Abstract
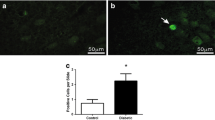
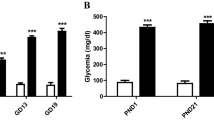
Compelling evidence shows that the offspring subjected to uncontrolled hyperlycemia during gestation display behavioral, neurochemical, and cellular abnormalities during adulthood. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying these defects remain elusive. Previous studies have shown an increased rate of apoptosis and a decreased index of neuronal proliferation associated with diabetic embryopathy. The aim of the present study was to determine whether impairments in apoptotic related proteins also occur in the developing central nervous system from non-malformed embryos exposed to uncontrolled gestational hyperglycemia. Pregnant rats injected with either streptozotocin or vehicle were killed on gestational day 19. Offspring brains were quickly removed to evaluate protein expression by Western blotting. Embryonic brains from diabetic rats exhibited a decrease in the cell survival p-Akt expression (52.83 ± 24.35%) and in the pro-apoptotic protein Bax (56.16 ± 6.47%). Moreover, the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 showed a non-significant increase while there were no changes in Procaspase 3 or cleaved Caspase 3 proteins. The cytoskeleton proteins NF-200 and GFAP were also examined. Neither NF-200 nor GFAP showed differences in embryonic brains from diabetic rats compared to controls. Altogether, these results indicate that both proliferation and apoptotic pathways are decreased in the brain from the developing offspring of diabetic rats. Since selective neuronal apoptosis, as well as selective cell proliferation, are specifically involved in brain organogenesis, it is possible that simultaneous impairments during the perinatal period contribute to the long lasting alterations observed in the adult brain.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhattacharya SK, Saraswati M (1991) Effect of intracerebroventricularly administered insulin on brain monoamines and acetylcholine in euglycaemic and alloxan-induced hyperglycaemic rats. Indian J Exp Biol 29:1095–1100
Biessels GJ, Kappelle AC, Bravenboer B, Erkelens DW, Gispen WH (1994) Cerebral function in diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 37:643–650
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Brazil DP, Hemmings BA (2001) Ten years of protein kinase B signalling: a hard Akt to follow. Trends Biochem Sci 26:657–664
Cannon M, Jones PB, Murray RM (2002) Obstetric complications and schizophrenia: historical and meta-analytic review. Am J Psychiatry 159:1080–1092
Casson IF, Clarke CA, Howard CV, McKendrick O, Pennycook S, Pharoah PO, Platt MJ, Stanisstreet M, van Velszen D, Walkinshaw S (1997) Outcomes of pregnancy in insulin dependent diabetic women: results of a five year population cohort study. BMJ 315:275–278
Christianson JA, Ryals JM, Johnson MS, Dobrowsky RT, Wright DE (2007) Neurotrophic modulation of myelinated cutaneous innervation and mechanical sensory loss in diabetic mice. Neuroscience 145:303–313
Coirini H, Weisenberg L, Tornello S, De Nicola AF (1980) Effect of experimental diabetes on estradiol binding by the anterior pituitary and hypothalamus in ovariectomized rats. Experientia 36:683–685
Datta SR, Brunet A, Greenberg ME (1999) Cellular survival: a play in three Akts. Genes Dev 13:2905–2927
Dennis JC, Coleman ES, Swyers SE, Moody SW, Wright JC, Judd R, Zhong Q, Morrison EE (2005) Changes in mitotic rate and GFAP expression in the primary olfactory axis of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Neurocytol 34:3–10
Dheen ST, Tay SS, Boran J, Ting LW, Kumar SD, Fu J, Ling EA (2009) Recent studies on neural tube defects in embryos of diabetic pregnancy: an overview. Curr Med Chem 16:2345–2354
Fernyhough P, Gallagher A, Averill SA, Priestley JV, Hounsom L, Patel J, Tomlinson DR (1999) Aberrant neurofilament phosphorylation in sensory neurons of rats with diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes 48:881–889
Fetita LS, Sobngwi E, Serradas P, Calvo F, Gautier JF (2006) Consequences of fetal exposure to maternal diabetes in offspring. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:3718–3724
Fine EL, Horal M, Chang TI, Fortin G, Loeken MR (1999) Evidence that elevated glucose causes altered gene expression, apoptosis, and neural tube defects in a mouse model of diabetic pregnancy. Diabetes 48:2454–2462
