Abstract
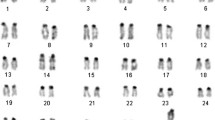
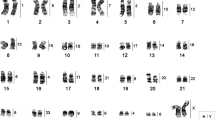
To better understand the evolution of genome organization of eutherian mammals, comparative maps based on chromosome painting have been constructed between human and representative species of three eutherian orders: Xenarthra, Pholidota, and Eulipotyphla, as well as between representative species of the Carnivora and Pholidota. These maps demonstrate the conservation of such syntenic segment associations as HSA3/21, 4/8, 7/16, 12/22, 14/15 and 16/19 in Eulipotyphla, Pholidota and Xenarthra and thus further consolidate the notion that they form part of the ancestral karyotype of the eutherian mammals. Our study has revealed many potential ancestral syntenic associations of human chromosomal segments that serve to link the families as well as orders within the major superordinial eutherian clades defined by molecular markers. The HSA2/8 and 7/10 associations could be the cytogenetic signatures that unite the Xenarthrans, while the HSA1/19p could be a putative signature that links the Afrotheria and Xenarthra. But caution is required in the interpretation of apparently shared syntenic associations as detailed analyses also show examples of apparent convergent evolution that differ in breakpoints and extent of the involved segments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amrine-Madsen H, Koepfli KP, Wayne RK, Springer MS (2003) A new phylogenetic marker, apolipoprotein B, provides compelling evidence for eutherian relationships. Mol Phylogenet Evol 28: 225–240.
Arnason U, Adegoke JA, Bodin K et al. (2002) Mammalian mitogenomic relationships and the root of the eutherian tree. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99: 8151–8156.
Bielec PE, Gallagher DS, Womack JE, Busbee DL (1998) Homologies between human and dolphin chromosomes detected by heterologous chromosome painting. Cytogenet Cell Genet 81: 18–25.
Biltueva LS, Yang F, Vorobieva NV, Graphodatsky AS (2004) Comparative map between the domestic pig and dog. Mamm Genome 15: 809–818.
Brinkmeyer-Langford C, Raudsepp T, Lee EJ et al. (2005) A high-resolution physical map of equine homologs of HSA19 shows divergent evolution compared with other mammals. Mamm Genome 16: 631–649.
Cavagna P, Menotti A, Stanyon R (2000) Genomic homology of the domestic ferret with cats and humans. Mamm Genome 11: 866–870.
Chowdhary BP, Raudsepp T, Frönicke L, Scherthan H (1998) Emerging patterns of comparative genome organization in some mammalian species as revealed by Zoo-FISH. Genome Res 8: 577–589.
Delsuc F, Scally M, Madsen O et al. (2002) Molecular phylogeny of living xenarthrans and the impact of character and taxon sampling on the placental tree rooting. Mol Biol Evol 19: 1656–1671.
Dixkens C, Klett C, Bruch J et al. (1998) Zoo-FISH analysis in insectivores: ‘Evolution extols the virtue of the status quo’. Cytogenet Cell Genet 80: 61–67.
Dobigny G, Yang F, O'Brien PCM et al. (2005) Low rate of genomic repatterning in Xenarthra inferred from chromosome painting data. Chromosome Res 13: 651–663.
Douady CJ, Chatelier PI, Madsen O et al. (2002) Molecular phylogenetic evidence confirming the Eulipotyphla concept and in support of hedgehogs as the sister group to shrews. Mol Phylogenet Evol 25: 200–209.
Frönicke L (2005) Origins of primate chromosomes – as delineated by Zoo-FISH and alignments of human and mouse draft genome sequences. Cytogenet Genome Res 108: 122–138.
Frönicke L, Müller-Navia J, Romanakis K, Scherthan H (1997) Chromosomal homeologies between human, harbor seal (Phoca vitulina) and the putative ancestral carnivore karyotype revealed by Zoo-FISH. Chromosoma 106: 108–113.
Frönicke L, Wienberg J, Stone G, Adams L, Stanyon R (2003) Towards the delineation of the ancestral eutherian genome organization: comparative genome maps of human and the African elephant (Loxodonta africana) generated by chromosome painting. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 270: 1331–1340.
Graphodatsky AS, Yang F, Serdukova N, Perelman P, Zhdanova NS, Ferguson-Smith MA (2000) Dog chromosome-specific paints reveal evolutionary inter- and intrachromosomal rearrangements in the American mink and human. Cytogenet Cell Genet 90: 275–278.
Haig D (1999) A brief history of human autosomes. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B 354: 1447–1470.
