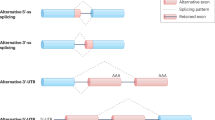
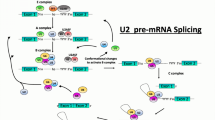
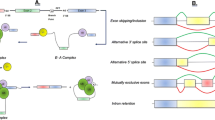
Abstract
Neurodegenerative disorders such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, and Huntington’s disease affect a rapidly increasing population worldwide. Although common pathogenic mechanisms have been identified (e.g., protein aggregation or dysfunction, immune response alteration and axonal degeneration), the molecular events underlying timing, dosage, expression, and location of RNA molecules are still not fully elucidated. In particular, the alternative splicing (AS) mechanism is a crucial player in RNA processing and represents a fundamental determinant for brain development, as well as for the physiological functions of neuronal circuits. Although in recent years our knowledge of AS events has increased substantially, deciphering the molecular interconnections between splicing and ALS remains a complex task and still requires considerable efforts. In the present review, we will summarize the current scientific evidence outlining the involvement of AS in the pathogenic processes of ALS. We will also focus on recent insights concerning the tuning of splicing mechanisms by epigenomic and epi-transcriptomic regulation, providing an overview of the available genomic technologies to investigate AS drivers on a genome-wide scale, even at a single-cell level resolution. In the future, gene therapy strategies and RNA-based technologies may be utilized to intercept or modulate the splicing mechanism and produce beneficial effects against ALS.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ALS:
-
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- AS:
-
Alternative splicing
- RBPs:
-
RNA-binding proteins
- fALS:
-
Familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- sALS:
-
Sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- FTD:
-
Frontotemporal dementia
- ES:
-
Exon skipping
- IR:
-
Intron retention
- C9:
-
C9ORF72
- snRNA:
-
Small nuclear RNA
- snRNPs:
-
Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins
- PPIases:
-
Peptidyl-propyl cis/trans isomerases
- ESEs:
-
Exonic splicing enhancers
- ISEs:
-
Intronic splicing enhancers
- ESSs:
-
Exonic splicing silencers
- ISSs:
-
Intronic splicing silencers
- PrLD:
-
Prion-like domain
- hnRNP:
-
Heterogenous nuclear ribonucleoprotein
- PTB:
-
Polypyrimidine tract-binding protein
- MN:
-
Motoneuron
- SMaRT:
-
Transcription of spliceosome-mediated RNA
- siRNA:
-
Small interfering RNA
References
Aartsma-Rus A et al (2017) Development of exon skipping therapies for duchenne muscular dystrophy: a critical review and a perspective on the outstanding issues. Nucleic Acid Ther 27:251–259. https://doi.org/10.1089/nat.2017.0682
Aizawa H, Hideyama T, Yamashita T, Kimura T, Suzuki N, Aoki M, Kwak S (2016) Deficient RNA-editing enzyme ADAR2 in an amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patient with a FUS(P525L) mutation. J Clin Neurosci 32:128–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2015.12.039
Arechavala-Gomeza V, Khoo B, Aartsma-Rus A (2014) Splicing modulation therapy in the treatment of genetic diseases. Appl Clin Genet 7:245–252. https://doi.org/10.2147/TACG.S71506
Arzalluz-Luque A, Conesa A (2018) Single-cell RNAseq for the study of isoforms-how is that possible? Genome Biol 19:110. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-018-1496-z
Ash PE et al (2010) Neurotoxic effects of TDP-43 overexpression in C. elegans. Hum Mol Genet 19:3206–3218. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddq230
Bailey JK, Shen W, Liang XH, Crooke ST (2017) Nucleic acid binding proteins affect the subcellular distribution of phosphorothioate antisense oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res 45:10649–10671. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx709
Baralle D, Buratti E (2017) RNA splicing in human disease and in the clinic. Clin Sci 131:355–368. https://doi.org/10.1042/CS20160211
Barker HV, Niblock M, Lee YB, Shaw CE, Gallo JM (2017) RNA misprocessing in C9orf72-linked neurodegeneration. Front Cell Neurosci 11:195. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2017.00195
Basei FL, Meirelles GV, Righetto GL, Dos Santos Migueleti DL, Smetana JH, Kobarg J (2015) New interaction partners for Nek4.1 and Nek4.2 isoforms: from the DNA damage response to RNA splicing. Proteome Sci 13:11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12953-015-0065-6
Baumer D, Hilton D, Paine SM, Turner MR, Lowe J, Talbot K, Ansorge O (2010) Juvenile ALS with basophilic inclusions is a FUS proteinopathy with FUS mutations. Neurology 75:611–618. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181ed9cde
