Abstract
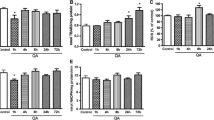
It is well known that traumatic or ischemic brain injury is followed by acute excitotoxicity caused by the presence of abnormally high glutamate (Glu) in brain fluids. It has recently been demonstrated that excess Glu can be eliminated from brain into blood following the intravenous administration of oxaloacetate (OxAc), which, by scavenging blood Glu, induces an enhanced and neuroprotective brain-to-blood Glu efflux. In this study, we subjected rats to intravenous OxAc administration (i.v., 12.5, 25, and 50 mg/kg, respectively), and studied its effects on somatosensory evoked cortical potentials (EPs). Against our expectation, the amplitudes of EPs did not decrease but increased in a dose- and time-dependent manner after OxAc administration. Similar effects were observed when blood Glu scavenging was enhanced by combining OxAc (12.5 mg/kgbw) with recombinant glutamate–oxaloacetate transaminase (GOT, 0.14 nmol/100 g rat). On the basis of these results, we suggest that the changes of amplitudes of the EPs involve not only a glutamatergic but also the weakening of a GABAergic component. We cannot rule out the possibility that OxAc penetrates into the brain and improves mitochondrial functions.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belan PV, Kostyuk PG (2002) Glutamate-receptor-induced modulation of GABAergic synaptic transmission in the hippocampus. Pflugers Arch 444:26–37
Castillo J, Davalos A, Naveiro J, Noya M (1996) Neuroexcitatory amino acids and their relation to infarct size and neurological deficit in ischemic stroke. Stroke 27:1060–1065
Danbolt NC (2001) Glutamate uptake. Prog Neurobiol 65:1–105
Engelman HS, MacDermott AB (2004) Presynaptic ionotropic receptors and control of transmitter release. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:135–145
Farazifard R, Wu SH (2010) Metabotropic glutamate receptors modulate glutamatergic and GABAergic synaptic transmission in the central nucleus of the inferior colliculus. Brain Res 1325:28–40
Farkas T, Kis Z, Toldi J, Wolff JR (1999) Activation of the primary motor cortex by somatosensory stimulation in adult rats is mediated mainly by associational connections from the somatosensory cortex. Neuroscience 90:353–361
Farkas T, Perge J, Kis Z, Wolff JR, Toldi J (2000) Facial nerve injury-induced disinhibition in the primary motor cortices of both hemispheres. Eur J Neurosci 12:2190–2194
Foster AC, Kemp JA (2006) Glutamate- and GABA-based CNS therapeutics. Curr Opin Pharmacol 6:7–17
Franceschini MA, Nissila I, Wu W, Diamond SG, Bonmassar G, Boas DA (2008) Coupling between somatosensory evoked potentials and hemodynamic response in the rat. Neuroimage 41:189–203
Gottlieb M, Wang Y, Teichberg VI (2003) Blood-mediated scavenging of cerebrospinal fluid glutamate. J Neurochem 87:119–126
Holmes O, Short AD (1970) Interaction of cortical evoked potentials in the rat. J Physiol 209:433–452
Johnston MV, Trescher WH, Ishida A, Nakajima W (2001) Neurobiology of hypoxic-ischemic injury in the developing brain. Pediatr Res 49:735–741
Kamsler A, Segal M (2003) Hydrogen peroxide modulation of synaptic plasticity. J Neurosci 23:269–276
Kessler M, Terramani T, Lynch G, Baudry M (1989) A glycine site associated with N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptors: characterization and identification of a new class of antagonists. J Neurochem 52:1319–1328
Kullmann DM, Semyanov A (2002) Glutamatergic modulation of GABAergic signaling among hippocampal interneurons: novel mechanisms regulating hippocampal excitability. Epilepsia 43(suppl 5):174–178
Liu SJ (2007) Biphasic modulation of GABA release from stellate cells by glutamatergic receptor subtypes. J Neurophysiol 98:550–556