Haig D (2005) The complex history of distal human chromosome 1q. Genomics 86: 767–770.
Itoh T, Watanabe T, Ihara N et al. (2005) A comprehensive radiation hybrid map of the bovine genome comprising 5593 loci. Genomics 85: 413–424.
Lahbib-Mansais Y, Karlskov-Mortensen P, Mompart F et al. (2005) A high-resolution comparative map between pig chromosome 17 and human chromosomes 4, 8, and 20: identification of synteny breakpoints. Genomics 86: 405–413.
Li T, O'Brien PCM, Biltueva L et al. (2004) Evolution of genome organizations of squirrels (Sciuridae) revealed by cross-species chromosome painting. Chromosome Res 12: 317–335.
Lin YH, McLenachan PA, Gore AR et al. (2002) Four new mitochondrial genomes and the increased stability of evolutionary trees of mammals from improved taxon sampling. Mol Biol Evol 19: 2060–2070.
Madsen O, Scally M, Douady CJ et al. (2001) Parallel adaptive radiations in two major clades of placental mammals. Nature 409: 610–614.
McKenna MC (1975) Toward a phylogenetic classification of the Mammalia. In: Luckett WP, Szalay FS, eds. Phylogeny of the Primates: A Multidisciplinary Approach. New York: Plenum Press, pp. 21–46.
Müller S, O'Brien PCM, Ferguson-Smith MA, Wienberg J (1997) Reciprocal chromosome painting between human and prosimians (Eulemur macaco macaco and E. fulvus mayottensis). Cytogenet Cell Genet 78: 260–271.
Murphy WJ, Eizirik E, Johnson WE, Zhang YP, Ryder OA, O'Brien SJ (2001a) Molecular phylogenetics and the origins of placental mammals. Nature 409: 614–618.
Murphy WJ, Stanyon R, O'Brien SJ (2001b) Evolution of mammalian genome organization inferred from comparative gene mapping. Genome Biol 2: reviews 0005.1–0005.8.
Murphy WJ, Frönicke L, O'Brien SJ, Stanyon R (2003) Evolution of human chromosome 1 and its homologues in placental mammals. Genome Res 13: 1880–1888.
Murphy WJ, Pevzner PA, O'Brien SJ (2004) Mammalian phylogenomics comes of age. Trends Genet 20: 631–639.
Nash WG, Wienberg J, Ferguson-Smith MA, Menninger JC, O'Brien SJ (1998) Comparative genomics: tracking chromosome evolution in the family Ursidae using reciprocal chromosome painting. Cytogenet Cell Genet 83: 182–192.
Nie W, Wang J, O'Brien PC et al. (2002) The genome phylogeny of domestic cat, red panda and five mustelid species revealed by comparative chromosome painting and G-banding. Chromosome Res 10: 209–222.
Nie W, O'Brien PC, Fu B et al. (2006) Chromosome painting between human and lorisiform prosimians: evidence for the HSA 7/16 synteny in the primate ancestral karyotype. Am J Phys Anthropol 129: 250–259.
Novacek MJ (1992) Mammalian phylogeny: shaking the tree. Nature 356: 121–125.
Nowak RM (1999) Walker's Mammals of the World, 6th edn, Vol. 1. Baltimore and London: Johns Hopkins University Press, pp. 169–243.
O'Brien SJ, Menotti-Raymond M, Murphy WJ et al. (1999) The promise of comparative genomics in mammals. Science 286: 458–481.
Patterson B, Pascual R (1972) The fossil mammal fauna of South-America. In: Evolution, Mammals and Southern Continents. Keast A, Erk FC, Glass BP, eds., Albany: State University of New York Press, pp. 247–309.
Perelman PL, Graphodatsky AS, Serdukova NA et al. (2005) Karyotypic conservatism in the suborder Feliformia (Order Carnivora). Cytogenet Genome Res 108: 348–354.
Rettenberger G, Klett C, Zechner U et al. (1995) ZOO-FISH analysis: cat and human karyotypes closely resemble the putative ancestral mammalian karyotype. Chromosome Res 3: 479–486.
Richard F, Lombard M, Dutrillaux B (2003) Reconstruction of the ancestral karyotype of eutherian mammals. Chromosome Res 11: 605–618.
Robinson TJ, Seiffert ER (2004) Afrotherian origins and interrelationships: new views and future prospects. Curr Top Dev Biol 63: 37–60.
Robinson TJ, Fu B, Ferguson-Smith MA, Yang F (2004) Cross-species chromosome painting in the golden mole and elephant-shrew: support for the mammalian clades Afrotheria and Afroinsectiphillia but not Afroinsectivora. Proc R Soc Lond B 271: 1477–1484.
