Abstract
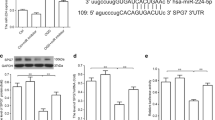
The imbalance between excess reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and insufficient antioxidant defenses contribute to a range of neurodegenerative diseases. High ROS levels damage cellular macromolecules such as DNA, proteins and lipids, leading to neuron vulnerability and eventual death. However, the underlying molecular mechanism of the ROS regulation is not fully elucidated. Recently, an increasing number of studies suggest that microRNAs (miRNAs) emerge as the targets in regulating oxidative stress. We recently reported the neuroprotective effect of miR-137-3p for brachial plexus avulsion-induced motoneuron death. The present study is sought to investigate whether miR-137-3p also could protect PC12 cells against hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) induced neurotoxicity. By using cell viability assay, ROS assay, gene and protein expression assay, we found that PC-12 cells exposed to H2O2 exhibited decreased cell viability, increased expression levels of calpain-2 and neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS), whereas a decreased miR-137-3p expression. Importantly, restoring the miR-137-3p levels in H2O2 exposure robustly inhibited the elevated nNOS, calpain-2 and ROS expression levels, which subsequently improved the cell viability. Furthermore, the suppressive effect of miR-137-3p on the elevated ROS level under oxidative stress was considerably blunted when we mutated the binding site of calpain-2 targted by miR-137-3p, suggesting the critical role of calpain-2 involving the neuroprotective effect of miR-137-3p. Collectively, these findings highlight the neuroprotective role of miR-137-3p through down-regulating calpain and NOS activity, suggesting its potential role for combating oxidative stress insults in the neurodegenerative diseases.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvira D, Ferrer I, Gutierrez-Cuesta J, Garcia-Castro B, Pallas M, Camins A (2008) Activation of the calpain/cdk5/p25 pathway in the girus cinguli in Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 14(4):309–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2007.09.005
Araujo IM, Carvalho CM (2005) Role of nitric oxide and calpain activation in neuronal death and survival. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord 4(4):319–324. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568007054546126
Avery SV (2011) Molecular targets of oxidative stress. Biochem J 434(2):201–210. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20101695
Barber SC, Shaw PJ (2010) Oxidative stress in ALS: Key role in motor neuron injury and therapeutic target. Free Radic Biol Med 48(5):629–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.11.018
Bartel DP (2009) MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136(2):215–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.002
Bartoszewski R, Sikorski AF (2019) Editorial focus: understanding off-target effects as the key to successful RNAi therapy. Cell Mol Biol Lett 24:69. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11658-019-0196-3
Chang H, Sheng JJ, Zhang L, Yue ZJ, Jiao B, Li JS, Yu ZB (2015) ROS-induced nuclear translocation of calpain-2 facilitates cardiomyocyte apoptosis in tail-suspended rats. J Cell Biochem 116(10):2258–2269. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.25176
Chen B, Zhao Q, Ni R, Tang F, Shan L, Cepinskas I, Cepinskas G, Wang W, Schiller PW, Peng T (2014) Inhibition of calpain reduces oxidative stress and attenuates endothelial dysfunction in diabetes. Cardiovasc Diabetol 13:88. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2840-13-88
Chen XH, Zhou X, Yang XY, Zhou ZB, Lu DH, Tang Y, Ling ZM, Zhou LH, Feng X (2016) Propofol protects against H2O2-induced oxidative injury in differentiated PC12 cells via inhibition of Ca2+-dependent NADPH oxidase. Cell Mol Neurobiol 36(4):541–551. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-015-0235-1
Cheng X, Fu R, Gao M, Liu S, Li YQ, Song FH, Bruce IC, Zhou LH, Wu W (2013) Intrathecal application of short interfering RNA knocks down c-jun expression and augments spinal motoneuron death after root avulsion in adult rats. Neuroscience 241:268–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.03.006
Cheng X, Luo HX, Hou ZJ, Huang Y, Sun JB, Zhuo LH (2014) Neuronal nitric oxide synthase, as a downstream signaling molecule of c-jun, regulates the survival of differentiated PC12 cells. Mol Med Rep 10(4):1881–1886. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2014.2415
