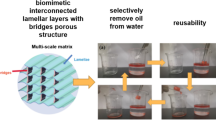
Abstract
The synthesis of a sponge-like carbon aerogel from microfibril cellulose, with high porosity (99 %), ultra-low density (0.01 g/cm3), hydrophobic properties (149° static contact angle) and reusability is reported in this paper. The physical properties, internal morphology, thermal properties, and chemical properties of carbon aerogels heat-treated at 700 and 900 °C (Samples C-700 and C-900) were examined. Stabilization and carbonization parameters were optimized in terms of residual carbon yield. The BET surface area of Sample C-700 (521 m2/g) was significantly higher than of Sample C-950 (145 m2/g). Graphitic-like domains were observed in C-950. The highest normalized sorption capacity (86 g/g) for paraffin oil was observed in sample C-700. The removal of hydrophilic function groups during carbonization causes carbon aerogel to present highly hydrophobic properties. Carbon aerogel’s ability to absorb oil is enhanced by its highly porous 3D network structure with interconnected cellulose nanofibrils.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bastani D, Safekordi AA, Alihosseini A, Taghikhani V (2006) Study of oil sorption by expanded perlite at 298.15 k. Sep Purif Technol 52:295–300. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2006.05.004
Brunauer S, Emmett PH, Teller E (1938) Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J Am Chem Soc 60:309–319. doi:10.1021/ja01269a023
Cervin NT, Aulin C, Larsson PT, Wagberg L (2012) Ultra porous nanocellulose aerogels as separation medium for mixtures of oil/water liquids. Cellulose 19:401–410. doi:10.1007/s10570-011-9629-5
Chen W, Yu H, Li Q, Liu Y, Li J (2011) Ultralight and highly flexible aerogels with long cellulose I nanofibers. Soft Matter 7:10360–10368. doi:10.1039/c1sm06179h
Cheng Q, Wang S, Rials T, Lee S (2007) Physical and mechanical properties of polyvinyl alcohol and polypropylene composite materials reinforced with fibril aggregates isolated from regenerated cellulose fibers. Cellulose 14:593–602. doi:10.1007/s10570-007-9141-0
Choi S-J, Kwon T-H, Im H, Moon D-I, Baek DJ, Seol M-L, Duarte JP, Choi Y-K (2011) A polydimethylsiloxane (pdms) sponge for the selective absorption of oil from water. Acs Appl Mater Interfaces 3:4552–4556. doi:10.1021/am201352w
Dong C, Zhang H, Pang Z, Liu Y, Zhang F (2013) Sulfonated modification of cotton linter and its application as adsorbent for high-efficiency removal of lead(II) in effluent. Bioresour Technol 146:512–518. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2013.07.108
Gaspar D, Fernandes SN, de Oliveira AG, Fernandes JG, Grey P, Pontes RV, Pereira L, Martins R, Godinho MH, Fortunato E (2014) Nanocrystalline cellulose applied simultaneously as the gate dielectric and the substrate in flexible field effect transistors. Nanotechnology 25:094008. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/25/9/094008
Gui X, Li H, Wang K, Wei J, Jia Y, Li Z, Fan L, Cao A, Zhu H, Wu D (2011) Recyclable carbon nanotube sponges for oil absorption. Acta Mater 59:4798–4804. doi:10.1016/j.actamat.2011.04.022
Harkins WD, Brown FE (1919) The determination of surface tension (free surface energy), and the weight of falling drops—the surface tension of water and benzene by the capillary height method. J Am Chem Soc 41:499–524. doi:10.1021/ja01461a003
Hoepfner S, Ratke L, Milow B (2008) Synthesis and characterisation of nanofibrillar cellulose aerogels. Cellulose 15:121–129. doi:10.1007/s10570-007-9146-8
Hu H, Zhao Z, Wan W, Gogotsi Y, Qiu J (2013) Ultralight and highly compressible graphene aerogels. Adv Mater 25:2219–2223. doi:10.1002/adma.201204530
Hubbe MA, Ayoub A, Daystar JS, Venditti RA, Pawlak JJ (2013) Enhanced absorbent products incorporating cellulose and its derivatives: a review. Bioresources 8:6556–6629
Jin H, Kettunen M, Laiho A, Pynnonen H, Paltakari J, Marmur A, Ikkala O, Ras RHA (2011) Superhydrophobic and superoleophobic nanocellulose aerogel membranes as bioinspired cargo carriers on water and oil. Langmuir 27:1930–1934. doi:10.1021/la103877r
Kipling JJ, Sherwood JN, Shooter PV, Thompson NR (1964) The pore structure and surface area of high-temperature polymer carbons. Carbon 1:321–328. doi:10.1016/0008-6223(64)90286-6
