Abstract
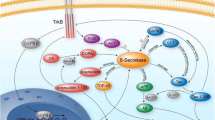
Although γ-secretase was first identified as a protease that cleaves amyloid precursor protein (APP) within the transmembrane domain, thus producing Aβ peptides that are thought to be pathogenic in Alzheimer’s disease (AD), its physiological functions have not been fully elucidated. In the canonical Notch signaling pathway, intramembrane cleavage by γ-secretase serves to release an intracellular domain of Notch that shows activity in the nucleus through binding to transcription factors. Many type 1 transmembrane proteins, including Notch, Delta, and APP, have recently been shown to be substrates for γ-secretase, and their intracellular domains are released from the cell membrane following cleavage by γ-secretase. The common enzyme γ-secretase modulates proteolysis and the turnover of possible signaling molecules, which has led to the attractive hypothesis that mechanisms similar to Notch signaling contribute widely to proteolysis-regulated signaling pathways. APP is also likely to have a signaling mechanism, although the physiological functions of APP have not been elucidated. Indeed, we have shown that the intracellular domain of APP alters gene expression and induces neuron-specific apoptosis. These results suggest that APP signaling responds to the onset of AD. Here, we review the possibility of γ-secretase-regulated signaling, including APP signaling, which leads to AD.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- APP:
-
Amyloid precursor protein
- AICD:
-
The intracellular domain of APP
- bHLH:
-
Basic helix-loop-helix
- C. elegans :
-
Caenorhabditis elegans
- Dll:
-
Delta-like protein
- Dll1IC:
-
The intracellular domain of Dll1
- EGF:
-
Epidermal growth factor
- GO:
-
Gene ontology
- Hes:
-
Hairy/enhancer of split
- JM:
-
Juxtamembrane
- PS:
-
Presenilin
- ICD:
-
Intracellular domain
- NICD:
-
The intracellular domain of Notch
- RA:
-
All-trans-retinoic acid
- RIP:
-
The regulated intramembrane proteolysis
- TM:
-
Transmembrane
References
Abbott A (2008) The plaque plan. Nature 456:161–164
Akazawa C, Sasai Y, Nakanishi S, Kageyama R (1992) Molecular characterization of a rat negative regulator with a basic helix-loop-helix structure predominantly expressed in the developing nervous system. J Biol Chem 267:21879–21885
Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Matsuno K, Fortini ME (1995) Notch signaling. Science 268:225–232
Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD, Lake RJ (1999) Notch signaling: cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science 284:770–776
Baek SH, Ohgi KA, Rose DW, Koo EH, Glass CK, Rosenfeld MG (2002) Exchange of N-CoR corepressor and Tip60 coactivator complexes links gene expression by NF-kappaB and beta-amyloid precursor protein. Cell 110:55–67
Bettenhausen B, Hrabe de Angelis M, Simon D, Guenet JL, Gossler A (1995) Transient and restricted expression during mouse embryogenesis of Dll1, a murine gene closely related to Drosophila Delta. Development 121:2407–2418
Bibel M, Richter J, Schrenk K, Tucker KL, Staiger V, Korte M, Goetz M, Barde YA (2004) Differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells into a defined neuronal lineage. Nat Neurosci 7:1003–1009
Blalock EM, Geddes JW, Chen KC, Porter NM, Markesbery WR, Landfield PW (2004) Incipient Alzheimer’s disease: microarray correlation analyses reveal major transcriptional and tumor suppressor responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:2173–2178
Bolos V, Grego-Bessa J, de la Pompa JL (2007) Notch signaling in development and cancer. Endocr Rev 28:339–363
Brown MS, Ye J, Rawson RB, Goldstein JL (2000) Regulated intramembrane proteolysis: a control mechanism conserved from bacteria to humans. Cell 100:391–398
Buoso E, Lanni C, Schettini G, Govoni S, Racchi M (2010) beta-Amyloid precursor protein metabolism: focus on the functions and degradation of its intracellular domain. Pharmacol Res 62:308–317
