Abstract
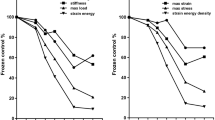
Although allografts for anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) replacement have shown advantages compared to autografts, their use is limited due to the risk of disease transmission and the limitations of available sterilization methods. Gamma sterilization has shown detrimental effects on graft properties at the high doses required for sufficient pathogen inactivation. In our previous in vitro study on human patellar tendon allografts, Electron beam (Ebeam) irradiation showed less detrimental effects compared to gamma sterilization (Hoburg et al. in Am J Sports Med 38(6):1134–1140, 2010). To investigate the biological healing and restoration of the mechanical properties of a 34 kGy Ebeam treated tendon allograft twenty-four sheep underwent ACL replacement with either a 34 kGy Ebeam treated allograft or a non-sterilized fresh frozen allograft. Biomechanical testing of stiffness, ultimate failure load and AP-laxity as well as histological analysis to investigate cell, vessel and myofibroblast-density were performed after 6 and 12 weeks. Native sheep ACL and hamstring tendons (HAT, each n = 9) served as controls. The results of a previous study analyzing the remodeling of fresh frozen allografts (n = 12) and autografts (Auto, n = 18) with the same study design were also included in the analysis. Statistics were performed using Mann–Whitney U test followed by Bonferroni-Holm correction. Results showed significantly decreased biomechanical properties during the early remodeling period in Ebeam treated grafts and this was accompanied with an increased remodeling activity. There was no recovery of biomechanical function from 6 to 12 weeks in this group in contrast to the results observed in fresh frozen allografts and autografts. Therefore, high dose Ebeam irradiation investigated in this paper cannot be recommended for soft tissue allograft sterilization.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen MJ, Houlton JE, Adams SB, Rushton N (1998) The surgical anatomy of the stifle joint in sheep. Vet Surg 27(6):596–605
Balsly CR, Cotter AT, Williams LA, Gaskins BD, Moore MA, Wolfinbarger L Jr (2008) Effect of low dose and moderate dose gamma irradiation on the mechanical properties of bone and soft tissue allografts. Cell Tissue Bank 9(4):289–298
Buck BE, Malinin TI, Brown MD (1989) Bone transplantation and human immunodeficiency virus. An estimate of risk of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). Clin Orthop Relat Res 240:129–136
Cheung DT, Perelman N, Tong D, Nimni ME (1990) The effect of gamma-irradiation on collagen molecules, isolated alpha-chains, and crosslinked native fibers. J Biomed Mater Res 24(5):581–589
Cohen SB, Sekiya JK (2007) Allograft safety in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Clin Sports Med 26(4):597–605
Curran AR, Adams DJ, Gill JL, Steiner ME, Scheller AD (2004) The biomechanical effects of low-dose irradiation on bone-patellar tendon-bone allografts. Am J Sports Med 32(5):1131–1135
Dziedzic-Goclawska A, Kaminski A, Uhrynowska-Tyszkiewicz I, Stachowicz W (2005) Irradiation as a safety procedure in tissue banking. Cell Tissue Bank 6(3):201–219
Fideler BM, Vangsness CT Jr, Moore T, Li Z, Rasheed S (1994) Effects of gamma irradiation on the human immunodeficiency virus. A study in frozen human bone-patellar ligament-bone grafts obtained from infected cadavera. J Bone Joint Surg Am 76(7):1032–1035
Fideler BM, Vangsness CT Jr, Lu B, Orlando C, Moore T (1995) Gamma irradiation: effects on biomechanical properties of human bone-patellar tendon-bone allografts. Am J Sports Med 23(5):643–646
Gerbi BJ, Antolak JA, Deibel FC, Followill DS, Herman MG, Higgins PD, Huq MS, Mihailidis DN, Yorke ED, Hogstrom KR, Khan FM (2009) Recommendations for clinical electron beam dosimetry: supplement to the recommendations of Task Group 25. Med Phys 36(7):3239–3279