Foglia VG, Heller CL, Becu-Villalobos D, Weisenberg LS, Lacau de Mengido IM, Piroli G, Libertun C, De Nicola AF (1987) Neuroendocrine changes in female rats born from streptozotocin-diabetic mothers. Horm Metab Res 19:545–548
Gao Q, Gao YM (2007) Hyperglycemic condition disturbs the proliferation and cell death of neural progenitors in mouse embryonic spinal cord. Int J Dev Neurosci 25:349–357
Garcia-Caceres C, Lechuga-Sancho A, Argente J, Frago LM, Chowen JA (2008) Death of hypothalamic astrocytes in poorly controlled diabetic rats is associated with nuclear translocation of apoptosis inducing factor. J Neuroendocrinol 20:1348–1360
Gareskog M, Cederberg J, Eriksson UJ, Wentzel P (2007) Maternal diabetes in vivo and high glucose concentration in vitro increases apoptosis in rat embryos. Reprod Toxicol 23:63–74
Gispen WH, Biessels GJ (2000) Cognition and synaptic plasticity in diabetes mellitus. Trends Neurosci 23:542–549
Goldman AS, Baker L, Piddington R, Marx B, Herold R, Egler J (1985) Hyperglycemia-induced teratogenesis is mediated by a functional deficiency of arachidonic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:8227–8231
Greene MF, Hare JW, Krache M, Phillippe M, Barss VA, Saltzman DH, Nadel A, Younger MD, Heffner L, Scherl JE (1989) Prematurity among insulin-requiring diabetic gravid women. Am J Obstet Gynecol 161:106–111
Han J, Xu J, Long YS, Epstein PN, Liu YQ (2007) Rat maternal diabetes impairs pancreatic beta-cell function in the offspring. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 293:E228–E236
Hanada M, Feng J, Hemmings BA (2004) Structure, regulation and function of PKB/AKT–a major therapeutic target. Biochim Biophys Acta 1697:3–16
Hawthorne G, Robson S, Ryall EA, Sen D, Roberts SH, Ward Platt MP (1997) Prospective population based survey of outcome of pregnancy in diabetic women: results of the Northern Diabetic Pregnancy Audit, 1994. BMJ 315:279–281
Homko CJ, Sivan E, Reece EA, Boden G (1999) Fuel metabolism during pregnancy. Semin Reprod Endocrinol 17:119–125
Jacobson M (1973) Genesis of neuronal specificity. In: Rockstein M (ed) Development and aging in the nervous system. Academic Press, New York, pp 105–119
Lechuga-Sancho AM, Arroba AI, Frago LM, Garcia-Caceres C, de Celix AD, Argente J, Chowen JA (2006) Reduction in the number of astrocytes and their projections is associated with increased synaptic protein density in the hypothalamus of poorly controlled diabetic rats. Endocrinology 147:5314–5324
Lei K, Nimnual A, Zong WX, Kennedy NJ, Flavell RA, Thompson CB, Bar-Sagi D, Davis RJ (2002) The Bax subfamily of Bcl2-related proteins is essential for apoptotic signal transduction by c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase. Mol Cell Biol 22:4929–4942
McLean WG (1997) The role of axonal cytoskeleton in diabetic neuropathy. Neurochem Res 22:951–956
Medori R, Autilio-Gambetti L, Monaco S, Gambetti P (1985) Experimental diabetic neuropathy: impairment of slow transport with changes in axon cross-sectional area. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:7716–7720
Moley KH (2001) Hyperglycemia and apoptosis: mechanisms for congenital malformations and pregnancy loss in diabetic women. Trends Endocrinol Metab 12:78–82
Moley KH, Chi MM, Knudson CM, Korsmeyer SJ, Mueckler MM (1998) Hyperglycemia induces apoptosis in pre-implantation embryos through cell death effector pathways. Nat Med 4:1421–1424
Pampfer S, Vanderheyden I, McCracken JE, Vesela J, De Hertogh R (1997) Increased cell death in rat blastocysts exposed to maternal diabetes in utero and to high glucose or tumor necrosis factor-alpha in vitro. Development 124:4827–4836
Phelan SA, Ito M, Loeken MR (1997) Neural tube defects in embryos of diabetic mice: role of the Pax-3 gene and apoptosis. Diabetes 46:1189–1197
Ramanathan M, Jaiswal AK, Bhattacharya SK (2000) Hyperglycaemia in pregnancy: effects on the offspring behaviour with special reference to anxiety paradigms. Indian J Exp Biol 38:231–236
Reagan LP (2012) Diabetes as a chronic metabolic stressor: causes, consequences and clinical complications. Exp Neurol 233(1):68–78
Reece EA (1999) Maternal fuels, diabetic embryopathy: pathomechanisms and prevention. Semin Reprod Endocrinol 17:183–194
Reece EA, Wu YK (1997) Prevention of diabetic embryopathy in offspring of diabetic rats with use of a cocktail of deficient substrates and an antioxidant. Am J Obstet Gynecol 176:790–797 discussion 797–798