Buxbaum JD, Liu KN, Luo Y, Slack JL, Stocking KL, Peschon JJ, Johnson RS, Castner BJ, Cerretti DP, Black RA (1998) Evidence that tumor necrosis factor alpha converting enzyme is involved in regulated alpha-secretase cleavage of the Alzheimer amyloid protein precursor. J Biol Chem 273:27765–27767
Cao X, Sudhof TC (2001) A transcriptionally [correction of transcriptively] active complex of APP with Fe65 and histone acetyltransferase Tip60. Science 293:115–120
Coulson EJ, Paliga K, Beyreuther K, Masters CL (2000) What the evolution of the amyloid protein precursor supergene family tells us about its function. Neurochem Int 36:175–184
Cupers P, Orlans I, Craessaerts K, Annaert W, De Strooper B (2001) The amyloid precursor protein (APP)-cytoplasmic fragment generated by gamma-secretase is rapidly degraded but distributes partially in a nuclear fraction of neurones in culture. J Neurochem 78:1168–1178
Daigle I, Li C (1993) apl-1, a Caenorhabditis elegans gene encoding a protein related to the human beta-amyloid protein precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:12045–12049
Dunwoodie SL, Henrique D, Harrison SM, Beddington RS (1997) Mouse Dll3: a novel divergent Delta gene which may complement the function of other Delta homologues during early pattern formation in the mouse embryo. Development 124:3065–3076
Edbauer D, Willem M, Lammich S, Steiner H, Haass C (2002) Insulin-degrading enzyme rapidly removes the beta-amyloid precursor protein intracellular domain (AICD). J Biol Chem 277:13389–13393
Ellisen LW, Bird J, West DC, Soreng AL, Reynolds TC, Smith SD, Sklar J (1991) TAN-1, the human homolog of the Drosophila notch gene, is broken by chromosomal translocations in T lymphoblastic neoplasms. Cell 66:649–661
Esch FS, Keim PS, Beattie EC, Blacher RW, Culwell AR, Oltersdorf T, McClure D, Ward PJ (1990) Cleavage of amyloid beta peptide during constitutive processing of its precursor. Science 248:1122–1124
Farzan M, Schnitzler CE, Vasilieva N, Leung D, Choe H (2000) BACE2, a beta -secretase homolog, cleaves at the beta site and within the amyloid-beta region of the amyloid-beta precursor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:9712–9717
Fleming RJ, Scottgale TN, Diederich RJ, Artavanis-Tsakonas S (1990) The gene Serrate encodes a putative EGF-like transmembrane protein essential for proper ectodermal development in Drosophila melanogaster. Genes Dev 4:2188–2201
Gao Y, Pimplikar SW (2001) The gamma-secretase-cleaved C-terminal fragment of amyloid precursor protein mediates signaling to the nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:14979–14984
Ghosal K, Vogt DL, Liang M, Shen Y, Lamb BT, Pimplikar SW (2009) Alzheimer’s disease-like pathological features in transgenic mice expressing the APP intracellular domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:18367–18372
Giliberto L, d’Abramo C, Acker CM, Davies P, D’Adamio L (2010) Transgenic expression of the amyloid-beta precursor protein-intracellular domain does not induce Alzheimer’s disease-like traits in vivo. PLoS One 5(7):e11609. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0011609
Goate A, Chartier-Harlin MC, Mullan M, Brown J, Crawford F, Fidani L, Giuffra L, Haynes A, Irving N, James L et al (1991) Segregation of a missense mutation in the amyloid precursor protein gene with familial Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 349:704–706
Guenette SY (2002) A role for APP in motility and transcription? Trends Pharmacol Sci 23:203–205 (discussion 205–206)
Haass C, Selkoe DJ (1993) Cellular processing of beta-amyloid precursor protein and the genesis of amyloid beta-peptide. Cell 75:1039–1042
Hardy J (1997) Amyloid, the presenilins and Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Neurosci 20:154–159
