Wang X, Schmutz J, Town CD, Edger PP, Pires JC, Schumaker KS, Jarvis DE, Mandakova T, Lysak MA, van den Bergh E, Schranz ME, Harrison PM, Moses AM, Bureau TE, Wright SI, Blanchette M (2013) An atlas of over 90,000 conserved noncoding sequences provides insight into crucifer regulatory regions. Nat Genet 45:891–898
Hoen DR, Bureau T (2012) Transposable element exaptation in plants. In: Grandbastien MA, Casacuberta JM (eds) Plant transposable elements. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Heidelberg
Hoen DR, Bureau TE (2014) Discovery of novel genes derived from transposable elements using integrative genomic analysis. In preparation
Hoen DR, Park KC, Elrouby N, Yu Z, Mohabir N, Cowan RK, Bureau TE (2006) Transposon-mediated expansion and diversification of a family of ULP-like genes. Mol Biol Evol 23:1254–1268
Hollister JD, Gaut BS (2007) Population and evolutionary dynamics of Helitron transposable elements in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Biol Evol 24:2515–2524
Hu TT, Pattyn P, Bakker EG, Cao J, Cheng JF, Clark RM, Fahlgren N, Fawcett JA, Grimwood J, Gundlach H, Haberer G, Hollister JD, Ossowski S, Ottilar RP, Salamov AA, Schneeberger K, Spannagl M, Wang X, Yang L, Nasrallah ME, Bergelson J, Carrington JC, Gaut BS, Schmutz J, Mayer KF, van de Peer Y, Grigoriev IV, Nordborg M, Weigel D, Guo YL (2011) The Arabidopsis lyrata genome sequence and the basis of rapid genome size change. Nat Genet 43:476–481
Hudson M, Ringli C, Boylan MT, Quail PH (1999) The FAR1 locus encodes a novel nuclear protein specific to phytochrome A signaling. Genes Dev 13:2017–2027
Jiang N, Bao Z, Zhang X, Eddy SR, Wessler SR (2004) Pack-MULE transposable elements mediate gene evolution in plants. Nature 431:569–573
Joly-Lopez Z, Forczek E, Hoen DR, Juretic N, Bureau TE (2012) A gene family derived from transposable elements during early angiosperm evolution has reproductive fitness benefits in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Genet 8:e1002931
Kaneko-Ishino T, Ishino F (2012) The role of genes domesticated from LTR retrotransposons and retroviruses in mammals. Front Microbiol 3:262
Kapitonov VV, Jurka J (2001) Rolling-circle transposons in eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:8714–8719
Kapitonov VV, Jurka J (2007) Helitrons on a roll: eukaryotic rolling-circle transposons. Trends Genet 23:521–529
Kawasaki S, Nitasaka E (2004) Characterization of Tpn1 family in the Japanese morning glory: En/Spm-related transposable elements capturing host genes. Plant Cell Physiol 45:933–944
Kazazian HH Jr (2004) Mobile elements: drivers of genome evolution. Science 303:1626–1632
Knip M, de Pater S, Hooykaas PJ (2012) The SLEEPER genes: a transposase-derived angiosperm-specific gene family. BMC Plant Biol 12:192
Kumar A, Bennetzen JL (1999) Plant retrotransposons. Annu Rev Genet 33:479–532
Leitch AR, Leitch IJ (2008) Genomic plasticity and the diversity of polyploid plants. Science 320:481–483
Lerat E (2010) Identifying repeats and transposable elements in sequenced genomes: how to find your way through the dense forest of programs. Heredity (Edinb) 104:520–533
Levin HL, Moran JV (2011) Dynamic interactions between transposable elements and their hosts. Nat Rev Genet 12:615–627
Li X, Kahveci T, Settles AM (2008) A novel genome-scale repeat finder geared towards transposons. Bioinformatics 24:468–476
Li G, Siddiqui H, Teng Y, Lin R, Wan XY, Li J, Lau OS, Ouyang X, Dai M, Wan J, Devlin PF, Deng XW, Wang H (2011) Coordinated transcriptional regulation underlying the circadian clock in Arabidopsis. Nat Cell Biol 13:616–622
Lin R, Wang H (2004) Arabidopsis FHY3/FAR1 gene family and distinct roles of its members in light control of Arabidopsis development. Plant Physiol 136:4010–4022
Lin R, Ding L, Casola C, Ripoll DR, Feschotte C, Wang H (2007) Transposase-derived transcription factors regulate light signaling in Arabidopsis. Science 318:1302–1305
Lin R, Teng Y, Park HJ, Ding L, Black C, Fang P, Wang H (2008) Discrete and essential roles of the multiple domains of Arabidopsis FHY3 in mediating phytochrome A signal transduction. Plant Physiol 148:981–992
Lisch D (2009) Epigenetic regulation of transposable elements in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 60:43–66
Lisch DR, Freeling M, Langham RJ, Choy MY (2001) Mutator transposase is widespread in the grasses. Plant Physiol 125:1293–1303
Madlung A, Tyagi AP, Watson B, Jiang H, Kagochi T, Doerge RW, Martienssen R, Comai L (2005) Genomic changes in synthetic Arabidopsis polyploids. Plant J 41:221–230
Mcclintock B (1950) The origin and behavior of mutable loci in maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 36:344–355
Mcclintock B (1984) The significance of responses of the genome to challenge. Science 226:792–801
Michael TP, Jackson S (2013) The first 50 plant genomes. Plant Genome 6:0
Miller JT, Dong F, Jackson SA, Song J, Jiang J (1998) Retrotransposon-related DNA sequences in the centromeres of grass chromosomes. Genetics 150:1615–1623
Miller WJ, Hagemann S, Reiter E, Pinsker W (1992) P-element homologous sequences are tandemly repeated in the genome of Drosophila guanche. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89(9):4018–4022