Bedford MT, Richard S (2005) Arginine methylation an emerging regulator of protein function. Mol Cell 18:263–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2005.04.003
Bennett CL et al (2018) Senataxin mutations elicit motor neuron degeneration phenotypes and yield TDP-43 mislocalization in ALS4 mice and human patients. Acta Neuropathol 136:425–443. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-018-1852-9
Benoit-Pilven C et al (2018) Complementarity of assembly-first and mapping-first approaches for alternative splicing annotation and differential analysis from RNAseq data. Sci Rep 8:4307. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-21770-7
Berger A, Maire S, Gaillard MC, Sahel JA, Hantraye P, Bemelmans AP (2016) mRNA trans-splicing in gene therapy for genetic diseases. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 7:487–498. https://doi.org/10.1002/wrna.1347
Bhandare VV, Ramaswamy A (2016) Identification of possible siRNA molecules for TDP43 mutants causing amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: in silico design and molecular dynamics study. Comput Biol Chem 61:97–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2016.01.001
Blackwell E, Ceman S (2012) Arginine methylation of RNA-binding proteins regulates cell function and differentiation. Mol Reprod Dev 79:163–175. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrd.22024
Borna H, Imani S, Iman M, Azimzadeh Jamalkandi S (2015) Therapeutic face of RNAi: in vivo challenges. Exp Opin Biol Ther 15:269–285. https://doi.org/10.1517/14712598.2015.983070
Boutz PL et al (2007) A post-transcriptional regulatory switch in polypyrimidine tract-binding proteins reprograms alternative splicing in developing neurons. Genes Dev 21:1636–1652. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1558107
Brenner D et al (2016) NEK1 mutations in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain 139:e28. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/aww033
Brenner D et al (2018) Hot-spot KIF5A mutations cause familial ALS. Brain 141:688–697. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awx370
Bristol LA, Rothstein JD (1996) Glutamate transporter gene expression in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis motor cortex. Ann Neurol 39:676–679. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.410390519
Brockmann SJ et al (2018) CHCHD10 mutations p. R15L and p.G66V cause motoneuron disease by haploinsufficiency. Hum Mol Genet 27:706–715. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddx436
Brown RH Jr (1997) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Insights from genetics. Arch Neurol 54:1246–1250
Buratti E, Baralle FE (2008) Multiple roles of TDP-43 in gene expression, splicing regulation, and human disease. Front Biosci 13:867–878
Butti Z, Patten SA (2018) RNA dysregulation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Front Genet 9:712. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2018.00712
Cirulli ET et al (2015) Exome sequencing in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis identifies risk genes and pathways. Science 347:1436–1441. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaa3650
Colombrita C et al (2015) From transcriptomic to protein level changes in TDP-43 and FUS loss-of-function cell models. Biochem Biophys Acta 1849:1398–1410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2015.10.015
Conlon EG, Manley JL (2017) RNA-binding proteins in neurodegeneration: mechanisms in aggregate. Genes Dev 31:1509–1528. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.304055.117
Conlon EG, Lu L, Sharma A, Yamazaki T, Tang T, Shneider NA, Manley JL (2016) The C9ORF72 GGGGCC expansion forms RNA G-quadruplex inclusions and sequesters hnRNP H to disrupt splicing in ALS brains. eLife. https://doi.org/10.7554/elife.17820
Conlon EG et al (2018) Unexpected similarities between C9ORF72 and sporadic forms of ALS/FTD suggest a common disease mechanism. eLife. https://doi.org/10.7554/elife.37754
Cooper-Knock J et al (2015) C9ORF72 GGGGCC expanded repeats produce splicing dysregulation which correlates with disease severity in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PLoS ONE 10:e0127376. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0127376
Couthouis J, Raphael AR, Daneshjou R, Gitler AD (2014) Targeted exon capture and sequencing in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PLoS Genet 10:e1004704. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1004704
Del Bo R et al (2011) Novel optineurin mutations in patients with familial and sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 82:1239–1243. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2011.242313
Deshaies JE et al (2018) TDP-43 regulates the alternative splicing of hnRNP A1 to yield an aggregation-prone variant in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain 141:1320–1333. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awy062