Korhonen JT, Kettunen M, Ras RHA, Ikkala O (2011) Hydrophobic nanocellulose aerogels as floating, sustainable, reusable, and recyclable oil absorbents. Acs Appl Mater Interfaces 3:1813–1816. doi:10.1021/am200475b
Li H, Gui X, Zhang L, Wang S, Ji C, Wei J, Wang K, Zhu H, Wu D, Cao A (2010) Carbon nanotube sponge filters for trapping nanoparticles and dye molecules from water. Chem Commun 46:7966–7968. doi:10.1039/c0cc03290e
Li J, Lu Y, Yang D, Sun Q, Liu Y, Zhao H (2011) Lignocellulose aerogel from wood-ionic liquid solution (1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride) under freezing and thawing conditions. Biomacromolecules 12:1860–1867. doi:10.1021/bm200205z
Li Y, Samad YA, Polychronopoulou K, Alhassan SM, Liao K (2014) Carbon aerogel from winter melon for highly efficient and recyclable oils and organic solvents absorption. Acs Sustian Chem Eng 2:1492–1497. doi:10.1021/sc500161b
Liu Y, Ma J, Wu T, Wang X, Huang G, Liu Y, Qiu H, Li Y, Wang W, Gao J (2013) Cost-effective reduced graphene oxide-coated polyurethane sponge as a highly efficient and reusable oil-absorbent. Acs Appl Mater Interfaces 5:10018–10026. doi:10.1021/am4024252
Milosavljevic I, Suuberg EM (1995) Cellulose thermal decomposition kinetics: global mass loss kinetics. Ind Eng Chem Res 34:1081–1091. doi:10.1021/ie00043a009
Moon RJ, Martini A, Nairn J, Simonsen J, Youngblood J (2011) Cellulose nanomaterials review: structure, properties and nanocomposites. Chem Soc Rev 40:3941–3994. doi:10.1039/c0cs00108b
Peng D, Lan Z, Guo C, Yang C, Dang Z (2013) Application of cellulase for the modification of corn stalk: leading to oil sorption. Bioresour Technol 137:414–418. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2013.03.178
Ryu Z, Zheng J, Wang M, Zhang B (1999) Characterization of pore size distributions on carbonaceous adsorbents by DFT. Carbon 37:1257–1264. doi:10.1016/S0008-6223(98)00322-4
Tang MM, Bacon R (1964) Carbonization of cellulose fibers.1. Low temperature pyrolysis. Carbon 1:390. doi:10.1016/0008-6223(64)90035-1
Upadhyayula VKK, Deng S, Mitchell MC, Smith GB (2009) Application of carbon nanotube technology for removal of contaminants in drinking water: a review. Sci Total Environ 408:1–13. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.09.027
Wang S, Cheng Q (2009) A novel process to isolate fibrils from cellulose fibers by high-intensity ultrasonication, part 1: process optimization. J Appl Polym Sci 113:1270–1275. doi:10.1002/app.30072
Wu Q, Pan N, Deng K, Pan D (2008) Thermogravimetry–mass spectrometry on the pyrolysis process of lyocell fibers with and without catalyst. Carbohydr Polym 72:222–228. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2007.08.005
Wu Z, Li C, Liang H, Chen J, Yu S (2013) Ultralight, flexible, and fire-resistant carbon nanofiber aerogels from bacterial cellulose. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 52:2925–2929. doi:10.1002/anie.201209676
Xie X, Goodell B, Zhang D, Nagle DC, Qian Y, Peterson ML, Jellison J (2009) Characterization of carbons derived from cellulose and lignin and their oxidative behavior. Bioresour Technol 100:1797–1802. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2008.09.057
Zhang W, Zhang Y, Lu C, Deng Y (2012) Aerogels from crosslinked cellulose nano/micro-fibrils and their fast shape recovery property in water. J Mater Chem 22:11642–11650. doi:10.1039/c2jm30688c
Zhang A, Chen M, Du C, Guo H, Bai H, Li L (2013) Poly(dimethylsiloxane) oil absorbent with a three-dimensionally interconnected porous structure and swellable skeleton. Acs Appl Mater Interfaces 5:10201–10206. doi:10.1021/am4029203
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support from the UTIA 2013 Innovation Grant and the US Forest Service Southern Research Station under contract agreement 07-CR-11330115-087, Southeastern Sun Grant Center. CIC acknowledges support for materials characterization from the US Department of Energy, Basic Energy Sciences, Materials Science and Technology Division.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, Y., Young, T.M., Liu, P. et al. Ultralight carbon aerogel from nanocellulose as a highly selective oil absorption material. Cellulose 22, 435–447 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0519-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0519-5