Ono R, Nakamura K, Inoue K, Naruse M, Usami T, Wakisaka-Saito N, Hino T, Suzuki-Migishima R, Ogonuki N, Miki H, Kohda T, Ogura A, Yokoyama M, Kaneko-Ishino T, Ishino F (2006) Deletion of Peg10, an imprinted gene acquired from a retrotransposon, causes early embryonic lethality. Nat Genet 38:101–106
Orgel LE, Crick FH (1980) Selfish DNA: the ultimate parasite. Nature 284:604–607
Ouyang X, Li J, Li G, Li B, Chen B, Shen H, Huang X, Mo X, Wan X, Lin R, Li S, Wang H, Deng XW (2011) Genome-wide binding site analysis of FAR-RED ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL3 reveals its novel function in Arabidopsis development. Plant Cell 23:2514–2535
Pardue ML, Debaryshe PG (2011) Retrotransposons that maintain chromosome ends. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:20317–20324
Parisod C, Alix K, Just J, Petit M, Sarilar V, Mhiri C, Ainouche M, Chalhoub B, Grandbastien MA (2010) Impact of transposable elements on the organization and function of allopolyploid genomes. New Phytol 186:37–45
Pereira V (2004) Insertion bias and purifying selection of retrotransposons in the Arabidopsis thaliana genome. Genome Biol 5:R79
Raizada M, Benito M, Walbot V (2001) The MuDR transposon terminal inverted repeat contains a complex plant promoter directing distinct somatic and germinal programs. Plant J 25:79–91
Rudenko GN, Walbot V (2001) Expression and post-transcriptional regulation of maize transposable element MuDR and its derivatives. Plant Cell 13:553–570
Saha S, Bridges S, Magbanua ZV, Peterson DG (2008) Computational approaches and tools used in identification of dispersed repetitive DNA sequences. Trop Plant Biol 1:85–96
Schnable PS, Ware D, Fulton RS, Stein JC, Wei F, Pasternak S, Liang C, Zhang J, Fulton L, Graves TA, Minx P, Reily AD, Courtney L, Kruchowski SS, Tomlinson C, Strong C, Delehaunty K, Fronick C, Courtney B, Rock SM, Belter E, Du F, Kim K, Abbott RM, Cotton M, Levy A, Marchetto P, Ochoa K, Jackson SM, Gillam B, Chen W, Yan L, Higginbotham J, Cardenas M, Waligorski J, Applebaum E, Phelps L, Falcone J, Kanchi K, Thane T, Scimone A, Thane N, Henke J, Wang T, Ruppert J, Shah N, Rotter K, Hodges J, Ingenthron E, Cordes M, Kohlberg S, Sgro J, Delgado B, Mead K, Chinwalla A, Leonard S, Crouse K, Collura K, Kudrna D, Currie J, He R, Angelova A, Rajasekar S, Mueller T, Lomeli R, Scara G, Ko A, Delaney K, Wissotski M, Lopez G, Campos D, Braidotti M, Ashley E, Golser W, Kim H, Lee S, Lin J, Dujmic Z, Kim W, Talag J, Zuccolo A, Fan C, Sebastian A, Kramer M, Spiegel L, Nascimento L, Zutavern T, Miller B, Ambroise C, Muller S, Spooner W, Narechania A, Ren L, Wei S, Kumari S, Faga B, Levy MJ, Mcmahan L, van Buren P, Vaughn MW et al (2009) The B73 maize genome: complexity, diversity, and dynamics. Science 326:1112–1115
Sinzelle L, Izsvak Z, Ivics Z (2009) Molecular domestication of transposable elements: from detrimental parasites to useful host genes. Cell Mol Life Sci 66:1073–1093
Wessler SR, Bureau TE, White SE (1995) LTR-retrotransposons and MITEs: important players in the evolution of plant genomes. Curr Opin Genet Dev 5:814–821
Whitelam GC, Johnson E, Peng J, Carol P, Anderson ML, Cowl JS, Harberd NP (1993) Phytochrome A null mutants of Arabidopsis display a wild-type phenotype in white light. Plant Cell 5:757–768
Wicker T (2012) So many repeats and so little time: how to classify transposable elements. In: Grandbastien MA, Casacuberta JM (eds) Plant transposable elements. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Heidelberg
Wicker T, Sabot F, Hua-Van A, Bennetzen JL, Capy P, Chalhoub B, Flavell A, Leroy P, Morgante M, Panaud O, Paux E, Sanmiguel P, Schulman AH (2007) A unified classification system for eukaryotic transposable elements. Nat Rev Genet 8:973–982
Witte CP, Le QH, Bureau T, Kumar A (2001) Terminal-repeat retrotransposons in miniature (TRIM) are involved in restructuring plant genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:13778–13783
Xie X, Kamal M, Lander ES (2006) A family of conserved noncoding elements derived from an ancient transposable element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:11659–11664
Yamasaki K, Kigawa T, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yokoyama S (2013) DNA-binding domains of plant-specific transcription factors: structure, function, and evolution. Trends Plant Sci 18:267–276
Yang L, Bennetzen JL (2009) Distribution, diversity, evolution, and survival of Helitrons in the maize genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:19922–19927
Ziolkowski PA, Koczyk G, Galganski L, Sadowski J (2009) Genome sequence comparison of Col and Ler lines reveals the dynamic nature of Arabidopsis chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res 37:3189–3201
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editors: Martin Lysak and Paul Fransz.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joly-Lopez, Z., Bureau, T.E. Diversity and evolution of transposable elements in Arabidopsis . Chromosome Res 22, 203–216 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-014-9418-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-014-9418-8