Gibbons MJ, Butler DL, Grood ES, Bylski-Austrow DI, Levy MS, Noyes FR (1991) Effects of gamma irradiation on the initial mechanical and material properties of goat bone-patellar tendon-bone allografts. J Orthop Res 9(2):209–218
Goertzen MJ, Clahsen H, Burrig KF, Schulitz KP (1995) Sterilisation of canine anterior cruciate allografts by gamma irradiation in argon. Mechanical and neurohistological properties retained one year after transplantation. J Bone Joint Surg Br 77(2):205–212
Gorschewsky O, Browa A, Vogel U, Stauffer E (2002) Clinico-histologic comparison of allogenic and autologous bone-tendon-bone using one-third of the patellar tendon in reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament. Unfallchirurg 105(8):703–714
Gouk SS, Lim TM, Teoh SH, Sun WQ (2008) Alterations of human acellular tissue matrix by gamma irradiation: histology, biomechanical property, stability, in vitro cell repopulation, and remodeling. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 84(1):205–217
Harner CD, Olson E, Irrgang JJ, Silverstein S, Fu FH, Silbey M (1996) Allograft versus autograft anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: 3- to 5-year outcome. Clin Orthop 324:134–144
Hoburg AT, Keshlaf S, Schmidt T, Smith M, Gohs U, Perka C, Pruss A, Scheffler S (2010) Effect of electron beam irradiation on biomechanical properties of patellar tendon allografts in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Am J Sports Med 38(6):1134–1140
Hunt P, Scheffler SU, Unterhauser FN, Weiler A (2005) A model of soft-tissue graft anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in sheep. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 125(4):238–248
Jackson DW, Windler GE, Simon TM (1990) Intraarticular reaction associated with the use of freeze-dried, ethylene oxide-sterilized bone-patella tendon-bone allografts in the reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament. Am J Sports Med 18(1):1–10 discussion 10–11
Kainer MA, Jarvis WR (2004) HIV-1 and HCV infections among antibody-negative blood donors. N Engl J Med 351(21):2232–2235 author reply 2232–2235
Kainer MA, Linden JV, Whaley DN, Holmes HT, Jarvis WR, Jernigan DB, Archibald LK (2004) Clostridium infections associated with musculoskeletal-tissue allografts. N Engl J Med 350(25):2564–2571
Krych AJ, Jackson JD, Hoskin TL, Dahm DL (2008) A meta-analysis of patellar tendon autograft versus patellar tendon allograft in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Arthroscopy 24(3):292–298
Mae T, Shino K, Maeda A, Toritsuka Y, Horibe S, Ochi T (2003) Effect of gamma irradiation on remodeling process of tendon allograft. Clin Orthop Relat Res 414:305–314
McAllister DR, Joyce MJ, Mann BJ, Vangsness CT Jr (2007) Allograft update: the current status of tissue regulation, procurement, processing, and sterilization. Am J Sports Med 35(12):2148–2158
McGilvray KC, Santoni BG, Turner AS, Bogdansky S, Wheeler DL, Puttlitz CM (2010) Effects of (60)Co gamma radiation dose on initial structural biomechanical properties of ovine bone-patellar tendon-bone allografts. Cell Tissue Bank. doi:10.1007/s10561-010-9170-z
Nemzek JA, Arnoczky SP, Swenson CL (1994) Retroviral transmission by the transplantation of connective-tissue allografts. An experimental study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 76(7):1036–1041
Pruss A, Kao M, Gohs U, Koscielny J, von Versen R, Pauli G (2002) Effect of gamma irradiation on human cortical bone transplants contaminated with enveloped and non-enveloped viruses. Biologicals 30(2):125–133
Radford WJP, Amis AA, Stead AC (1996) The ovine stifle as a model for human cruciate ligament surgery. Vet Comp Orthop Traumatol 9:134–139
Rappe M, Horodyski M, Meister K, Indelicato PA (2007) Nonirradiated versus irradiated Achilles allograft: in vivo failure comparison. Am J Sports Med 35(10):1653–1658