Donnelly CJ et al (2013) RNA toxicity from the ALS/FTD C9ORF72 expansion is mitigated by antisense intervention. Neuron 80:415–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2013.10.015
Errichelli L et al (2017) FUS affects circular RNA expression in murine embryonic stem cell-derived motor neurons. Nat Commun 8:14741. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms14741
Furge LL, Chen K, Cohen S (1999) Annexin VII and annexin XI are tyrosine phosphorylated in peroxovanadate-treated dogs and in platelet-derived growth factor-treated rat vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 274:33504–33509
Geuens T, Bouhy D, Timmerman V (2016) The hnRNP family: insights into their role in health and disease. Hum Genet 135:851–867. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-016-1683-5
Gijselinck I et al (2012) A C9orf72 promoter repeat expansion in a Flanders-Belgian cohort with disorders of the frontotemporal lobar degeneration-amyotrophic lateral sclerosis spectrum: a gene identification study. Lancet Neurol 11:54–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(11)70261-7
Grabowski PJ (1998) Splicing regulation in neurons: tinkering with cell-specific control. Cell 92:709–712
Greenway MJ et al (2006) ANG mutations segregate with familial and ‘sporadic’ amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat Genet 38:411–413. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1742
Harrison AF, Shorter J (2017) RNA-binding proteins with prion-like domains in health and disease. Biochem J 474:1417–1438. https://doi.org/10.1042/BCJ20160499
Havens MA, Hastings ML (2016) Splice-switching antisense oligonucleotides as therapeutic drugs. Nucleic Acids Res 44:6549–6563. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw533
He Y, Zeng MY, Yang D, Motro B, Nunez G (2016) NEK7 is an essential mediator of NLRP3 activation downstream of potassium efflux. Nature 530:354–357. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature16959
Hideyama T, Yamashita T, Aizawa H, Tsuji S, Kakita A, Takahashi H, Kwak S (2012) Profound downregulation of the RNA editing enzyme ADAR2 in ALS spinal motor neurons. Neurobiol Dis 45:1121–1128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2011.12.033
Hofmann S et al (2008) Genome-wide association study identifies ANXA11 as a new susceptibility locus for sarcoidosis. Nat Genet 40:1103–1106. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.198
Hsiao YE et al (2018) RNA editing in nascent RNA affects pre-mRNA splicing. Genome Res 28:812–823. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.231209.117
Hu M, Guo Y, Chen H, Duan W, Li C (2013) Exon array analysis of alternative splicing of genes in SOD1G93A transgenic mice. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 170:301–319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0155-9
Hwang B, Lee JH, Bang D (2018) Single-cell RNA sequencing technologies and bioinformatics pipelines. Exp Mol Med 50:96. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-018-0071-8
Ishigaki S et al (2012) Position-dependent FUS-RNA interactions regulate alternative splicing events and transcriptions. Sci Rep 2:529. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep00529
Ishihara T et al (2013) Decreased number of Gemini of coiled bodies and U12 snRNA level in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Hum Mol Genet 22:4136–4147. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddt262
Johnson BS, Snead D, Lee JJ, McCaffery JM, Shorter J, Gitler AD (2009) TDP-43 is intrinsically aggregation-prone, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-linked mutations accelerate aggregation and increase toxicity. J Biol Chem 284:20329–20339. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.010264
Johnson L et al (2012) Screening for OPTN mutations in a cohort of British amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. Neurobiol Aging 33(2948):e2915–e2947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2012.06.023
Jyotsana N, Heuser M (2018) Exploiting differential RNA splicing patterns: a potential new group of therapeutic targets in cancer. Exp Opin Ther Targets 22:107–121. https://doi.org/10.1080/14728222.2018.1417390
Kabashi E et al (2008) TARDBP mutations in individuals with sporadic and familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat Genet 40:572–574. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.132
Kanekura K, Suzuki H, Aiso S, Matsuoka M (2009) ER stress and unfolded protein response in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Mol Neurobiol 39:81–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-009-8054-3