Hardy J, Selkoe DJ (2002) The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 297:353–356
Henderson ST, Gao D, Christensen S, Kimble J (1997) Functional domains of LAG-2, a putative signaling ligand for LIN-12 and GLP-1 receptors in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol Biol Cell 8:1751–1762
Hiratochi M, Nagase H, Kuramochi Y, Koh CS, Ohkawara T, Nakayama K (2007) The Delta intracellular domain mediates TGF-beta/Activin signaling through binding to Smads and has an important bi-directional function in the Notch-Delta signaling pathway. Nucleic Acids Res 35:912–922
Ho A, Sudhof TC (2004) Binding of F-spondin to amyloid-beta precursor protein: a candidate amyloid-beta precursor protein ligand that modulates amyloid-beta precursor protein cleavage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:2548–2553
Hung AY, Koo EH, Haass C, Selkoe DJ (1992) Increased expression of beta-amyloid precursor protein during neuronal differentiation is not accompanied by secretory cleavage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:9439–9443
Ikeuchi T, Sisodia SS (2003) The Notch ligands, Delta1 and Jagged2, are substrates for presenilin-dependent “gamma-secretase” cleavage. J Biol Chem 278:7751–7754
Iso T, Sartorelli V, Poizat C, Iezzi S, Wu HY, Chung G, Kedes L, Hamamori Y (2001) HERP, a novel heterodimer partner of HES/E(spl) in Notch signaling. Mol Cell Biol 21:6080–6089
Iwatsubo T (2004) The gamma-secretase complex: machinery for intramembrane proteolysis. Curr Opin Neurobiol 14:379–383
Joutel A, Corpechot C, Ducros A, Vahedi K, Chabriat H, Mouton P, Alamowitch S, Domenga V, Cecillion M, Marechal E, Maciazek J, Vayssiere C, Cruaud C, Cabanis EA, Ruchoux MM, Weissenbach J, Bach JF, Bousser MG, Tournier-Lasserve E (1996) Notch3 mutations in CADASIL, a hereditary adult-onset condition causing stroke and dementia. Nature 383:707–710
Justice NJ, Jan YN (2002) Variations on the Notch pathway in neural development. Curr Opin Neurobiol 12:64–70
Kageyama R, Ohtsuka T, Kobayashi T (2007) The Hes gene family: repressors and oscillators that orchestrate embryogenesis. Development 134:1243–1251
Kang J, Lemaire HG, Unterbeck A, Salbaum JM, Masters CL, Grzeschik KH, Multhaup G, Beyreuther K, Muller-Hill B (1987) The precursor of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor. Nature 325:733–736
Kimberly WT, Zheng JB, Guenette SY, Selkoe DJ (2001) The intracellular domain of the beta-amyloid precursor protein is stabilized by Fe65 and translocates to the nucleus in a notch-like manner. J Biol Chem 276:40288–40292
Kimberly WT, Zheng JB, Town T, Flavell RA, Selkoe DJ (2005) Physiological regulation of the beta-amyloid precursor protein signaling domain by c-Jun N-terminal kinase JNK3 during neuronal differentiation. J Neurosci 25:5533–5543
Klein WL, Krafft GA, Finch CE (2001) Targeting small Abeta oligomers: the solution to an Alzheimer’s disease conundrum? Trends Neurosci 24:219–224
Koo EH, Kopan R (2004) Potential role of presenilin-regulated signaling pathways in sporadic neurodegeneration. Nat Med 10(Suppl):S26–S33
Kopan R, Ilagan MX (2004) Gamma-secretase: proteasome of the membrane? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5:499–504
Kopczynski CC, Alton AK, Fechtel K, Kooh PJ, Muskavitch MA (1988) Delta, a Drosophila neurogenic gene, is transcriptionally complex and encodes a protein related to blood coagulation factors and epidermal growth factor of vertebrates. Genes Dev 2:1723–1735
Lammich S, Kojro E, Postina R, Gilbert S, Pfeiffer R, Jasionowski M, Haass C, Fahrenholz F (1999) Constitutive and regulated alpha-secretase cleavage of Alzheimer’s amyloid precursor protein by a disintegrin metalloprotease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:3922–3927
LaVoie MJ, Selkoe DJ (2003) The Notch ligands, Jagged and Delta, are sequentially processed by alpha-secretase and presenilin/gamma-secretase and release signaling fragments. J Biol Chem 278:34427–34437
