Abstract
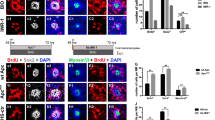
The neuromasts of the lateral line system are regarded as a model to study the mechanisms of hearing, deafness, and ototoxicity. The neurotrophins (NTs), especially brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), and its signaling receptor TrkB are involved in the development and maintenance of neuromasts. To know the period in which the BDNF/TrkB complex has more effects in the neuromast biology, the age-related changes were studied. Normal zebrafish from 10 to 180 days post-fertilization (dpf), as well as transgenic ET4 zebrafish 10 and 20 dpf, was analyzed using qRT-PCR, western blot, and immunohistochemistry. BDNF and TrkB mRNAs followed a parallel course, peaking at 20 dpf, and thereafter progressively decreased. Specific immunoreactivity for BDNF and TrkB was found co-localized in all hairy cells of neuromasts in 20 and 30 dpf; then, the number of immunoreactive cells decreased, and by 180 dpf BDNF remains restricted to a subpopulation of hairy cells, and TrkB to a few number of sensory and non-sensory cells. At all ages examined, TrkB immunoreactivity was detected in sensory ganglia innervating the neuromasts. The present results demonstrate that there is a parallel time-related decline in the expression of BDNF and TrkB in zebrafish. Also, the patterns of cell expression suggest that autocrine/paracrine mechanisms for this NT system might occur within the neuromasts. Because TrkB in lateral line ganglia did not vary with age, their neurons are potentially capable to respond to BDNF during the entire lifespan of zebrafish.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexandre D, Ghysen A (1999) Somatotopy of the lateral line projection in larval zebrafish. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:7558–7562
Caminos E, Becker E, Martín-Zanca D, Vecino E (1999) Neurotrophins and their receptors in the tench retina during optic nerve regeneration. J Comp Neurol 404:321–331
Catania S, Germanà A, Cabo R, Ochoa-Erena FJ, Guerrera MC, Hannestad J, Represa J, Vega JA (2007) Neurotrophin and Trk neurotrophin receptors in the inner ear of Salmo salar and Salmo trutta. J Anat 210:78–88
Cernuda-Cernuda R, García-Fernández JM (1996) Structural diversity of the ordinary and specialized lateral line organs. Microsc Res Tech 34:302–312
Chiu LL, Cunningham LL, Raible DW, Rubel EW, Ou HC (2008) Using the zebrafish lateral line to screen for ototoxicity. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 9:178–190
Coombs S, Fay RR, Janssen J (1989) Hot-film anemometry for measuring lateral line stimuli. J Acoust Soc Am 85:2185–2193
Dufourcq P, Roussigné M, Blader P, Rosa F, Peyrieras N, Vriz S (2006) Mechano-sensory organ regeneration in adults: the zebrafish lateral line as a model. Mol Cell Neurosci 33:180–187
Fritzsch B, Silos-Santiago I, Biacnhi LM, Fariñas I (1997) The role of neurotrophic factors in regulating the development of inner ear innervation. Trends Neurosci 16:493–505
Fritzsch B, Tessarollo L, Coppola E, Reichardt LF (2004) Neurotrophins in the ear: their roles in sensory neuron survival and fiber guidance. Prog Brain Res 146:265–278
Froehlicher M, Liedtke A, Groh KJ, Neuhauss SC, Segner H, Eggen RI (2009) Zebrafish (Danio rerio) neuromast: promising biological endpoint linking developmental and toxicological studies. Aquat Toxicol 95:307–319
Germanà A, Catania S, Cavallaro M, González-Martínez T, Ciriaco E, Hannestad J, Vega JA (2002) Immunohistochemical localization of BDNF-, TrkB- and TrkA-like proteins in the teleost lateral line system. J Anat 200:477–485
Germanà A, González-Martínez T, Catania S, Laurà R, Cobo J, Ciriaco E, Vega JA (2004) Neurotrophin receptors in taste buds of adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Neurosci Lett 354:189–192
Germanà A, Marino F, Guerrera MC, Campo S, De Girolamo P, Montalbano G, Germanà GP, Ochoa-Erena FJ, Ciriaco E, Vega JA (2008) Expression and distribution of S100 protein in the nervous system of the adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Microsc Res Tech 71:248–255
Götz R, Schartl M (1994) The conservation of neurotrophic factors during vertebrate evolution. Comp Biochem Physiol Pharmacol Toxicol Endocrinol 108:1–10 Review
Hallböök F, Lundin LG, Kullander K (1998) Lampetra fluviatilis neurotrophin homolog, descendant of a neurotrophin ancestor, discloses the early molecular evolution of neurotrophins in the vertebrate subphylum. J Neurosci 18:8700–8711
Hallböök F, Wilson K, Thorndyke M, Olinski RP (2006) Formation and evolution of the chordate neurotrophin and Trk receptor genes. Brain Behav Evol 68:133–144 Review