Reid BD (1998) The Sterways process: a new approach to inactivating viruses using gamma radiation. Biologicals 26(2):125–129
Roberts TS, Drez D Jr, McCarthy W, Paine R (1991) Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using freeze-dried, ethylene oxide-sterilized, bone-patellar tendon-bone allografts. Two year results in thirty-six patients. Am J Sports Med 19(1):35–41
Salehpour A, Butler DL, Proch FS, Schwartz HE, Feder SM, Doxey CM, Ratcliffe A (1995) Dose-dependent response of gamma irradiation on mechanical properties and related biochemical composition of goat bone-patellar tendon-bone allografts. J Orthop Res 13(6):898–906
Scheffler S, Trautmann S, Smith M, Kalus U, von Versen R, Pauli G, Pruss A (2007) No influence of collagenous proteins of Achilles tendon, skin and cartilage on the virus-inactivating efficacy of peracetic acid-ethanol. Biologicals 35(4):355–359
Scheffler SU, Gonnermann J, Kamp J, Przybilla D, Pruss A (2008a) Remodeling of ACL allografts is inhibited by peracetic acid sterilization. Clin Orthop Relat Res 466(8):1810–1818
Scheffler SU, Schmidt T, Gangey I, Dustmann M, Unterhauser F, Weiler A (2008b) Fresh-frozen free-tendon allografts versus autografts in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: delayed remodeling and inferior mechanical function during long-term healing in sheep. Arthroscopy 24(4):448–458
Seitz H, Hausner T, Schlenz I, Lang S, Eschberger J (1997) Vascular anatomy of the ovine anterior cruciate ligament. A macroscopic, histological and radiographic study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 116(1–2):19–21
Seto A, Gatt CJ Jr, Dunn MG (2008) Radioprotection of tendon tissue via crosslinking and free radical scavenging. Clin Orthop Relat Res 466(8):1788–1795
Simonds RJ, Holmberg SD, Hurwitz RL, Coleman TR, Bottenfield S, Conley LJ, Kohlenberg SH, Castro KG, Dahan BA, Schable CA (1992) Transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 from a seronegative organ and tissue donor. N Engl J Med 326(11):726–732
Sun K, Tian SQ, Zhang JH, Xia CS, Zhang CL, Yu TB (2009) ACL reconstruction with BPTB autograft and irradiated fresh frozen allograft. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 10(4):306–316
Unterhauser FN (2004) Revaskularisierung und Nachweis von Myofibroblasten im freien Sehnentransplantat nach vorderem Kreuzbandersatz—Histologische 2-Jahres Untersuchung am Schaf. Tierexperimentelle Langzeitstudie, Medizinische Fakultät—Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin
Update (2002) Update: allograft associated bacterial infections-United States. vol 51. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Weiler A, Peters G, Maurer J, Unterhauser FN, Sudkamp NP (2001) Biomechanical properties and vascularity of an anterior cruciate ligament graft can be predicted by contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. A two-year study in sheep. Am J Sports Med 29(6):751–761
Weiler A, Peters G, Maurer J, Unterhauser FN, Sudkamp NP (2002) Biomechanical properties and vascularity of an anterior cruciate ligament graft can be predicted by contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. A two-year study in sheep. Am J Sports Med 29(6):751–761
Yoshikawa T, Tohyama H, Katsura T, Kondo E, Kotani Y, Matsumoto H, Toyama Y, Yasuda K (2006) Effects of local administration of vascular endothelial growth factor on mechanical characteristics of the semitendinosus tendon graft after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in sheep. Am J Sports Med 34(12):1918–1925
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmidt, T., Hoburg, A., Broziat, C. et al. Sterilization with electron beam irradiation influences the biomechanical properties and the early remodeling of tendon allografts for reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). Cell Tissue Bank 13, 387–400 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-011-9289-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-011-9289-6