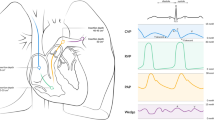
Abstract
Short-term regulation of cerebral blood flow (CBF) is controlled by myogenic, metabolic and neurogenic mechanisms, which maintain flow within narrow limits, despite large changes in arterial blood pressure (ABP). Static cerebral autoregulation (CA) represents the steady-state relationship between CBF and ABP, characterized by a plateau of nearly constant CBF for ABP changes in the interval 60–150 mmHg. The transient response of the CBF–ABP relationship is usually referred to as dynamic CA and can be observed during spontaneous fluctuations in ABP or from sudden changes in ABP induced by thigh cuff deflation, changes in posture and other manoeuvres. Modelling the dynamic ABP–CBFV relationship is an essential step to gain better insight into the physiology of CA and to obtain clinically relevant information from model parameters. This paper reviews the literature on the application of CA models to different clinical conditions. Although mathematical models have been proposed and should be pursued, most studies have adopted linear input–output (‘black-box’) models, despite the inherently non-linear nature of CA. The most common of these have been transfer function analysis (TFA) and a second-order differential equation model, which have been the main focus of the review. An index of CA (ARI), and frequency-domain parameters derived from TFA, have been shown to be sensitive to pathophysiological changes in patients with carotid artery disease, stroke, severe head injury, subarachnoid haemorrhage and other conditions. Non-linear dynamic models have also been proposed, but more work is required to establish their superiority and applicability in the clinical environment. Of particular importance is the development of multivariate models that can cope with time-varying parameters, and protocols to validate the reproducibility and ranges of normality of dynamic CA parameters extracted from these models.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaslid R, Lindegaard KF, Sorteberg W, Nornes H. Cerebral autoregulation dynamics in humans. Stroke 1989;20:45–52.
Bendat JS, Piersol AG. Random data analysis and measurement procedures. New York: John Wiley & Sons;1986.
Beneken JEW. A mathematical approach to cardiovascular function. The uncontrolled human system. Int. Re. 2.45/6 Inst Med Phys. Utrecht:TNO; 1965.
Birch AA, Dirnhuber MJ, Hartley-Davies R, Iannotti F, Neil-Dwyer G. Assessment of autoregulation by means of periodic changes in blood pressure. Stroke 1995;26:834–7.
Blaber AP, Bondar RL, Stein F, Dunphy PT, Moradshahi P, Kassam MS, Freeman R. Transfer function analysis of cerebral autoregulation dynamics in autonomic failure patients. Stroke 1997;28:1686–92.
Branston NM. Neurogenic control of the cerebral circulation. Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev 1995;7:338–49.
Busija DW, Heistad DD. Factors involved in the physiological regulation of the cerebral circulation. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharm 1984;101:162–211.
Buxton RB, Uludag K, Dubowitz DJ, Liu TT. Modeling the hemodynamic response to brain activation. NeuroImage 2004;23:S220–33.
Carey BJ, Eames PJ, Blake MJ, Panerai RB, Potter JF. Dynamic cerebral autoregulation is unaffected by aging. Stroke 2000;31:2895–900.
Carey BJ, Manktelow BN, Panerai RB, Potter JF. Cerebral autoregulatory responses to head-up tilt in normal subjects and patients with recurrent vasovagal syncope. Circulation 2001;104:898–902.
Cencetti S, Lagi A, Cipriani M, Fattorini L, Bandinelli G, Bernardi L. Autonomic control of the cerebral circulation during normal and impaired peripheral circulatory control. Heart 1999;82:365–72.
Czosnyka M, Smielewski P, Kirkpatrick P, Menon DK, Pickard JD. Monitoring of cerebral autoregulation in head-injured patients. Stroke 1996;27:1829–34.
Dawson SL, Blake MJ, Panerai RB, Potter JF. Dynamic but not static cerebral autoregulation is impaired in acute ischaemic stroke. Cerebrovasc Dis 2000;10:126–32.
Dawson SL, Panerai RB, Potter JF. Serial changes in static and dynamic cerebral autoregulation after acute ischaemic stroke. Cerebrovasc Dis 2003;16:69–75.
Diehl RR, Linden D, Lucke D, Berlit P. Phase relationship between cerebral blood flow velocity and blood pressure. A clinical test of autoregulation. Stroke 1995;26:1801–4.
Diehl RR, Linden D, Chalkiadaki A, Diehl A. Cerebrovascular mechanisms in neurocardiogenic syncope with and without postural tachycardia syndrome. J Autonom Nerv Syst 1999;76:159–66.