Chi SW, Zang JB, Mele A, Darnell RB (2009) Argonaute HITS-CLIP decodes microRNA-mRNA interaction maps. Nature 460(7254):479–486. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08170
Chocry M, Leloup L, Kovacic H (2017) Reversion of resistance to oxaliplatin by inhibition of p38 MAPK in colorectal cancer cell lines: involvement of the calpain/Nox1 pathway. Oncotarget 8(61):103710–103730. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.21780
Crocker SJ, Smith PD, Jackson-Lewis V, Lamba WR, Hayley SP, Grimm E, Callaghan SM, Slack RS, Melloni E, Przedborski S, Robertson GS, Anisman H, Merali Z, Park DS (2003) Inhibition of calpains prevents neuronal and behavioral deficits in an MPTP mouse model of Parkinson's disease. J Neurosci 23(10):4081–4091
Curtin JF, Donovan M, Cotter TG (2002) Regulation and measurement of oxidative stress in apoptosis. J Immunol Methods 265(1–2):49–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-1759(02)00070-4
Dai J, Xu LJ, Han GD, Sun HL, Zhu GT, Jiang HT, Yu GY, Tang XM (2018) MiR-137 attenuates spinal cord injury by modulating NEUROD4 through reducing inflammation and oxidative stress. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22(7):1884–1890
Davila D, Torres-Aleman I (2008) Neuronal death by oxidative stress involves activation of FOXO3 through a two-arm pathway that activates stress kinases and attenuates insulin-like growth factor I signaling. Mol Biol Cell 19(5):2014–2025. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E07-08-0811
Dias V, Junn E, Mouradian MM (2013) The role of oxidative stress in Parkinson's disease. J Parkinsons Dis 3(4):461–491. https://doi.org/10.3233/JPD-130230
Dringen R (2005) Oxidative and antioxidative potential of brain microglial cells. Antioxid Redox Signal 7(9–10):1223–1233. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2005.7.1223
Edlund J, Fasching A, Liss P, Hansell P, Palm F (2010) The roles of NADPH-oxidase and nNOS for the increased oxidative stress and the oxygen consumption in the diabetic kidney. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 26(5):349–356. https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.1099
Enokido Y, Hatanaka H (1993) Apoptotic cell death occurs in hippocampal neurons cultured in a high oxygen atmosphere. Neuroscience 57(4):965–972. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-4522(93)90041-d
Eruslanov E, Kusmartsev S (2010) Identification of ROS using oxidized DCFDA and flow-cytometry. Adv Protoc Oxid Stress II 594:57–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60761-411-1_4
Forstermann U, Sessa WC (2012) Nitric oxide synthases: regulation and function. Eur Heart J. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehr304
Gao L, Dai C, Feng Z, Zhang L, Zhang Z (2018) MiR-137 inhibited inflammatory response and apoptosis after spinal cord injury via targeting of MK2. J Cell Biochem 119(4):3280–3292. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.26489
Gao F, Lei J, Zhang Z, Yang Y, You H (2019) Curcumin alleviates LPS-induced inflammation and oxidative stress in mouse microglial BV2 cells by targeting miR-137-3p/NeuroD1. RSC Adv 9(66):38397–38406. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra07266g
Gurtan AM, Sharp PA (2013) The role of miRNAs in regulating gene expression networks. J Mol Biol 425(19):3582–3600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2013.03.007
Hara T, Mahadevan J, Kanekura K, Hara M, Lu SM, Urano F (2014) Calcium efflux from the endoplasmic reticulum leads to beta-cell death. Endocrinology 155(3):758–768. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2013-1519
Hong ZW, Tian YJ, Yuan YB, Qi MW, Li YC, Di YM, Chen L, Chen L (2016) Enhanced oxidative stress is responsible for TRPV4-induced neurotoxicity. Front Cell Neurosci 10:232. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2016.00232
Huang CJ, Gurlo T, Haataja L, Costes S, Daval M, Ryazantsev S, Wu XJ, Butler AE, Butler PC (2010) Calcium-activated calpain-2 is a mediator of beta cell dysfunction and apoptosis in type 2 diabetes. J Biol Chem 285(1):339–348. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.024190
Huang WJ, Zhang X, Chen WW (2016) Role of oxidative stress in Alzheimer's disease. Biomed Rep 4(5):519–522. https://doi.org/10.3892/br.2016.630
Junn E, Mouradian MM (2012) MicroRNAs in neurodegenerative diseases and their therapeutic potential. Pharmacol Ther 133(2):142–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2011.10.002