Reece EA, Wu YK, Wiznitzer A, Homko C, Yao J, Borenstein M, Sloskey G (1996) Dietary polyunsaturated fatty acid prevents malformations in offspring of diabetic rats. Am J Obstet Gynecol 175:818–823
Reece EA, Ma XD, Zhao Z, Wu YK, Dhanasekaran D (2005) Aberrant patterns of cellular communication in diabetes-induced embryopathy in rats: II, apoptotic pathways. Am J Obstet Gynecol 192:967–972
Reece EA, Wu YK, Zhao Z, Dhanasekaran D (2006) Dietary vitamin and lipid therapy rescues aberrant signaling and apoptosis and prevents hyperglycemia-induced diabetic embryopathy in rats. Am J Obstet Gynecol 194:580–585
Sadler TW (1980a) Effects of maternal diabetes on early embryogenesis: I. The teratogenic potential of diabetic serum. Teratology 21:339–347
Sadler TW (1980b) Effects of maternal diabetes on early embryogenesis: II. Hyperglycemia-induced exencephaly. Teratology 21:349–356
Scheid MP, Woodgett JR (2001) PKB/AKT: functional insights from genetic models. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:760–768
Scott JN, Clark AW, Zochodne DW (1999) Neurofilament and tubulin gene expression in progressive experimental diabetes: failure of synthesis and export by sensory neurons. Brain 122(Pt 11):2109–2118
Sivan E, Lee YC, Wu YK, Reece EA (1997) Free radical scavenging enzymes in fetal dysmorphogenesis among offspring of diabetic rats. Teratology 56:343–349
Sun F, Kawasaki E, Akazawa S, Hishikawa Y, Sugahara K, Kamihira S, Koji T, Eguchi K (2005) Apoptosis and its pathway in early post-implantation embryos of diabetic rats. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 67:110–118
Van Lieshout RJ, Voruganti LP (2008) Diabetes mellitus during pregnancy and increased risk of schizophrenia in offspring: a review of the evidence and putative mechanisms. J Psychiatry Neurosci 33:395–404
Varma S, Lal BK, Zheng R, Breslin JW, Saito S, Pappas PJ, Hobson RW II, Duran WN (2005) Hyperglycemia alters PI3k and Akt signaling and leads to endothelial cell proliferative dysfunction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 289:H1744–H1751
Vosseller K, Wells L, Lane MD, Hart GW (2002) Elevated nucleocytoplasmic glycosylation by O-GlcNAc results in insulin resistance associated with defects in Akt activation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:5313–5318
Wentzel P, Gareskog M, Eriksson UJ (2008) Decreased cardiac glutathione peroxidase levels and enhanced mandibular apoptosis in malformed embryos of diabetic rats. Diabetes 57:3344–3352
White LD, Barone S Jr (2001) Qualitative and quantitative estimates of apoptosis from birth to senescence in the rat brain. Cell Death Differ 8:345–356
Yamano T, Shimada M, Fujizeki Y, Kawasaki H, Onaga A (1986) Quantitative synaptic changes on Purkinje cell dendritic spines of rats born from streptozotocin-induced diabetic mothers. Brain Dev 8:269–273
Yang P, Zhao Z, Reece EA (2008a) Activation of oxidative stress signalling that is implicated in apoptosis with a mouse model of diabetic embryopathy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 198(130):e131–e137
Yang P, Zhao Z, Reece EA (2008b) Blockade of c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation abrogates hyperglycemia-induced yolk sac vasculopathy in vitro. Am J Obstet Gynecol 198(321):e321–e327
Zabihi S, Eriksson UJ, Wentzel P (2007) Folic acid supplementation affects ROS scavenging enzymes, enhances Vegf-A, and diminishes apoptotic state in yolk sacs of embryos of diabetic rats. Reprod Toxicol 23:486–498
Zdychova J, Komers R (2005) Emerging role of Akt kinase/protein kinase B signaling in pathophysiology of diabetes and its complications. Physiol Res 54:1–16
Zhao Z, Yang P, Eckert RL, Reece EA (2009) Caspase-8: a key role in the pathogenesis of diabetic embryopathy. Birth Defects Res B Dev Reprod Toxicol 86:72–77
Acknowledgments
This study was partially supported by grants from the University of Buenos Aires (UBACYT, M012), and the Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas de la República Argentina (CONICET, PIP860), J B. was supported by CONICET fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
María Sol Kruse and Joaquín Barutta contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kruse, M.S., Barutta, J., Vega, M.C. et al. Down regulation of the Proliferation and Apoptotic Pathways in the Embryonic Brain of Diabetic Rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol 32, 1031–1037 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-012-9820-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-012-9820-8