Doering TJ, Aaslid R, Steuernagel B, Brix J, Niederstadt C, Breull AB, Schneider B, Fischer GC. Cerebral autoregulation during whole-body hypothermia and hyperthermia stimulus. Am J Phys Med Rehab 1999;78:33–8.
Eames PJ, Blake MJ, Dawson SL, Panerai RB, Potter JF. Dynamic cerebral autoregulation and beat to beat blood pressure control are impaired in acute ischaemic stroke. J Neurol Neurosurg Psych 2002;72:467–73.
Eames PJ, Blake MJ, Panerai RB, Potter JF. Cerebral autoregulation indices are unimpaired by hypertension in middle aged and older people. Am J Hypert 2003;16:746–53.
Eames PJ, Robinson TG, Panerai RB, Potter JF. The systemic haemodynamic and cerebral autoregulatory effects of bendrofluazide in the subacute post-stroke period. J Hypertension 2004;22:2017–24.
Edwards MR, Lin DC, Hughson RL. Modeling the interaction between perfusion pressure and CO2 on cerebral blood flow. Adv Exper Med Biol 2001;499:285–90.
Faraci FM, Baumbach GL, Heistad DD. Myogenic mechanisms in the cerebral circulation. J Hypertension 1989;7(suppl 4):S61–4.
Faraci FM, Brian J. Nitric oxide and the cerebral circulation. Stroke 1994;25:692–703.
Faraci FM, Heistad DD. Regulation of large cerebral arteries and cerebral microvascular pressure. Circ Res 1990;66:8–17.
Faraci FM, Heistad DD. Regulation of the cerebral circulation: role of endothelium and potassium channels. Physiol Rev 1998;78:53–97.
Fink M, Batzel JJ, Kappel F. An optimal control approach to modeling the cardiovascular-respiratory system: an application to orthostatic stress. Cardiovasc Eng 2004;4:27–38.
Giller CA. The frequency-dependent behavior of cerebral autoregulation. Neurosurgery 1990;27:362–8.
Giller CA, Bowman G, Dyer H, Mootz L, Krippner W. Cerebral arterial diameters during changes in blood pressure and carbon dioxide during craniotomy. Neurosurgery 1993;32:737–42.
Golding EM, Golding RM. Mathematical modelling of responses of cerebral blood vessels to changing intraluminal pressure. Physiol Meas 2001;22:727–43.
Grodins FS. Integrative cardiovascular physiology: A mathematical synthesis of cardiac and blood vessel haemodynamics. Quart Rev Biol 1959;34:93–116.
Guyton AC and Coleman TG. Long-term regulation of the circulation: interrelationship with body fluid volumes. In: Reeve EB, Guyton AC, editors. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 1967.
Hamel E. Perivascular nerves and the regulation of cerebrovascular tone. J Appl Physiol 2006;100:1059–64.
Haubrich C, Kohnke A, Diehl RR, Moller-Hartmann W, Klotzsch C. Impact of vertebral artery disease on dynamic cerebral autoregulation. Acta Neurol Scand 2005;112:309–16.
Haubrich C, Kohnke A, Kloetzsch C, Moeller-Hartmann W, Diehl RR. Bilateral vertebral artery disease: transcranial Doppler assessment of the hemodynamic vulnerability to changes in posture. Ultrasound Med Biol 2006;32:1485–91.
Haubrich C, Kruska W, Diehl RR, Moller-Hartmann W, Klotzsch C. Dynamic autoregulation testing in patients with middle cerebral artery stenosis. Stroke 2003;34:1881–5.
Hlatky R, Furuya Y, Valadka AB, Gonzalez J, Chacko A, Mizutani Y, Contant CF, Robertson CS. Dynamic autoregulatory response after severe head injury. J Neurosurg 2002;97:1054–61.
Hlatky R, Valadka AB, Robertson CS. Intracranial pressure response to induced hypertension: role of dynamic pressure autoregulation. Neurosurgery 2005;57:917–23.
Hu HH, Kuo TBJ, Wong WJ, Luk YO, Chern CM, Hsu LC, Sheng WY. Transfer function analysis of cerebral hemodynamics in patients with carotid stenosis. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1999;19:460–5.
Hyder F, Shulman RG, Rothman DL. A model for the regulation of cerebral oxygen delivery. J Appl Physiol 1998;85:554–64.