Lur G, Rakos G, Juhasz-Vedres G, Farkas T, Kis Z, Toldi J (2006) Effects of dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate on the evoked cortical activity of controls and of brain-injured rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol 26:1505–1519
Marosi M, Fuzik J, Nagy D, Rakos G, Kis Z, Vecsei L, Toldi J, Ruban-Matuzani A, Teichberg VI, Farkas T (2009) Oxaloacetate restores the long-term potentiation impaired in rat hippocampus CA1 region by 2-vessel occlusion. Eur J Pharmacol 604:51–57
Nagy D, Marosi M, Kis Z, Farkas T, Rakos G, Vecsei L, Teichberg VI, Toldi J (2009) Oxaloacetate decreases the infarct size and attenuates the reduction in evoked responses after photothrombotic focal ischemia in the rat cortex. Cell Mol Neurobiol 29:827–835
Sas K, Robotka H, Toldi J, Vecsei L (2007) Mitochondria, metabolic disturbances, oxidative stress and the kynurenine system, with focus on neurodegenerative disorders. J Neurol Sci 257:221–239
Sattler R, Tymianski M (2001) Molecular mechanisms of glutamate receptor-mediated excitotoxic neuronal cell death. Mol Neurobiol 24:107–129
Stoffel M, Plesnila N, Eriskat J, Furst M, Baethmann A (2002) Release of excitatory amino acids in the penumbra of a focal cortical necrosis. J Neurotrauma 19:467–477
Stone TW, Forrest CM, Mackay GM, Stoy N, Darlington LG (2007) Tryptophan, adenosine, neurodegeneration and neuroprotection. Metab Brain Dis 22:337–352
Suzuki M, Kudo A, Sugawara A, Yoshida K, Kubo Y, Suzuki T, Ogasawara K, Doi M, Ogawa A (2002) Amino acid concentrations in the blood of the jugular vein and peripheral artery after traumatic brain injury: decreased release of glutamate into the jugular vein in the early phase. J Neurotrauma 19:285–292
Teichberg VI, Cohen-Kashi-Malina K, Cooper I, Zlotnik A (2009) Homeostasis of glutamate in brain fluids: an accelerated brain-to-blood efflux of excess glutamate is produced by blood glutamate scavenging and offers protection from neuropathologies. Neuroscience 158:301–308
Toldi J, Farkas T, Volgyi B (1994) Neonatal enucleation induces cross-modal changes in the barrel cortex of rat. A behavioural and electrophysiological study. Neurosci Lett 167:1–4
Toldi J, Farkas T, Perge J, Wolff JR (1999) Facial nerve injury produces a latent somatosensory input through recruitment of the motor cortex in the rat. Neuroreport 10:2143–2147
Vesce S, Rossi D, Brambilla L, Volterra A (2007) Glutamate release from astrocytes in physiological conditions and in neurodegenerative disorders characterized by neuroinflammation. Int Rev Neurobiol 82:57–71
Zlotnik A, Gurevich B, Tkachov S, Maoz I, Shapira Y, Teichberg VI (2007) Brain neuroprotection by scavenging blood glutamate. Exp Neurol 203:213–220
Zlotnik A, Gurevich B, Cherniavsky E, Tkachov S, Matuzani-Ruban A, Leon A, Shapira Y, Teichberg VI (2008) The contribution of the blood glutamate scavenging activity of pyruvate to its neuroprotective properties in a rat model of closed head injury. Neurochem Res 33:1044–1050
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the OTKA K75628. FT is a Bolyai Fellow of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences. V.I.T. has received support from Nella and Leon Benoziyo Center for Neurological Diseases at the Weizmann Institute.
Disclosure statement
No conflicting financial interests exist.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagy, D., Knapp, L., Marosi, M. et al. Effects of Blood Glutamate Scavenging on Cortical Evoked Potentials. Cell Mol Neurobiol 30, 1101–1106 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-010-9542-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-010-9542-8