Kannan K, Jain SK (2000) Oxidative stress and apoptosis. Pathophysiology 7(3):153–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0928-4680(00)00053-5
Kar R, Kellogg DL, Roman LJ (2015) Oxidative stress induces phosphorylation of neuronal NOS in cardiomyocytes through AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 459(3):393–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.02.113
Khan M, Dhammu TS, Matsuda F, Annamalai B, Dhindsa TS, Singh I, Singh AK (2016) Targeting the nNOS/peroxynitrite/calpain system to confer neuroprotection and aid functional recovery in a mouse model of TBI. Brain Res 1630:159–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2015.11.015
Kong LF, Wei QW, Fedail JS, Shi FX, Nagaoka K, Watanabe G (2015) Effects of thyroid hormones on the antioxidative status in the uterus of young adult rats. J Reprod Dev 61(3):219–227. https://doi.org/10.1262/jrd.2014-129
Kopincova J, Puzserova A, Bernatova I (2011) Biochemical aspects of nitric oxide synthase feedback regulation by nitric oxide. Interdiscip Toxicol 4(2):63–68. https://doi.org/10.2478/v10102-011-0012-z
Lai X, Eberhardt M, Schmitz U, Vera J (2019) Systems biology-based investigation of cooperating microRNAs as monotherapy or adjuvant therapy in cancer. Nucleic Acids Res 47(15):7753–7766. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz638
Li R, Yin F, Guo YY, Zhao KC, Ruan Q, Qi YM (2017) Knockdown of ANRIL aggravates H2O2-induced injury in PC-12 cells by targeting microRNA-125a. Biomed Pharmacother 92:952–961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.05.122
Luo P, Chen T, Zhao YB, Xu HX, Huo K, Zhao MM, Yang YF, Fei Z (2012) Protective effect of Homer 1a against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in PC12 cells. Free Radical Res 46(6):766–776. https://doi.org/10.3109/10715762.2012.678340
Mahmoudi E, Cairns MJ (2017) MiR-137: an important player in neural development and neoplastic transformation. Mol Psychiatry 22(1):44–55. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2016.150
Mesenge C, Verrecchia C, Allix M, Boulu RR, Plotkine M (1996) Reduction of the neurological deficit in mice with traumatic brain injury by nitric oxide synthase inhibitors. J Neurotrauma 13(4):209–214
Momeni HR (2011) Role of calpain in apoptosis. Cell J 13(2):65–72
Nathan C (1997) Inducible nitric oxide synthase: what difference does it make? J Clin Investig 100(10):2417–2423. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI119782
Nixon RA, Saito KI, Grynspan F, Griffin WR, Katayama S, Honda T, Mohan PS, Shea TB, Beermann M (1994) Calcium-activated neutral proteinase (calpain) system in aging and Alzheimer's disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 747:77–91. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1994.tb44402.x
Ray SK, Fidan M, Nowak MW, Wilford GG, Hogan EL, Banik NL (2000) Oxidative stress and Ca2+ influx upregulate calpain and induce apoptosis in PC12 cells. Brain Res 852(2):326–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-8993(99)02148-4
Saatman KE, Creed J, Raghupathi R (2010) Calpain as a therapeutic target in traumatic brain injury. Neurotherapeutics 7(1):31–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nurt.2009.11.002
Saito K, Elce JS, Hamos JE, Nixon RA (1993) Widespread activation of calcium-activated neutral proteinase (calpain) in the brain in Alzheimer disease: a potential molecular basis for neuronal degeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90(7):2628–2632. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.90.7.2628
Salim S (2017) Oxidative stress and the central nervous system. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 360(1):201–205. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.116.237503
Shafi G, Aliya N, Munshi A (2010) MicroRNA signatures in neurological disorders. Can J Neurol Sci 37(2):177–185. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0317167100009902
Simonian NA, Coyle JT (1996) Oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 36:83–106. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pa.36.040196.000503
Slivka A, Mytilineou C, Cohen G (1987a) Histochemical evaluation of glutathione in brain. Brain Res 409(2):275–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(87)90712-8
Slivka A, Spina MB, Cohen G (1987b) Reduced and oxidized glutathione in human and monkey brain. Neurosci Lett 74(1):112–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3940(87)90061-9