Immink RV, van den Born BJH, Montfrans GA, Koopmans RP, Karemaker JM, van Lieshout JJ. Impaired cerebral autoregulation in patients with malignant hypertension. Circulation 2004;110:2241–5.
Immink RV, van Montfrans GA, Stam J, Karemaker JM, Diamant M, van Lieshout JJ. Dynamic cerebral autoregulation in acute lacunar and middle cerebral artery territory ischemic stroke. Stroke 2005;36:2595–600.
Junger EC, Newell DW, Grant GA, Avellino AM, Ghatan S, Douville CM, Lam AM, Aaslid R, Winn HR. Cerebral autoregulation following minor head injury. J Neurosurg 1997;86:425–32.
Kuschinsky W. Coupling of function, metabolism, and blood flow in the brain. Neurosurg Rev 1991;14:163–8.
Kwan J, Lunt M, Jenkinson D. Assessing dynamic cerebral autoregulation after stroke using a novel technique of combining transcranial Doppler ultrasonography and rhythmic handgrip. Blood Press Monit 2004;9:3–8.
Lanzarone E, Liani P, Baselli G, Constantino ML. Model of arterial tree and peripheral control for the study of physiological and assisted circulation. Med Eng Phys 2007;29:542–55.
Lassen NA. Cerebral blood flow and oxygen consumption in man. Physiol Rev 1959;39:183–238.
Latka M, Turalska M, Glaubic-Latka M, Kolodziej W, Latka D, West BJ. Phase dynamics in cerebral autoregulation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2005;289:H2272–9.
Leftheriotis G, Dupuis JM, Victor J. Cerebral hemodynamics in carotid sinus syndrome and atrioventricular block. Am J Cardiol 2000;86:504–8.
Lipsitz LA, Mukai S, Hamner J, Gagnon M, Babikian V. Dynamic regulation of middle cerebral artery blood flow velocity in aging and hypertension. Stroke 2000;31:1897–03.
Liu Y, Birch AA, Allen R. Dynamic cerebral autoregulation assessment using an ARX model: comparative study using step response and phase shift analysis. Med Eng Phys 2003;25:647–53.
Liu J, Simpson DM, Allen R. High spontaneous fluctuations in arterial blood pressure improves the assessment of cerebral autoregulation. Physiol Meas 2005;26:725–41.
Mahony P, Panerai RB, Deverson ST, Hayes PD, Evans DH. Assessment of the thigh cuff technique for measurement of dynamic cerebral autoregulation. Stroke 2000;31:476–80.
Marmarelis VZ. Identification of nonlinear biological systems using Laguerre expansion of kernels. Ann Biomed Eng 1993;21:573–89.
Menke J, Michel E, Hillebrand S, Twickel J, Jorch G. Cross-spectral analysis pf cerebral autoregulation dynamics in high risk preterm infants during the perinatal period. Ped Res 1997;42:690–9.
Micieli G, Tassorelli C, Bosone D, Cavallini A, Viotti E, Nappi G. Intracerebral vascular changes induced by cold pressor test: A model of sympathetic activation. Neurol Res 1994;16:163–7.
Mitsis GD, Zhang R, Levine BD, Marmarelis VZ. Modeling of nonlinear physiological systems with fast and slow dynamics.II. Application to cerebral autoregulation. Ann Biomed Eng 2002;30:555–65.
Mitsis GD, Zhang R, Levine BD, Marmarelis VZ. Cerebral hemodynamics during orthostatic stress assessed by nonlinear modeling. J Applied Physiol 2006;101:354–66.
Moody M, Panerai RB, Eames PJ, Potter JF. Cerebral and systemic hemodynamic changes during cognitive and motor activation paradigms. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2005;288:R1581–8.
Newell DW, Aaslid R, Lam A, Mayberg TS, Winn HR. Comparison of flow and velocity during dynamic autoregulation testing in humans. Stroke 1994;25:793–7.
Ngai AC, Winn HR. Modulation of cerebral arterioloar diameter by intraluminarl flow and pressure. Circ Res 1995;77:832–40.
Novak V, Yang ACC, Lepicovsky L, Goldberger AL, Lipsitz LA and Peng CK. Multimodal pressure-flow method to assess dynamics of cerebral autoregulation in stroke and hypertension. BioMedical Engineering OnLine 2004;3:39.
Panerai RB. Assessment of cerebral pressure autoregulation in humans—a review of measurement methods. Physiol Meas 1998;19:305–38.
Panerai RB. System identification of human cerebral blood flow regulatory mechanisms. Cardiovasc Eng 2004;4:59–71.