Leimeister C, Externbrink A, Klamt B, Gessler M (1999) Hey genes: a novel subfamily of hairy- and enhancer of split related genes specifically expressed during mouse embryogenesis. Mech Dev 85:173–177
Levitan D, Greenwald I (1995) Facilitation of lin-12-mediated signalling by sel-12, a Caenorhabditis elegans S182 Alzheimer’s disease gene. Nature 377:351–354
Levy-Lahad E, Wasco W, Poorkaj P, Romano DM, Oshima J, Pettingell WH, Yu CE, Jondro PD, Schmidt SD, Wang K et al (1995) Candidate gene for the chromosome 1 familial Alzheimer’s disease locus. Science 269:973–977
Lewis J (1998) Notch signalling and the control of cell fate choices in vertebrates. Semin Cell Dev Biol 9:583–589
Leyssen M, Ayaz D, Hebert SS, Reeve S, De Strooper B, Hassan BA (2005) Amyloid precursor protein promotes post-developmental neurite arborization in the Drosophila brain. EMBO J 24:2944–2955
Liang WS, Dunckley T, Beach TG, Grover A, Mastroeni D, Ramsey K, Caselli RJ, Kukull WA, McKeel D, Morris JC, Hulette CM, Schmechel D, Reiman EM, Rogers J, Stephan DA (2008) Altered neuronal gene expression in brain regions differentially affected by Alzheimer’s disease: a reference data set. Physiol Genomics 33:240–256
Lindsell CE, Shawber CJ, Boulter J, Weinmaster G (1995) Jagged: a mammalian ligand that activates Notch1. Cell 80:909–917
Lorenzo A, Yuan M, Zhang Z, Paganetti PA, Sturchler-Pierrat C, Staufenbiel M, Mautino J, Vigo FS, Sommer B, Yankner BA (2000) Amyloid beta interacts with the amyloid precursor protein: a potential toxic mechanism in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Neurosci 3:460–464
Lott IT, Head E (2005) Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome: factors in pathogenesis. Neurobiol Aging 26:383–389
Luo LQ, Martin-Morris LE, White K (1990) Identification, secretion, and neural expression of APPL, a Drosophila protein similar to human amyloid protein precursor. J Neurosci 10:3849–3861
McCarthy JV, Twomey C, Wujek P (2009) Presenilin-dependent regulated intramembrane proteolysis and gamma-secretase activity. Cell Mol Life Sci 66:1534–1555
McGowan E, Pickford F, Dickson D (2003) Alzheimer animal models: models of Abeta deposition in transgenic mice. In: Dickson D (ed) Neurodegeneration: the molecular pathology of dementia and movement disorders. ISN Neuropath Press, Basel, pp 74–79
Muller T, Meyer HE, Egensperger R, Marcus K (2008) The amyloid precursor protein intracellular domain (AICD) as modulator of gene expression, apoptosis, and cytoskeletal dynamics-relevance for Alzheimer’s disease. Prog Neurobiol 85:393–406
Nagase H, Koh CS, Nakayama K (2010) gamma-Secretase-regulated signaling pathways, such as Notch signaling, mediate the differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells, development of the immune system, and peripheral immune responses. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther [Epub ahead of print]
Nakayama K, Nagase K, Tokutake Y, Koh CS, Hiratochi M, Ohkawara T, Nakayama N (2004) Multiple POU-binding motifs, recognized by tissue-specific nuclear factors, are important for Dll1 gene expression in neural stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 325:991–996
Nakayama K, Nagase H, Hiratochi M, Koh CS, Ohkawara T (2008a) Similar mechanisms regulated by gamma-secretase are involved in both directions of the bi-directional Notch-Delta signaling pathway as well as play a potential role in signaling events involving type 1 transmembrane proteins. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther 3:288–302
Nakayama K, Ohkawara T, Hiratochi M, Koh CS, Nagase H (2008b) The intracellular domain of amyloid precursor protein induces neuron-specific apoptosis. Neurosci Lett 444:127–131
Ni CY, Murphy MP, Golde TE, Carpenter G (2001) gamma-Secretase cleavage and nuclear localization of ErbB-4 receptor tyrosine kinase. Science 294:2179–2181