Kapeli K et al (2016) Distinct and shared functions of ALS-associated proteins TDP-43, FUS and TAF15 revealed by multisystem analyses. Nat Commun 7:12143. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms12143
Kapeli K, Martinez FJ, Yeo GW (2017) Genetic mutations in RNA-binding proteins and their roles in ALS. Hum Genet 136:1193–1214. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-017-1830-7
Kenna KP et al (2016) NEK1 variants confer susceptibility to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat Genet 48:1037–1042. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3626
Klim JR et al (2019) ALS-implicated protein TDP-43 sustains levels of STMN2, a mediator of motor neuron growth and repair. Nat Neurosci 22:167–179. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0300-4
Kuzma-Kozakiewicz M, Chudy A, Kazmierczak B, Dziewulska D, Usarek E, Baranczyk-Kuzma A (2013) Dynactin deficiency in the CNS of humans with sporadic ALS and mice with genetically determined motor neuron degeneration. Neurochem Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-1160-7
La Cognata V, D’Agata V, Cavalcanti F, Cavallaro S (2015) Splicing: is there an alternative contribution to Parkinson’s disease? Neurogenetics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-015-0449-x
La Cognata V, Morello G, Gentile G, D’Agata V, Criscuolo C, Cavalcanti F, Cavallaro S (2016) A customized high-resolution array-comparative genomic hybridization to explore copy number variations in Parkinson’s disease. Neurogenetics 17:233–244. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-016-0494-0
Lagier-Tourenne C, Polymenidou M, Cleveland DW (2010) TDP-43 and FUS/TLS: emerging roles in RNA processing and neurodegeneration. Hum Mol Genet 19:R46–R64. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddq137
Lagier-Tourenne C et al (2013) Targeted degradation of sense and antisense C9orf72 RNA foci as therapy for ALS and frontotemporal degeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:E4530–E4539. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1318835110
LaMonte BH et al (2002) Disruption of dynein/dynactin inhibits axonal transport in motor neurons causing late-onset progressive degeneration. Neuron 34:715–727
Lazarus JE, Moughamian AJ, Tokito MK, Holzbaur EL (2013) Dynactin subunit p150(Glued) is a neuron-specific anti-catastrophe factor. PLoS Biol 11:e1001611. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1001611
Lee YB et al (2013) Hexanucleotide repeats in ALS/FTD form length-dependent RNA foci, sequester RNA binding proteins, and are neurotoxic. Cell Rep 5:1178–1186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2013.10.049
Licht K, Kapoor U, Mayrhofer E, Jantsch MF (2016) Adenosine to inosine editing frequency controlled by splicing efficiency. Nucleic Acids Res 44:6398–6408. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw325
Lin CL, Bristol LA, Jin L, Dykes-Hoberg M, Crawford T, Clawson L, Rothstein JD (1998) Aberrant RNA processing in a neurodegenerative disease: the cause for absent EAAT2, a glutamate transporter, in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuron 20:589–602
Liscic RM (2015) Molecular basis of ALS and FTD: implications for translational studies. Arh Hig Rada Toksikol 66:285–290. https://doi.org/10.1515/aiht-2015-66-2679
Ludolph AC et al (2010) Guidelines for preclinical animal research in ALS/MND: a consensus meeting. Amyotroph Lateral Scler 11:38–45. https://doi.org/10.3109/17482960903545334
Luisier R et al (2018) Intron retention and nuclear loss of SFPQ are molecular hallmarks of ALS. Nat Commun. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04373-8
Mackenzie IR, Neumann M (2012) FET proteins in frontotemporal dementia and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain Res 1462:40–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2011.12.010
Maruyama H et al (2010) Mutations of optineurin in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nature 465:223–226. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08971
Matera AG, Wang Z (2014) A day in the life of the spliceosome. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15:108–121. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3742
McCampbell A et al (2018) Antisense oligonucleotides extend survival and reverse decrement in muscle response in ALS models. J Clin Investig 128:3558–3567. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI99081
McClorey G, Wood MJ (2015) An overview of the clinical application of antisense oligonucleotides for RNA-targeting therapies. Curr Opin Pharmacol 24:52–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coph.2015.07.005
Mendonca DM et al (2012) Neuroproteomics: an insight into ALS. Neurol Res 34:937–943. https://doi.org/10.1179/1743132812Y.0000000092
