Abstract
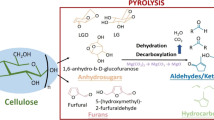
The catalytic and non-catalytic pyrolysis of microcrystalline cellulose and phosphoric acid pre-treated cellulose was investigated. The thermal processes were carried out applying two different methodologies: conventional fast pyrolysis and microwave-induced pyrolysis. For the catalytic experiments different catalysts were evaluated: CeO2, Nb2O5, SiO2, high surface area SiO2, Si-MCM-48 and Al-Fe-MCM-48. In all cases the liquid fraction was evaluated by quantifying the yields of anhydrosugars (mainly levoglucosan, levoglucosenone and 1,4:3,6-dianhydro-α-d-glucopyranose) and aromatic hydrocarbons. In the reaction of microcrystalline cellulose levoglucosan was the main product, while levoglucosenone was predominant in the pyrolysis of phosphoric acid pre-treated cellulose. Catalysts improved the fraction of bio-oil and the product distribution depended on the nature of catalytic materials as well as the starting cellulose. On the other hand, the microwave induced pyrolysis favored the formation of char at expenses of liquid fraction. In this case levoglucosenone and other anhydrosugars in conjunction with furan compounds were the main products.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antal MJ (1982) Biomass pyrolysis: a review of the literature. Part I. Carbohydrate pyrolysis. In: Boer KW, Duffie JA (eds) Advances in solar energy, vol I. American Solar Energy Society, Boulder, pp 61–111
Antal M, Varhegyi G (1995) Cellulose pyrolysis kinetics: the current state of knowledge. Ind Eng Chem Res 34:703–717
Bore M, Mokhonoana M, Ward T, Coville N, Datye A (2006) Synthesis and reactivity of gold nanoparticles supported on transition metal doped mesoporous silica. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 95:118–125
Bridgwater A, Grassi G (1991) Biomass pyrolysis liquids upgrading and utilisation. Elsevier Applied Science, England
Choi S-S, Kim M-C, Kim Y-K (2011) Influence of silica on formation of levoglucosan from carbohydrates by pyrolysis. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 90:56–62
Cid R, Pecchi G (1985) Potentiometric method for determining the number and relative strength of acid sites in colored catalysts. Appl Catal 14:15–21
Covarrubias R, Quijada R, Rojas R (2009) Synthesis of nanosized ZSM-2 zeolite with potential acid catalytic properties. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 117:118–125
Czernik S, Bridgwater A (2004) Overview of applications of biomass fast pyrolysis oil. Energy Fuels 18:590–598
Diez A, Graziano-Mayer M, Radivoy G, Volpe M (2014) Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling of aryl iodides and phenylboronic acid over palladium-free CeO2 catalysts. Appl Catal A 482:24–30
Dobele G, Rossinskaja G, Telysheva G, Meier D, Faix O (1999) Cellulose dehydration and depolymerization reactions during pyrolysis in the presence of phosphoric acid. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 49:307–317
Dobele G, Meier D, Faix O, Radtke S, Rossinskaya G, Telysheva G (2001) Volatile products of catalytic flash pyrolysis of celluloses. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 58(59):453–463
Dobele G, Dizhbite T, Rossinskaja G, Telysheva G, Meier D, Radtke S, Faix O (2003) Pre-treatment of biomass with phosphoric acid prior to fast pyrolysis: a promising method for obtaining 1,6-anhydrosaccharides in high yields. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 68–69:197–211
Fabbri D, Torri C, Baravelli V (2007) Effect of zeolites and nanopowder metal oxides on the distribution of chiral anhydrosugars evolved from pyrolysis of cellulose: an analytical study. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 80:24–29
Furneaux R, Mason J, Miller I (1988) A novel hydroxylactone from the Lewis acid catalysed pyrolysis of cellulose. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans 1:49–51
Garcia E, Tonetto G, Sanchez M, Volpe M (2005) Preparation of USY zeolite image supported catalysts from V(AcAc)3 and NH4VO3. Catalytic properties for the dehydrogenation of N-butane in oxygen-free atmosphere. J Colloid Interface Sci 292:179–185
Ioelovich M, Tupureine A, Veveris G (1989) Investigation of the crystalline structure of cellulose in plant materials. Khimija Drev 5:3–9
Jha R, Shylesh S, Bhoware S, Singh A (2006) Oxidation of ethyl benzene and diphenyl methane over ordered mesoporous M-MCM-41 (M = Ti, V, Cr): synthesis, characterization and structure–activity correlations. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 95:154