Nikolaev A, McLaughlin T, O’Leary DD, Tessier-Lavigne M (2009) APP binds DR6 to trigger axon pruning and neuron death via distinct caspases. Nature 457:981–989
Ohkawara T, Nagase H, Koh CS, Nakayama K (2011) The amyloid precursor protein intracellular domain alters gene expression and induces neuron-specific apoptosis. Gene 475(1):1–9
Park JH, Gimbel DA, GrandPre T, Lee JK, Kim JE, Li W, Lee DH, Strittmatter SM (2006) Alzheimer precursor protein interaction with the Nogo-66 receptor reduces amyloid-beta plaque deposition. J Neurosci 26:1386–1395
Rebay I, Fleming RJ, Fehon RG, Cherbas L, Cherbas P, Artavanis-Tsakonas S (1991) Specific EGF repeats of Notch mediate interactions with Delta and Serrate: implications for Notch as a multifunctional receptor. Cell 67:687–699
Roehl H, Bosenberg M, Blelloch R, Kimble J (1996) Roles of the RAM and ANK domains in signaling by the C. elegans GLP-1 receptor. EMBO J 15:7002–7012
Rogaev EI, Sherrington R, Rogaeva EA, Levesque G, Ikeda M, Liang Y, Chi H, Lin C, Holman K, Tsuda T et al (1995) Familial Alzheimer’s disease in kindreds with missense mutations in a gene on chromosome 1 related to the Alzheimer’s disease type 3 gene. Nature 376:775–778
Rohn JL, Lauring AS, Linenberger ML, Overbaugh J (1996) Transduction of Notch2 in feline leukemia virus-induced thymic lymphoma. J Virol 70:8071–8080
Rosen DR, Martin-Morris L, Luo LQ, White K (1989) A Drosophila gene encoding a protein resembling the human beta-amyloid protein precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 86:2478–2482
Ryan KA, Pimplikar SW (2005) Activation of GSK-3 and phosphorylation of CRMP2 in transgenic mice expressing APP intracellular domain. J Cell Biol 171:327–335
Sarkar NH, Haga S, Lehner AF, Zhao W, Imai S, Moriwaki K (1994) Insertional mutation of int protooncogenes in the mammary tumors of a new strain of mice derived from the wild in China: normal- and tumor-tissue-specific expression of int-3 transcripts. Virology 203:52–62
Schnabel J (2009) Alzheimer’s theory makes a splash. Nature 459:310
Schroeter EH, Kisslinger JA, Kopan R (1998) Notch-1 signalling requires ligand-induced proteolytic release of intracellular domain. Nature 393:382–386
Schulz JG, Annaert W, Vandekerckhove J, Zimmermann P, De Strooper B, David G (2003) Syndecan 3 intramembrane proteolysis is presenilin/gamma-secretase-dependent and modulates cytosolic signaling. J Biol Chem 278:48651–48657
Selkoe DJ (2001) Alzheimer’s disease: genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol Rev 81:741–766
Selkoe DJ (2002) Alzheimer’s disease is a synaptic failure. Science 298:789–791
Selkoe D, Kopan R (2003) Notch and Presenilin: regulated intramembrane proteolysis links development and degeneration. Annu Rev Neurosci 26:565–597
Selkoe DJ, Wolfe MS (2007) Presenilin: running with scissors in the membrane. Cell 131:215–221
Shah S, Lee SF, Tabuchi K, Hao YH, Yu C, LaPlant Q, Ball H, Dann CE 3rd, Sudhof T, Yu G (2005) Nicastrin functions as a gamma-secretase-substrate receptor. Cell 122:435–447
Shawber C, Boulter J, Lindsell CE, Weinmaster G (1996) Jagged2: a serrate-like gene expressed during rat embryogenesis. Dev Biol 180:370–376
Sherrington R, Rogaev EI, Liang Y, Rogaeva EA, Levesque G, Ikeda M, Chi H, Lin C, Li G, Holman K, Tsuda T, Mar L, Foncin JF, Bruni AC, Montesi MP, Sorbi S, Rainero I, Pinessi L, Nee L, Chumakov I, Pollen D, Brookes A, Sanseau P, Polinsky RJ, Wasco W, Da Silva HA, Haines JL, Perkicak-Vance MA, Tanzi RE, Roses AD, Fraser PE, Rommens JM, St George-Hyslop PH (1995) Cloning of a gene bearing missense mutations in early-onset familial Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 375:754–760
Shutter JR, Scully S, Fan W, Richards WG, Kitajewski J, Deblandre GA, Kintner CR, Stark KL (2000) Dll4, a novel Notch ligand expressed in arterial endothelium. Genes Dev 14:1313–1318