Miller TM et al (2013) An antisense oligonucleotide against SOD1 delivered intrathecally for patients with SOD1 familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a phase 1, randomised, first-in-man study. Lancet Neurol 12:435–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70061-9
Moniz L, Dutt P, Haider N, Stambolic V (2011) Nek family of kinases in cell cycle, checkpoint control and cancer. Cell Div 6:18. https://doi.org/10.1186/1747-1028-6-18
Morello G, Guarnaccia M, Spampinato AG, La Cognata V, D’Agata V, Cavallaro S (2017) Copy number variations in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: piecing the mosaic tiles together through a systems biology approach. Mol Neurobiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0393-x
Mori K et al (2013) hnRNP A3 binds to GGGGCC repeats and is a constituent of p62-positive/TDP43-negative inclusions in the hippocampus of patients with C9orf72 mutations. Acta Neuropathol 125:413–423. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-013-1088-7
Morohoshi F, Ootsuka Y, Arai K, Ichikawa H, Mitani S, Munakata N, Ohki M (1998) Genomic structure of the human RBP56/hTAFII68 and FUS/TLS genes. Gene 221:191–198
Munch C et al (2004) Point mutations of the p150 subunit of dynactin (DCTN1) gene in ALS. Neurology 63:724–726
Munch C et al (2005) Heterozygous R1101K mutation of the DCTN1 gene in a family with ALS and FTD. Ann Neurol 58:777–780. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.20631
Mure F, Corbin A, Benbahouche NEH, Bertrand E, Manet E, Gruffat H (2018) The splicing factor SRSF3 is functionally connected to the nuclear RNA exosome for intronless mRNA decay. Sci Rep 8:12901. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-31078-1
Nachreiner T, Esser M, Tenten V, Troost D, Weis J, Kruttgen A (2010) Novel splice variants of the amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-associated gene VAPB expressed in human tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 394:703–708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.03.055
Naro C, Barbagallo F, Chieffi P, Bourgeois CF, Paronetto MP, Sette C (2014) The centrosomal kinase NEK2 is a novel splicing factor kinase involved in cell survival. Nucleic Acids Res 42:3218–3227. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1307
Nicolas A et al (2018) Genome-wide analyses identify KIF5A as a novel ALS. Gene Neuron 97(1268–1283):e1266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2018.02.027
Niks EH, Aartsma-Rus A (2017) Exon skipping: a first in class strategy for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Exp Opin Biol Ther 17:225–236. https://doi.org/10.1080/14712598.2017.1271872
Nissim-Rafinia M, Kerem B (2005) The splicing machinery is a genetic modifier of disease severity. Trends Genet 21:480–483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2005.07.005
Orlacchio A et al (2010) SPATACSIN mutations cause autosomal recessive juvenile amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain 133:591–598. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awp325
Ozcan G, Ozpolat B, Coleman RL, Sood AK, Lopez-Berestein G (2015) Preclinical and clinical development of siRNA-based therapeutics. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 87:108–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2015.01.007
Pippucci T et al (2009) Autosomal recessive hereditary spastic paraplegia with thin corpus callosum: a novel mutation in the SPG11 gene and further evidence for genetic heterogeneity. Eur J Neurol 16:121–126. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2008.02367.x
Prasad J, Colwill K, Pawson T, Manley JL (1999) The protein kinase Clk/Sty directly modulates SR protein activity: both hyper- and hypophosphorylation inhibit splicing. Mol Cell Biol 19:6991–7000
Prudencio M et al (2015) Distinct brain transcriptome profiles in C9orf72-associated and sporadic ALS. Nat Neurosci 18:1175–1182. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4065
Ram O, Ast G (2007) SR proteins: a foot on the exon before the transition from intron to exon definition. Trends Genet 23:5–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2006.10.002
Reber S et al (2016) Minor intron splicing is regulated by FUS and affected by ALS-associated FUS mutants. EMBO J 35:1504–1521. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201593791
Ren X, Deng R, Wang L, Zhang K, Li J (2017) RNA splicing process analysis for identifying antisense oligonucleotide inhibitors with padlock probe-based isothermal amplification. Chem Sci 8:5692–5698. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7sc01336a
Rindt H, Tom CM, Lorson CL, Mattis VB (2017) Optimization of trans-splicing for Huntington’s disease RNA Therapy. Front Neurosci 11:544. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2017.00544