Hannestad J, Marino F, Germanà A, Catania S, Abbate F, Ciriaco E, Vega JA (2000) Trk neurotrophin receptor-like proteins in the teleost Dicentrarchus labrax. Cell Tissue Res 300:1–9
Hashimoto M, Heinrich G (1997) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene expression in the developing zebrafish. Int J Dev Neurosci 15:983–997
Heinrich G, Lum T (2000) Fish neurotrophins and Trk receptors. Int J Dev Neurosci 18:1–27 Review
Heinrich G, Pagtakhan CJ (2004) Both 5’ and 3’ flanks regulate Zebrafish brainderived neurotrophic factor gene expression. BMC Neurosci 5:19. doi:10.1186/1471-2202-5-19
Huynh G, Heinrich G (2001) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene organization and transcription in the zebrafish embryo. Int J Dev Neurosci 19:663–673
Kimmel CB, Ballard WW, Kimmel SR, Ullmann B, Schilling TF (1995) Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev Dyn 203:253–310
Lai KO, Fu WY, Ip FC, Ip NY (1998) Cloning and expression of a novel neurotrophin, NT-7, from carp. Mol Cell Neurosci 11:64–76
Lewin GR, Barde YA (1996) Physiology of the neurotrophins. Annu Rev Neurosci 19:289–317
Luikart BW, Nef S, Shipman T, Parada LF (2003) In vivo role of truncated TrkB receptors during sensory ganglion neurogenesis. Neuroscience 117:847–858
Lum T, Huynh G, Heinrich G (2001) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and TrkB tyrosine kinase receptor gene expression in zebrafish embryo and larva. Int J Dev Neurosci 19:569–587
Martin SC, Marazzi G, Sandell JH, Heinrich G (1995) Five Trk receptors in the zebrafish. Dev Biol 169:745–758
Martin SC, Sandell JH, Heinrich G (1998) Zebrafish TrkC1 and TrkC2 receptors define two different cell populations in the nervous system during the period of axonogenesis. Dev Biol 195:114–130
McGuinness SL, Shepherd RK (2005) Exogenous BDNF rescues rat spiral ganglion neuronsin vivo. Otol Neurotol 26:1064–1072
Meen E, Blakley B, Quddusi T (2009) Brain-derived nerve growth factor in the treatment of sensorineural hearing loss. Laryngoscope 119:1590–1593
Minichiello L, Piehl F, Vazquez E, Schimmang T, Hökfelt T, Represa J, Klein R (1995) Differential effects of combined Trk receptor mutations on dorsal root ganglion and inner ear sensory neurons. Development 121:4067–4075
Nagiel A, Andor-Ardó D, Hudspeth AJ (2008) Specificity of afferent synapses onto plane-polarized hair cells in the posterior lateral line of the zebrafish. J Neurosci 28:8442–8453
Nilsson AS, Fainzilber M, Falck P, Ibáñez CF (1998) Neurotrophin-7: a novel member of the neurotrophin family from the zebrafish. FEBS Lett 424:285–290
Qun LX, Pirvola U, Saarma M, Ylikoski J (1999) Neurotrophic factors in the auditory periphery. Ann N Y Acad Sci 884:292–304
Reichardt LF (2006) Neurotrophin-regulated signaling pathways. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 361:1545–1564
Rejali D, Lee VA, Abrashkin KA, Humayun N, Swiderski DL, Raphael Y (2007) Cochlear implants and ex vivo BDNF gene therapy protect spiral ganglion neurons. Hear Res 228:180–187
Rouse GW, Pickles JO (1991) Paired development of hair cells in neuromasts of the teleost lateral line. Proc Biol Sci 246:123–128
Schimmang T, Minichiello L, Vazquez E, San Jose I, Giraldez F, Klein R, Represa J (1995) Developing inner ear sensory neurons require TrkB and TrkC receptors for innervation of their peripheral targets. Development 121:3381–3391
Vazquez E, Van de Water TR, Del Valle M, Vega JA, Staecker H, Giráldez F, Represa J (1994) Pattern of trkB protein-like immunoreactivity in vivo and the in vitro effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) on developing cochlear and vestibular neurons. Anat Embryol 189:157–167
Vega JA, San Jose I, Cabo R, Rodriguez S, Represa J (1999) Trks and p75 genes are differentially expressed in the inner ear of human embryos. What may Trks and p75 null mutant mice suggest on human development? Neurosci Lett 272:103–106
Webb JF (1989) Neuromast morphology and lateral line trunk canal ontogeny in two species of cichlids: an SEM study. J Morphol 202:53–68
Whitfield TT (2002) Zebrafish as a model for hearing and deafness. J Neurobiol 53:157–171
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Germanà, A., Laurà, R., Montalbano, G. et al. Expression of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and TrkB in the Lateral Line System of Zebrafish During Development. Cell Mol Neurobiol 30, 787–793 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-010-9506-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-010-9506-z