Sisodia SS, Koo EH, Hoffman PN, Perry G, Price DL (1993) Identification and transport of full-length amyloid precursor proteins in rat peripheral nervous system. J Neurosci 13:3136–3142
Six E, Ndiaye D, Laabi Y, Brou C, Gupta-Rossi N, Israel A, Logeat F (2003) The Notch ligand Delta1 is sequentially cleaved by an ADAM protease and gamma-secretase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:7638–7643
Slomnicki LP, Lesniak W (2008) A putative role of the Amyloid Precursor Protein Intracellular Domain (AICD) in transcription. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 68:219–228
Soba P, Eggert S, Wagner K, Zentgraf H, Siehl K, Kreger S, Lower A, Langer A, Merdes G, Paro R, Masters CL, Muller U, Kins S, Beyreuther K (2005) Homo- and heterodimerization of APP family members promotes intercellular adhesion. EMBO J 24:3624–3634
Struhl G, Adachi A (2000) Requirements for presenilin-dependent cleavage of notch and other transmembrane proteins. Mol Cell 6:625–636
Tax FE, Yeargers JJ, Thomas JH (1994) Sequence of C. elegans lag-2 reveals a cell-signalling domain shared with Delta and Serrate of Drosophila. Nature 368:150–154
Terry RD, Katzman R, Bick KL, Sisodia SS (1999) Alzheimer’s disease. Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Vassar R, Bennett BD, Babu-Khan S, Kahn S, Mendiaz EA, Denis P, Teplow DB, Ross S, Amarante P, Loeloff R, Luo Y, Fisher S, Fuller J, Edenson S, Lile J, Jarosinski MA, Biere AL, Curran E, Burgess T, Louis JC, Collins F, Treanor J, Rogers G, Citron M (1999) Beta-secretase cleavage of Alzheimer’s amyloid precursor protein by the transmembrane aspartic protease BACE. Science 286:735–741
Vazquez MC, Vargas LM, Inestrosa NC, Alvarez AR (2009) c-Abl modulates AICD dependent cellular responses: transcriptional induction and apoptosis. J Cell Physiol 220:136–143
Vogt DL, Thomas D, Galvan V, Bredesen DE, Lamb BT, Pimplikar SW (2009) Abnormal neuronal networks and seizure susceptibility in mice overexpressing the APP intracellular domain. Neurobiol Aging. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2009.09.002
Wallberg AE, Pedersen K, Lendahl U, Roeder RG (2002) p300 and PCAF act cooperatively to mediate transcriptional activation from chromatin templates by notch intracellular domains in vitro. Mol Cell Biol 22:7812–7819
Wang Y, Ha Y (2004) The X-ray structure of an antiparallel dimer of the human amyloid precursor protein E2 domain. Mol Cell 15:343–353
Wharton KA, Johansen KM, Xu T, Artavanis-Tsakonas S (1985) Nucleotide sequence from the neurogenic locus notch implies a gene product that shares homology with proteins containing EGF-like repeats. Cell 43:567–581
Wu L, Aster JC, Blacklow SC, Lake R, Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Griffin JD (2000) MAML1, a human homologue of Drosophila mastermind, is a transcriptional co-activator for NOTCH receptors. Nat Genet 26:484–489
Yoshikai S, Sasaki H, Doh-ura K, Furuya H, Sakaki Y (1990) Genomic organization of the human amyloid beta-protein precursor gene. Gene 87:257–263
Yu G, Nishimura M, Arawaka S, Levitan D, Zhang L, Tandon A, Song YQ, Rogaeva E, Chen F, Kawarai T, Supala A, Levesque L, Yu H, Yang DS, Holmes E, Milman P, Liang Y, Zhang DM, Xu DH, Sato C, Rogaev E, Smith M, Janus C, Zhang Y, Aebersold R, Farrer LS, Sorbi S, Bruni A, Fraser P, St George-Hyslop P (2000) Nicastrin modulates presenilin-mediated notch/glp-1 signal transduction and betaAPP processing. Nature 407:48–54
Zheng H, Koo EH (2006) The amyloid precursor protein: beyond amyloid. Mol Neurodegener 1:5
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakayama, K., Nagase, H., Koh, CS. et al. γ-Secretase-Regulated Mechanisms Similar to Notch Signaling May Play a Role in Signaling Events, Including APP Signaling, Which Leads to Alzheimer’s Disease. Cell Mol Neurobiol 31, 887–900 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-011-9688-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-011-9688-z