Rothstein JD (2009) Current hypotheses for the underlying biology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol 65(Suppl 1):S3–S9. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.21543
Sardone V, Zhou H, Muntoni F, Ferlini A, Falzarano MS (2017) Antisense oligonucleotide-based therapy for neuromuscular disease. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22040563
Shang Y, Huang EJ (2016) Mechanisms of FUS mutations in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain Res 1647:65–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2016.03.036
Shi H et al (2016) NLRP3 activation and mitosis are mutually exclusive events coordinated by NEK7, a new inflammasome component. Nat Immunol 17:250–258. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.3333
Shiga A et al (2012) Alteration of POLDIP3 splicing associated with loss of function of TDP-43 in tissues affected with ALS. PLoS ONE 7:e43120. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0043120
Shorter J, Taylor JP (2013) Disease mutations in the prion-like domains of hnRNPA1 and hnRNPA2/B1 introduce potent steric zippers that drive excess RNP granule assembly. Rare Dis 1:e25200. https://doi.org/10.4161/rdis.25200
Singh NN, Luo D, Singh RN (2018) Pre-mRNA splicing modulation by antisense oligonucleotides. Methods Mol Biol 1828:415–437. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-8651-4_26
Slotkin W, Nishikura K (2013) Adenosine-to-inosine RNA editing and human disease. Genome Med 5:105. https://doi.org/10.1186/gm508
Smith BN et al (2017) Mutations in the vesicular trafficking protein annexin A11 are associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Sci Transl Med. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aad9157
Suzuki H, Kanekura K, Levine TP, Kohno K, Olkkonen VM, Aiso S, Matsuoka M (2009) ALS-linked P56S-VAPB, an aggregated loss-of-function mutant of VAPB, predisposes motor neurons to ER stress-related death by inducing aggregation of co-expressed wild-type VAPB. J Neurochem 108:973–985. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0022-3042.2008.05857.x
Tawani A, Kumar A (2015) structural insights reveal the dynamics of the repeating r(CAG) transcript found in Huntington’s disease (HD) and spinocerebellar ataxias (SCAs). PLoS ONE 10:e0131788. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0131788
Tazi J, Bakkour N, Stamm S (2009) Alternative splicing and disease. Biochem Biophys Acta 1792:14–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2008.09.017
Teyssou E et al (2016) Genetic analysis of CHCHD10 in French familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. Neurobiol Aging 42(218):e211–e213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2016.03.022
Torres P et al (2018) Cryptic exon splicing function of TARDBP interacts with autophagy in nervous tissue. Autophagy 14:1398–1403. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2018.1474311
Tosolini AP, Sleigh JN (2017) Motor neuron gene therapy: lessons from spinal muscular atrophy for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Front Mol Neurosci 10:405. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2017.00405
Toth RP, Atkin JD (2018) Dysfunction of optineurin in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and glaucoma. Front Immunol 9:1017. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.01017
Tripolszki K et al (2017) High-throughput sequencing revealed a novel SETX mutation in a Hungarian patient with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain Behav 7:e00669. https://doi.org/10.1002/brb3.669
Tsuji H et al (2012) Molecular analysis and biochemical classification of TDP-43 proteinopathy. Brain 135:3380–3391. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/aws230
Valadkhan S (2010) Role of the snRNAs in spliceosomal active site. RNA Biol 7:345–353
Van Deerlin VM et al (2008) TARDBP mutations in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with TDP-43 neuropathology: a genetic and histopathological analysis. Lancet Neurol 7:409–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(08)70071-1
Vanderweyde T, Youmans K, Liu-Yesucevitz L, Wolozin B (2013) Role of stress granules and RNA-binding proteins in neurodegeneration: a mini-review. Gerontology 59:524–533. https://doi.org/10.1159/000354170
Verma A (2018) Recent advances in antisense oligonucleotide therapy in genetic neuromuscular diseases. Ann Indian Acad Neurol 21:3–8. https://doi.org/10.4103/aian.AIAN_298_17
Verma B, Akinyi MV, Norppa AJ, Frilander MJ (2018) Minor spliceosome and disease. Semin Cell Dev Biol 79:103–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.09.036