Su YR, Wang J, Wu JJ, Chen Y, Jiang YP (2007) Overexpression of lentivirus-mediated glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in bone marrow stromal cells and its neuroprotection for the PC12 cells damaged by lactacystin. Neurosci Bull 23(2):67–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-007-0010-5
Suzuki K (1991) Nomenclature of calcium dependent proteinase. Biomed Biochim Acta 50(4–6):483–484
Tang Y, Fu R, Ling ZM, Liu LL, Yu GY, Li W, Fang XY, Zhu Z, Wu WT, Zhou LH (2018) MiR-137-3p rescue motoneuron death by targeting calpain-2. Nitric Oxide Biol Chem 74:74–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2018.01.008
Uttara B, Singh AV, Zamboni P, Mahajan RT (2009) Oxidative stress and neurodegenerative diseases: a review of upstream and downstream antioxidant therapeutic options. Curr Neuropharmacol 7(1):65–74. https://doi.org/10.2174/157015909787602823
Vosler PS, Brennan CS, Chen J (2008) Calpain-mediated signaling mechanisms in neuronal injury and neurodegeneration. Mol Neurobiol 38(1):78–100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-008-8036-x
Wang Z, Liu Y, Han N, Chen X, Yu W, Zhang W, Zou F (2010) Profiles of oxidative stress-related microRNA and mRNA expression in auditory cells. Brain Res 1346:14–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2010.05.059
Wang S, Guo C, Yu M, Ning X, Yan B, Zhao J, Yang A, Yan H (2018) Identification of H2O2 induced oxidative stress associated microRNAs in HLE-B3 cells and their clinical relevance to the progression of age-related nuclear cataract. BMC Ophthalmol 18(1):93. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12886-018-0766-6
Wei G, Dawson VL, Zweier JL (1999) Role of neuronal and endothelial nitric oxide synthase in nitric oxide generation in the brain following cerebral ischemia. Biochim Biophys Acta 1455(1):23–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0925-4439(99)00051-4
Wingrave JM, Schaecher KE, Sribnick EA, Wilford GG, Ray SK, Hazen-Martin DJ, Hogan EL, Banik NL (2003) Early induction of secondary injury factors causing activation of calpain and mitochondria-mediated neuronal apoptosis following spinal cord injury in rats. J Neurosci Res 73(1):95–104. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.10607
Wu W (1993) Expression of nitric-oxide synthase (NOS) in injured CNS neurons as shown by NADPH diaphorase histochemistry. Exp Neurol 120(2):153–159. https://doi.org/10.1006/exnr.1993.1050
Wu W, Li L (1993) Inhibition of nitric oxide synthase reduces motoneuron death due to spinal root avulsion. Neurosci Lett 153(2):121–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3940(93)90303-3
Xu W, Chi L, Xu R, Ke Y, Luo C, Cai J, Qiu M, Gozal D, Liu R (2005) Increased production of reactive oxygen species contributes to motor neuron death in a compression mouse model of spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 43(4):204–213. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.sc.3101674
Yun HY, Dawson VL, Dawson TM (1997) Nitric oxide in health and disease of the nervous system. Mol Psychiatry 2(4):300–310. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4000272
Zeevalk GD, Bernard LP, Nicklas WJ (1998) Role of oxidative stress and the glutathione system in loss of dopamine neurons due to impairment of energy metabolism. J Neurochem 70(4):1421–1430. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.1998.70041421.x
Zhu H, Bhattacharyya B, Lin H, Gomez CM (2013) Skeletal muscle calpain acts through nitric oxide and neural miRNAs to regulate acetylcholine release in motor nerve terminals. J Neurosci 33(17):7308–7324. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0224-13.2013
Funding
This work was supported by research grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81771325) and Sun Yat-sen University Research Startup Foundation (59000-18841219).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YT and RF performed the experiment, wrote the manuscript, acquired the data, and created the figures. YQL,GYY,ZML,KZ, PLMZ, and WFL performed experiments and data analysis. RF and LHZ designed the study and revised the manuscript for important intellectual content. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, Y., Li, Y., Yu, G. et al. MicroRNA-137-3p Protects PC12 Cells Against Oxidative Stress by Downregulation of Calpain-2 and nNOS. Cell Mol Neurobiol 41, 1373–1387 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00908-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00908-0