Kong Y, Jiang S, Wang J, Wang S, Yan Q, Lu Y (2005) Synthesis and characterization of Cu–Ti–MCM41. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 86:191
Li X, Zhang H, Li J, Su L, Zuo J, Komarneni S, Wang Y (2013) Improving the aromatic production in catalytic fast pyrolysis of cellulose by co-feeding low-density polyethylene. Appl Catal A 455:114–121
Lu Q, Xiong W, Li W, Guo X, Zhu X (2009) Catalytic pyrolysis of cellulose with sulfated metal oxides: a promising method for obtaining high yield of light furan compounds. Bioresour Technol 100:4871–4876
Mosier N, Wyman C, Dale B, Elander R, Lee Y, Holtzapple M, Ladisch M (2005) Features of promising technologies for pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour Technol 96:673–686
Motasemi F, Afzal M (2013) A review on the microwave-assisted pyrolysis technique. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 28:317–330
Oknishi A, Katö K, Hori T, Nakayama M (1981) Crystal structure and 1H- and 13C-n.m.r. studies of 1,4:3,6-dianhydro-α-d-glucopyranose obtained from pyrolysis of cellulose. Carbohydr Res 96:161–166
Orozco A, Ahmad M, Rooney D, Walker G (2007) Dilute acid hydrolysis of cellulose and cellulosic bio-waste using a microwave reactor system. Process Saf Environ Prot 85(B5):446–449
Paine J, Pithawalla Y, Naworal J (2008) Carbohydrate pyrolysis mechanisms from isotopic labeling: part 2. The pyrolysis of d-glucose: general disconnective analysis and the formation of C1 and C2 carbonyl compounds by electrocyclic fragmentation mechanisms. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 82:10–41
Pikorz J, Radlein D, Scott D (1986) On the mechanism of the rapid pyrolysis of cellulose. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 9:121–137
Rutkowski P (2012) Pyrolytic behavior of cellulose in presence of montmorillonite K10 as catalyst. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 98:115–122
Shafizadeh F, Furneaux R, Stevenson T, Cochran T (1978) Acid-catalyzed pyrolytic synthesis and decomposition of 1,4:3,6-dianhydro-α-d-glucopyranose. Carbohydr Res 61:519–528
Shaik S, Sharratt P, Tan R (2013) Influence of selected mineral acids and alkalis on cellulose pyrolysis pathways and anhydrosaccharide formation. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 104:234–242
Shen D, Gu S (2009) The mechanism for thermal decomposition of cellulose and its main products. Bioresour Technol 100:6496–6504
Shra’ah A, Helleur R (2014) Microwave pyrolysis of cellulose at low temperature. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 105:91–99
Tonetto G, De Lasa H, Volpe M (2004) Butane dehydrogenation on vanadium supported catalysts under oxygen free atmosphere. Appl Catal A 272(1-2):69–78
Torri C, Giorgio Lesci I, Fabbri D (2009) Analytical study on the pyrolytic behaviour of cellulose in the presence of MCM-41 mesoporous materials. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 85:192–196
Vinu R, Broadbelt L (2012) A mechanistic model of fast pyrolysis of glucose-based carbohydrates to predict bio-oil composition. Energy Environ Sci 5:9808–9826
Wang X, Chen H, Luo K, Shao J, Yang H (2008) The influence of microwave drying on biomass pyrolysis. Energy Fuels 22:67–74
Xu J, Luan Z, He H, Zhou W, Kevan L (1998) A reliable synthesis of cubic mesoporous MCM-48 molecular sieve. Chem Mater 10:3690–3698
Yin C (2012) Microwave-assisted pyrolysis of biomass for liquid biofuels production. Bioresour Technol 120:273–284
Zhang J, Zhang J, Lin L, Chen T, Zhang J, Liu S, Li Z, Ouyang P (2009) Dissolution of microcrystalline cellulose in phosphoric acid- molecular changes and kinetics. Molecules 14:5027–5041
Zhao H, Kwak J, Zhang Z, Brown H, Arey B, Holladay J (2007) Studying cellulose fiber structure by SEM, XRD, NMR and acid hydrolysis. Carbohydr Polym 68:235–241
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support of CONICET and SECYT-UNC. Authors also thank Prof. A. Blanc, Prof. R. Carbonio, Dr. G. Lener and Dr. Cecilia Blanco for their contribution in the XRD analysis of cellulose samples and catalysts.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nieva, M.L., Volpe, M.A. & Moyano, E.L. Catalytic and catalytic free process for cellulose conversion: fast pyrolysis and microwave induced pyrolysis studies. Cellulose 22, 215–228 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0484-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0484-z