Abstract
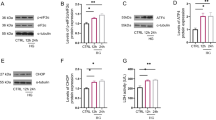
Diabetes is known to be associated with neurodegenerative diseases. Resveratrol, a plant-derived polyphenolic compound found in red wine, possesses antioxidant properties. In this study, we aimed to investigate the effects of resveratrol on the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/protein kinase B (PI3K/Akt)/FoxO3a pathway in mediating high glucose (HG)-induced injuries in neuronal PC12 cells. PC12 cells were exposed to HG to establish a model of HG neurotoxicity. Results showed that pre-treating PC12 cells with resveratrol before exposure to HG led to increased cell viability, decreased apoptotic cells, and reactive oxygen species generation. Western blot analysis showed that HG decreased the phosphorylation of Akt and FoxO3a and led to the nuclear localization of FoxO3a. These effects were significantly alleviated by resveratrol co-treatment. Furthermore, the protective effects of resveratrol were abolished by PI3K/Akt inhibitor LY294002. All these results demonstrate that resveratrol protected the PC12 cells from HG-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis via the activation of PI3K/Akt/FoxO3a signaling pathway.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhter R, Sanphui P, Biswas SC (2014) The essential role of p53-up-regulated modulator of apoptosis (Puma) and its regulation by FoxO3a transcription factor in beta-amyloid-induced neuron death. J Biol Chem 289(15):10812–10822
Albani D, Polito L, Signorini A, Forloni G (2010) Neuroprotective properties of resveratrol in different neurodegenerative disorders. BioFactors 36(5):370–376
Arab L, Sadeghi R, Walker DG, Lue LF, Sabbagh MN (2011) Consequences of aberrant insulin regulation in the brain: can treating diabetes be effective for Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Neuropharmacol 9(4):693–705
Bournival J, Quessy P, Martinoli MG (2009) Protective effects of resveratrol and quercetin against MPP+-induced oxidative stress act by modulating markers of apoptotic death in dopaminergic neurons. Cell Mol Neurobiol 29(8):1169–1180
Bournival J, Francoeur MA, Renaud J, Martinoli MG (2012) Quercetin and sesamin protect neuronal PC12 cells from high-glucose-induced oxidation, nitrosative stress, and apoptosis. Rejuvenation Res 15(3):322–333
Cao M, Jiang J, Du Y, Yan P (2012) Mitochondria-targeted antioxidant attenuates high glucose-induced P38 MAPK pathway activation in human neuroblastoma cells. Mol Med Rep 5(4):929–934
Cui H, Kong Y, Zhang H (2012) Oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and aging. J Signal Transduct 2012:646354
de la Monte SM, Tong M (2014) Brain metabolic dysfunction at the core of Alzheimer’s disease. Biochem Pharmacol 88(4):548–559
Foti Cuzzola V, Ciurleo R, Giacoppo S, Marino S, Bramanti P (2011) Role of resveratrol and its analogues in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases: focus on recent discoveries. CNS Neurol Disord: Drug Targets 10(7):849–862
Hoeijmakers JG, Faber CG, Merkies IS, Waxman SG (2014) Channelopathies, painful neuropathy, and diabetes: which way does the causal arrow point? Trends Mol Med 20(10):544–550
Hsieh HL, Yang CM (2013) Role of redox signaling in neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. Biomed Res Int 2013:484613
Jia Y, Mo SJ, Feng QQ, Zhan ML, Ouyang LS, Chen JC, Ma YX, Wu JJ, Lei WL (2014) EPO-dependent activation of PI3K/Akt/FoxO3a signalling mediates neuroprotection in in vitro and in vivo models of Parkinson’s disease. J Mol Neurosci 53(1):117–124
Kamal MA, Priyamvada S, Anbazhagan AN, Jabir NR, Tabrez S, Greig NH (2014) Linking Alzheimer’s disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus via aberrant insulin signaling and inflammation. CNS Neurol Disord: Drug Targets 13(2):338–346
Li D, Qu Y, Mao M, Zhang X, Li J, Ferriero D, Mu D (2009) Involvement of the PTEN-AKT-FOXO3a pathway in neuronal apoptosis in developing rat brain after hypoxia-ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 29(12):1903–1913
Liu X, Xiao Q, Zhao K, Gao Y (2013) Ghrelin inhibits high glucose-induced PC12 cell apoptosis by regulating TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway. Inflammation 36(6):1286–1294