Rokas A, Holland PWH (2000) Rare genomic changes as a tool for phylogenetics. Trends Ecol Evol 15: 454–459.
Scherthan H, Cremer T, Arnason U, Weier HU, Lima-de-Faria A, Frönicke L (1994) Comparative chromosome painting discloses homologous segments in distantly related mammals. Nat Genet 6: 342–347.
Shoshani J, McKenna MC (1998) Higher taxonomic relationships among extant Mammals based on morphology, with selected comparisons of results from molecular data. Mol Phylogenet Evol 9: 572–584.
Springer MS, Stanhope MJ, Madsen O, de Jong WW (2004) Molecules consolidate the placental mammal tree. Trends Ecol Evol 19: 430–438.
Stanyon R, Stone G, Garica M, Frönicke L (2003) Reciprocal chromosome painting shows that the squirrels, unlike murid rodents, have a highly conserved genome organization. Genomics 82: 245–249.
Svartman M, Stone G, Page JE, Stanyon R (2004) A chromosome painting test of the basal eutherian karyotype. Chromosome Res 12: 45–53.
Telenius H, Pelmear AH, Tunnacliffe A et al. (1992) Cytogenetic analysis by chromosome painting using DOP-PCR amplified flow-sorted chromosomes. Gene Chrom Cancer 4: 257–263.
Trifonov V, Yang F, Ferguson-Smith MA, Robinson TJ (2003) Cross-species chromosome painting in the Perissodactyla: delimitation of homologous regions in Burchell's zebra (Equus Burchellii) and the white (Ceratotherium Simum) and black rhinoceros (Diceros Bicornis). Cytogenet Genome Res 103: 104–110.
Volleth M, Klett C, Kollak A et al. (1999) Zoo-FISH analysis in a species of the order Chiroptera: Glossophaga soricina (Phyllostomidae). Chromosome Res 7: 57–64.
Volleth M, Heller K-G, Pfeiffer RA, Hameister H (2002) A comparative Zoo-FISH analysis in bats elucidates the phylogenetic relationships between Megachiroptera and five microchiropteran families. Chromosome Res 10: 477–497.
Waddell PJ, Kishino H, Ota R (2001) A phylogenetic foundation for comparative mammalian genomics. Genome Inform 12: 141–154.
Wienberg J (2004) The evolution of eutherian chromosomes. Curr Opin Genet Dev 14: 657–666.
Wienberg J, Stanyon R, Nash WG et al. (1997) Conservation of human vs. feline genome organization revealed by reciprocal chromosome painting. Cytogenet Cell Genet 77: 211–217.
Yang F, Carter NP, Shi L, Ferguson-Smith MA (1995) A comparative study of karyotypes of muntjacs by chromosome painting. Chromosoma 103: 642–652.
Yang F, Müller S, Just R, Ferguson-Smith MA, Wienberg J (1997) Comparative chromosome painting in mammals: human and the Indian muntjac (Muntiacus muntjak vaginalis). Genomics 39: 396–401.
Yang F, O'Brien PCM, Milne BS et al. (1999) A complete comparative chromosome map for the dog, red fox, and human and its integration with canine genetic maps. Genomics 62: 189–202.
Yang F, Graphodatsky AS, O'Brien PCM et al. (2000) Reciprocal chromosome painting illuminates the history of genome evolution of the domestic cat, dog and human. Chromosome Res 8: 393–404.
Yang F, Alkalaeva EZ, Perelman PL et al. (2003) Reciprocal chromosome painting among human, aardvark, and elephant (superorder Afrotheria) reveals the likely eutherian ancestral karyotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 1062–1066.
Yang F, Fu B, O'Brien PCM, Nie W, Ryder OA, Ferguson-Smith MA (2004) Refined genome-wide comparative map of the domestic horse, donkey and human based on cross-species chromosome painting: insight into the occasional fertility of mules. Chromosome Res 12: 65–76.
Ye J, Biltueva L, Huang L et al. (2006) Cross-species chromosome painting unveils cytogenetic signatures for the Eulipotyphla and evidence for the polyphyly of Insectivora. Chromosome Res 14: 151–159.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, F., Graphodatsky, A.S., Li, T. et al. Comparative genome maps of the pangolin, hedgehog, sloth, anteater and human revealed by cross-species chromosome painting: further insight into the ancestral karyotype and genome evolution of eutherian mammals. Chromosome Res 14, 283–296 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-006-1045-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-006-1045-6