Panerai RB, Kelsall AWR, Rennie JM, Evans DH. Cerebral autoregulation dynamics in premature newborns. Stroke 1995;26:74–80.
Panerai RB, Kelsall AWR, Rennie JM, Evans DH. Analysis of cerebral blood flow autoregulation in neonates. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 1996;43:779–88.
Panerai RB, Rennie JM, Kelsall AWR, Evans DH. Frequency-domain analysis of cerebral autoregulation from spontaneous fluctuations in arterial blood pressure. Med Biol Eng Comput 1998;36:315–22.
Panerai RB, White RP, Markus HS, Evans DH. Grading of cerebral dynamic autoregulation from spontaneous fluctuations in arterial blood pressure. Stroke 1998;29:2341–6.
Panerai RB, Dawson SL, Potter JF. Linear and nonlinear analysis of human dynamic cerebral autoregulation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 1999a;277:H1089–99.
Panerai RB, Deverson ST, Mahony P, Hayes P, Evans DH. Effect of CO2 on dynamic cerebral autoregulation measurement. Physiol Meas 1999b;20:265–75.
Panerai RB, Simpson DM, Deverson ST, Mahony P, Hayes P, Evans DH. Multivariate dynamic analysis of cerebral blood flow regulation in humans. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 2000;47:419–23.
Panerai RB, Dawson SL, Eames PJ, Potter JF. Cerebral blood flow velocity response to induced and spontaneous sudden changes in arterial blood pressure. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2001;280:H2162–74.
Panerai RB, Hudson V, Fan L, Mahony P, Yeoman PM, Hope T, Evans DH. Assessment of dynamic cerebral autoregulation based on spontaneous fluctuations in arterial blood pressure and intracranial pressure. Physiol Meas 2002;23:59–72.
Panerai RB, Carey BJ, Potter JF. Short-term variability of cerebral blood flow velocity responses to arterial blood pressure transients. Ultrasound Med Biol 2003a;29:31–8.
Panerai RB, Chacon M, Pereira R, Evans DH. Neural network modelling of dynamic cerebral autoregulation: assessment and comparison with established methods. Med Eng & Phys 2003b;26:43–52.
Panerai RB, Eames PJ, Potter JF. Variability of time-domain indices of dynamic cerebral autoregulation. Physiol Meas 2003c;24:367–81.
Panerai RB, Kerins V, Fan L, Yeoman PM, Hope T, Evans DH. Association between dynamic cerebral autoregulation and mortality in severe head injury. Brit J Neurosurg 2004;18:471–9.
Panerai RB, Moody M, Eames PJ, Potter JF. Dynamic cerebral autoregulation during brain activation paradigms. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2005;289:H1202–8.
Panerai RB, Eames PJ, Potter JF. Multiple coherence of cerebral blood flow velocity in humans. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2006;291:H251–9.
Panerai RB, Sammons EL, Rathbone WE, Bentley S, Potter JF and Samani NJ. Transient drifts between Finapres and continuous intra-aortic measurements of arterial blood pressure. Blood Press Monitor 2007 (in press).
Paulson OB, Strandgaard S, Edvinson L. Cerebral autoregulation. Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev 1990;2:161–92.
Payne SJ. A model of the interaction between autoregulation and neural activation in the brain. Math Biosci 2006;204:260–81.
Purves MJ. Do vasomotor nerves significantly regulate cerebral blood flow? Circ Res 1978;43:485–93.
Ramos EG, Simpson DM, Panerai RB, Nadal J, Lopes JMA, Evans DH. Objective selection of signals for assessment of cerebral blood flow autoregulation in neonates. Physiol Meas 2006;27:35–49.
Reinhard M, Hetzel A, Lauk M, Lucking CH. Dynamic cerebral autoregulation testing as a diagnostic tool in patients with carotid artery stenosis. Neurol Res 2001;23:55–63.
Reinhard M, Roth M, Muller T, Guschlbauer B, Timmer J, Cznosnyka M, Hetzel A. Effect of carotid endarterectomy or stenting on impairment of dynamic cerebral autoregulation. Stroke 2004;35:1381–7.
Reinhard M, Roth M, Guschlbauer B, Harloff A, Timmer J, Czosnyka M, Hetzel A. Dynamic cerebral autoregulation in acute ischemic stroke assessed from spontaneous blood pressure fluctuations. Stroke 2005;36:1684–1689.
