Abstract
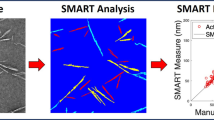
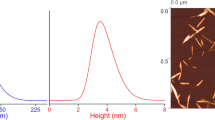
A semi-automatic image analysis program, SMART, was used to analyze transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images from four laboratories that participated in an interlaboratory comparison study by Meija et al. on CNC particle size measurement by TEM using conventional manual image analysis approaches. Detailed image-to-image comparisons found that the percentage of “correctly” identified CNCs by SMART was 58% to 78%, while manual was 70% to 87%, depending on TEM image quality from a given laboratory. SMART was able to parameterize image quality, and it was found that SMART had difficulties in CNC identification for images with a combination of higher noise, lower contrast, and higher CNC density. Overall, the SMART image analysis was consistent with the manual approach. SMART showed lower laboratory-laboratory variation as compared to manual, suggesting that the variability of analyst bias of manual approach was removed and demonstrates an opportunity with SMART to improve the standardization of CNC size characterization. An approach to estimate the likelihood of reaching a representative measurement for CNC particle size was developed. SMART area analysis found that less than 10% of CNCs were used in morphology characterization; to assess more CNC material, SMART was used to analyze CNC agglomerates as a proof-of-concept demonstration. The total SMART image analysis time for each laboratory, having between 115 and 244 images, was less than 15 min, after selection of appropriate parameters. The SMART code is now available for the public to use for free at Github™.
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bushell M et al (2021) Particle size distributions for cellulose nanocrystals measured by atomic force microscopy: an interlaboratory comparison. Cellulose 28:1387–1403. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03618-4
CNCD-1 (2016) National Research Council Canada. CNCD-1: Cellulose Nanocrystal Powder Certified Reference Material. https://doi.org/10.4224/crm.2016.cncd-1
da Silva LC, Cassago A, Battirola LC, Gonçalves MdC, Portugal RV (2020) Specimen preparation optimization for size and morphology characterization of nanocellulose by TEM. Cellulose 27:5435–5444. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03116-7
Delepierre G, Vanderfleet OM, Niinivaara E, Zakani B, Cranston ED (2021) Benchmarking cellulose nanocrystals part II: new industrially produced materials. Langmuir 37:8393–8409. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.1c00550
Dunlop MJ et al (2020) Towards the scalable isolation of cellulose nanocrystals from tunicates. Sci Rep 10:19090. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-76144-9
Foster EJ et al (2018) Current characterization methods for cellulose nanomaterials. Chem Soc Rev 47:2609–2679. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CS00895J
Gicquel E, Bras J, Rey C, Putaux J-L, Pignon F, Jean B, Martin C (2019) Impact of sonication on the rheological and colloidal properties of highly concentrated cellulose nanocrystal suspensions. Cellulose 26:7619–7634. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02622-7
Jakubek ZJ et al (2018) Characterization challenges for a cellulose nanocrystal reference material: dispersion and particle size distributions. J Nanopart Res 20:98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-018-4194-6
Kaushik M, Fraschini C, Chauve G, Putaux J-L, Moores A (2015) Transmission electron microscopy for the characterization of cellulose nanocrystals. In: Khan M (ed) Transmission Electron microscopy theory and applications. Intech Open, pp 130–163
MATLAB (2020) Version R2020a. The MathWorks Inc. https://www.mathworks.com/help/images/ref/imclearborder.html?s_tid=doc_ta. https://www.mathworks.com/help/images/ref/regionprops.html
Meija J et al (2020) Particle size distributions for cellulose nanocrystals measured by transmission electron microscopy: an interlaboratory comparison. Anal Chem 92:13434–13442. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c02805
Moon RJ, Martini A, Nairn J, Simonsen J, Youngblood J (2011) Cellulose nanomaterials review: structure, properties and nanocomposites. Chem Soc Rev 40:3941–3994. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CS00108B
Ogawa Y, Putaux J-L (2019) Transmission electron microscopy of cellulose. Part 2: technical and practical aspects. Cellulose 26:17–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2075-x
Reid MS, Villalobos M, Cranston ED (2017) Benchmarking cellulose nanocrystals: from the laboratory to industrial production. Langmuir 33:1583–1598. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b03765
Sacui IA et al (2014) Comparison of the properties of cellulose nanocrystals and cellulose nanofibrils isolated from bacteria, tunicate, and wood processed using acid, enzymatic, mechanical, and oxidative methods. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:6127–6138. https://doi.org/10.1021/am500359f
Sokolov P, Belousov M, Bondarev SA, Zhouravleva GA, Kasyanenko N (2017) FibrilJ: ImageJ plugin for fibrils’ diameter and persistence length determination. Comput Phys Commun 214:199–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpc.2017.01.011
Stinson-Bagby KL, Roberts R, Foster EJ (2018) Effective cellulose nanocrystal imaging using transmission electron microscopy. Carbohydr Polym 186:429–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.01.054
Usov I, Mezzenga R (2015) FiberApp: an open-source software for tracking and analyzing polymers, filaments, biomacromolecules, and fibrous objects. Macromolecules 48:1269–1280. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma502264c
Wang X et al (2021) AutoDetect-mNP: an unsupervised machine learning algorithm for automated analysis of transmission electron microscope images of metal nanoparticles. JACS Au 1:316–327. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacsau.0c00030
Yucel S, Moon RJ, Johnston LJ, Yucel B, Kalidindi SR (2021) Semi-automatic image analysis of particle morphology of cellulose nanocrystals. Cellulose 28:2183–2201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03668-8
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the USDA Forest Service, Forest Products laboratory for funding this research (Grant Number: 18-JV-11111129-040) and the Renewable Biomaterials Institute at Georgia Institute of Technology. We would like recognize Kai Cui of National Research Council Canada for providing one of the ILC data sets (TEM images, and manual image analysis).
Funding
This work was supported by USDA Forest Service, Forest Products laboratory (Grant Number: 18-JV-11111129-040) and the Renewable Biomaterials Institute at Georgia Institute of Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The study conception was developed by Sezen Yucel, Robert Moon, Linda Johnston, and Surya Kalidindi. The study design was developed by Sezen Yucel and Robert Moon. Coding design was developed by Sezen Yucel and Surya Kalidindi. Code testing and verification studies was completed by Sezen Yucel and Robert Moon. Results analysis was completed by Robert Moon, Sezen Yucel, and Linda Johnston. TEM images were supplied by Douglas Fox, Byong Chon Park, and E. Johan Foster. First draft of the manuscript was written by Sezen Yucel and Robert Moon. All authors critically reviewed a draft manuscript(s), which resulted in revisions to the document. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yucel, S., Moon, R.J., Johnston, L.J. et al. Transmission electron microscopy image analysis effects on cellulose nanocrystal particle size measurements. Cellulose 29, 9035–9053 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04818-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04818-w