Volk AE, Weishaupt JH, Andersen PM, Ludolph AC, Kubisch C (2018) Current knowledge and recent insights into the genetic basis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Med Genet 30:252–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11825-018-0185-3
Walker AK, Atkin JD (2011) Stress signaling from the endoplasmic reticulum: a central player in the pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. IUBMB Life 63:754–763. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.520
Wang GS, Cooper TA (2007) Splicing in disease: disruption of the splicing code and the decoding machinery. Nat Rev Genet 8:749–761. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2164
Wasser CR, Herz J (2016) Splicing therapeutics for Alzheimer’s disease. EMBO Mol Med 8:308–310. https://doi.org/10.15252/emmm.201506067
Wojciechowska M, Krzyzosiak WJ (2011) Cellular toxicity of expanded RNA repeats: focus on RNA foci. Hum Mol Genet 20:3811–3821. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddr299
Wu S, Green MR (1997) Identification of a human protein that recognizes the 3′ splice site during the second step of pre-mRNA splicing. EMBO J 16:4421–4432. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/16.14.4421
Yahara M, Kitamura A, Kinjo M (2017) U6 snRNA expression prevents toxicity in TDP-43-knockdown cells. PLoS ONE 12:e0187813. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0187813
Yin S et al (2017) Evidence that C9ORF72 dipeptide repeat proteins associate with U2 snRNP to cause mis-splicing in ALS/FTD patients. Cell Rep 19:2244–2256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.05.056
Yu AC, Chan AY, Au WC, Shen Y, Chan TF, Chan HE (2016) Whole-genome sequencing of two probands with hereditary spastic paraplegia reveals novel splice-donor region variant and known pathogenic variant in SPG11. Cold Spring Harbor Mol Case Stud 2:a001248. https://doi.org/10.1101/mcs.a001248
Zhang J et al (2015) Disease-associated mutation in SRSF2 misregulates splicing by altering RNA-binding affinities. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:E4726–E4734. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1514105112
Zhang K et al (2018) ANXA11 mutations prevail in Chinese ALS patients with and without cognitive dementia. Neurol Genet 4:e237. https://doi.org/10.1212/NXG.0000000000000237
Zhao M, Kim JR, van Bruggen R, Park J (2018) RNA-binding proteins in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Mol Cells 41:818–829. https://doi.org/10.14348/molcells.2018.0243
Zhou Y, Liu S, Liu G, Ozturk A, Hicks GG (2013) ALS-associated FUS mutations result in compromised FUS alternative splicing and autoregulation. PLoS Genet 9:e1003895. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003895
Zhu LY, Zhu YR, Dai DJ, Wang X, Jin HC (2018) Epigenetic regulation of alternative splicing. Am J Cancer Res 8:2346–2358
Zucca S et al (2019) RNA-seq profiling in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients and controls. Sci Data 6:190006. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2019.6
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the projects “Un approccio diagnostico multidisciplinare per le malattie neurodegenerative dell’invecchiamento” (DSB.AD009.001) and “Life Analytics, human centric platform per la salute ed il benessere dell’uomo” (DSB.AD008.456), and Angelo Bagalà, Ariangela Belvedere, Benedetto Bruno, Walter Carpino, Tiziana Martire, and Patrizia Rizzuto for their administrative and technical support.
Funding
This work has been supported by Grants: (i) “Un approccio diagnostico multidisciplinare per le malattie neurodegenerative dell’invecchiamento”, DSB.AD009.001; (ii) “Sviluppo ed applicazione di tecnologie biosensoristiche in Genomica” CIP 2014.IT.05.SFOP.014/3/10.4/9.2.10/0008, CUP G67B17000170009, n. 11/2017 “Rafforzare l’Occupabilità nel sistema R&S e la nascita di spin off di ricerca in Sicilia—PROGRAMMA OPERATIVO DEL FONDO SOCIALE EUROPEO REGIONE SICILIA 2014–2020”, and (iii) “Life Analytics, human centric platform per la salute ed il benessere dell’uomo”, DSB.AD008.456.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BP and VLC reviewed the literature and wrote the manuscript. FLC participated in revising the manuscripts. TS, CU, SA provided critical inputs to the manuscript. SC conceived, directed, and supervised the project. All authors have read and approved the final version of this manuscript, and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work and consent for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perrone, B., La Cognata, V., Sprovieri, T. et al. Alternative Splicing of ALS Genes: Misregulation and Potential Therapies. Cell Mol Neurobiol 40, 1–14 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-019-00717-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-019-00717-0