Luque-Contreras D, Carvajal K, Toral-Rios D, Franco-Bocanegra D, Campos-Pena V (2014) Oxidative stress and metabolic syndrome: cause or consequence of Alzheimer’s disease? Oxid Med Cell Longev 2014:497802
Martin TF, Grishanin RN (2003) PC12 cells as a model for studies of regulated secretion in neuronal and endocrine cells. Methods Cell Biol 71:267–286
Monsalve M, Olmos Y (2011) The complex biology of FOXO. Curr Drug Targets 12(9):1322–1350
Nakamura T, Sakamoto K (2008) Forkhead transcription factor FOXO subfamily is essential for reactive oxygen species-induced apoptosis. Mol Cell Endocrinol 281(1–2):47–55
Peng C, Ma J, Gao X, Tian P, Li W, Zhang L (2013) High glucose induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in cardiac microvascular endothelial cells are regulated by FoxO3a. PLoS ONE 8(11):e79739
Radi E, Formichi P, Battisti C, Federico A (2014) Apoptosis and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. J Alzheimers Dis 42(Suppl 3):S125–S152
Renaud J, Bournival J, Zottig X, Martinoli MG (2014) Resveratrol protects DAergic PC12 cells from high glucose-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis: effect on p53 and GRP75 localization. Neurotox Res 25(1):110–123
Sanphui P, Biswas SC (2013) FoxO3a is activated and executes neuron death via Bim in response to beta-amyloid. Cell Death Dis 4:e625
Simao F, Matte A, Pagnussat AS, Netto CA, Salbego CG (2012) Resveratrol prevents CA1 neurons against ischemic injury by parallel modulation of both GSK-3beta and CREB through PI3-K/Akt pathways. Eur J Neurosci 36(7):2899–2905
Styskal J, Van Remmen H, Richardson A, Salmon AB (2012) Oxidative stress and diabetes: what can we learn about insulin resistance from antioxidant mutant mouse models? Free Radic Biol Med 52(1):46–58
Tomlinson DR, Gardiner NJ (2008) Glucose neurotoxicity. Nat Rev Neurosci 9(1):36–45
Uranga RM, Katz S, Salvador GA (2013) Enhanced phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt signaling has pleiotropic targets in hippocampal neurons exposed to iron-induced oxidative stress. J Biol Chem 288(27):19773–19784
Wang H, Zhou X, Huang J, Mu N, Guo Z, Wen Q, Wang R, Chen S, Feng ZP, Zheng W (2013) The role of Akt/FoxO3a in the protective effect of venlafaxine against corticosterone-induced cell death in PC12 cells. Psychopharmacology 228(1):129–141
Wilk A, Urbanska K, Yang S, Wang JY, Amini S, Del Valle L, Peruzzi F, Meggs L, Reiss K (2011) Insulin-like growth factor-I-forkhead box O transcription factor 3a counteracts high glucose/tumor necrosis factor-alpha-mediated neuronal damage: implications for human immunodeficiency virus encephalitis. J Neurosci Res 89(2):183–198
Wu PF, Xie N, Zhang JJ, Guan XL, Zhou J, Long LH, Li YL, Xiong QJ, Zeng JH, Wang F, Chen JG (2013) Resveratrol preconditioning increases methionine sulfoxide reductases A expression and enhances resistance of human neuroblastoma cells to neurotoxins. J Nutr Biochem 24(6):1070–1077
Yan LJ (2014) Pathogenesis of chronic hyperglycemia: from reductive stress to oxidative stress. J Diabetes Res 2014:137919
Zhang S, Zhao Y, Xu M, Yu L, Chen J, Yuan Y, Zheng Q, Niu X (2013) FoxO3a modulates hypoxia stress induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in cardiac microvascular endothelial cells. PLoS ONE 8(11):e80342
Zheng WH, Kar S, Quirion R (2000) Insulin-like growth factor-1-induced phosphorylation of the forkhead family transcription factor FKHRL1 is mediated by Akt kinase in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem 275(50):39152–39158
Zhou XM, Zhou ML, Zhang XS, Zhuang Z, Li T, Shi JX, Zhang X (2014) Resveratrol prevents neuronal apoptosis in an early brain injury model. J Surg Res 189(1):159–165
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from Medical scientific research funds of Guangdong Province (A2014810) and Graduate student research innovation project of Hunan Province (CX2013B397).
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Cong Yuan contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, MH., Yuan, C., He, J. et al. Resveratrol Protects PC12 Cells from High Glucose-Induced Neurotoxicity Via PI3K/Akt/FoxO3a Pathway. Cell Mol Neurobiol 35, 513–522 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-014-0147-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-014-0147-5