Roatta S, Micieli G, Bosone D, Losano G, Bini R, Anna C, Passatore M. Effect of generalized sympathetic activation by cold pressor test on cerebral haemodynamics in healthy humans. J Autonom Nerv Syst 1998;71:159–66.
Rosenblum WI. Autoregulatory plateau: does it exist ? J Cereb Blood Flow Metabol 1995;15:174.
Sayers BM, Beagley HA, Henshall WR. Mechanism of auditory evoked responses. Nature 1974;247:481–3.
Schmieder K, Schregel W, Harders A, Cunitz G. Dynamic cerebral autoregulation in patients undergoing surgery for intracranial tumors. Eur J Ultrasound 2000;12:1–7.
Schondorf R, Stein R, Roberts R, Benoit J, Cupples W. Dynamic cerebral autoregulation is preserved in neurally mediated syncope. J Appl Physiol 2001;91:2493–502.
Schubert R, Mulvany MJ. The myogenic response: established facts and attractive hypotheses. Clin Sci 1999;96:313–26.
Serrador JM, Picot PA, Rutt BK, Shoemaker JK, Bondar RL. MRI measures of middle cerebral artery diameter in conscious humans during simulated orthostasis. Stroke 2000;31:1672–8.
Serrador JM, Sorond FA, Vyas M, Gagnon M, Iloputaife ID, Lipsitz LA. Cerebral pressure-flow relations in hypertensive elderly humans: transfer gain in different frequency domains. J Appl Physiol 2005;98:151–9.
Simpson DM, Panerai RB, Evans DH, Garnham J, Naylor AR, Bell PRF. Estimating normal and pathological dynamic responses in cerebral blood flow velocity to step changes in end-tidal pCO2. Med Biol Eng Comput 2000;38:535–9.
Simpson DM, Panerai RB, Evans DH, Naylor AR. A parametric approach to measuring cerebral blood flow autoregulation from spontaneous variations in blood pressure. Ann Biomed Eng 2001;29:18–25.
Simpson DM, Panerai RB, Ramos EG, Lopes JMA, Marinatto MNV, Nadal J, Evans DH. Assessing blood flow control through a bootstrap method. IEEE Trans BME 2004;51:1284–6.
Strandgaard S. Autoregulation of cerebral blood flow in hypertensive patients. Circulation 1976;53:720–7.
Thorin-Trescases N, Bartolotta T, Hyman N, Penar PL, Walters CL, Bevan RD, Bevan JA. Diameter dependence of myogenic tone of human pial arteries. Stroke 1997;28:2486–92.
Tiecks FP, Lam AM, Aaslid R, Newell DW. Comparison of static and dynamic cerebral autoregulation measurements. Stroke 1995;26:1014–9.
Tutaj M, Brown CM, Brys M, Marthol H, Hecht MJ, Dutsch M, Michelson G, Hilz MJ. Dynamic cerebral autoregulation in impaired in glaucoma. J Neurol Sci 2004;220:49–54.
van Osta A, Moraine JJ, Melot C, Mairbaurl H, Maggiorini M, Naeije R. Effects of high altitude exposure on cerebral hemodynamics in normal subjects. Stroke 2005;36:557–60.
Vavilala MS, Newell DW, Junger E, Douville CM, Aaslid R, Rivara FP, Lam AM. Dynamic cerebral autoregulation in healthy adolescents. Acta Anaesth Scand 2002;46:393–7.
White RP, Markus HS. Impaired dynamic cerebral autoregulation in carotid artery stenosis. Stroke 1997;28:1340–4.
Zhang R, Zuckerman JH, Giller CA, Levine BD. Transfer function analysis of dynamic cerebral autoregulation in humans. Am J Physiol 1998a;274:H233–41.
Zhang R, Zuckerman JH, Levine BD. Deterioration of cerebral autoregulation during orthostatic stress: insights from the frequency domain. J Appl Physiol 1998b;85:1113–22.
Zhang R, Zuckerman JH, Iwasaki K, Wilson TE, Crandall CG, Levine BD. Autonomic neural control of dynamic cerebral autoregulation in humans. Circulation 2002;106:1814–20.
Zonta M, Angulo MC, Gobbo S, Rosengarten B, Hossmann KA, Pozzan T, Carmignoto G. Neuron-to-astrocyte signalling is central to the dynamic control of brain microcirculation. Nature Neurosci 2003;6:43–50.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panerai, R.B. Cerebral Autoregulation: From Models to Clinical Applications. Cardiovasc Eng 8, 42–59 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10558-007-9044-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10558-007-9044-6