Abstract
Background/Aims
LncRNA metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) is reported to be highly expressed in myocardial I/R injury and closely related to autophagy. However, the exact biological role of MALAT1 and its underlying mechanism in myocardial I/R injury remain to be elucidated.
Methods
We established incultured H9C2 cardiomyocytes an oxygen-glucose deprivation and reoxygenation (OGD/R) model for 6 h and then reoxygen-glucose for 4 h. We measured cell damage and autophagy levels after OGD/R by real-time quantitative PCR and Western blot. The relationships between miR-20b and MALAT1, beclin1 were confirmed by luciferase reporter assay.
Results
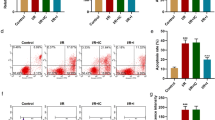
We found that the expression of MALAT1 and beclin1, cell damage levels (lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release, 222.4 ± 29.4 vs. 577.5 ± 27.4 U/L; creatine kinase MB isoenzyme (CK-MB), 1.0 ± 0.2 vs. 4.3 ± 0.4; cardiac troponin I (cTn-I), 1.0 ± 0.3 vs. 3.0 ± 0.3; p < 0.05), and autophagy levels were significantly increased after OGD/R model, while cell viability (100.0 vs. 54.2 ± 2.2%, p < 0.05) and the expression of miR-20b and P62 were reduced; the trend of all the above data was significantly reversed by MALAT1 siRNA. In addition, the luciferase reporter assay results confirmed that MALAT1 directly binds to miR-20b-5p and functions as a ceRNA for miR-20b-5p to regulate beclin1. As a result, MALAT1 overexpression antagonized while MALAT1 knockdown enhanced the inhibitory effects of miR-20b-5p on beclin1-related cardiomyocytes autophagy in OGD/R injury.
Conclusion
LncRNA MALAT1 promotes OGD/R-induced cardiomyocytes injury through sponging miR-20b to enhance beclin1-mediated autophagy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bi X, Zhang G, Wang X, Nguyen C, May HI, Li X, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum chaperone GRP78 protects heart from ischemia/reperfusion injury through Akt activation. Circ Res. 2018;122:1545–54.
Alqahtani F, Ziada K, Rihal CS, Alkhouli M. Incidence and outcomes of early percutaneous coronary intervention after isolated valve surgery. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2019;93:583–9.
Liu CY, Zhang YH, Li RB, Zhou LY, An T, Zhang RC, et al. LncRNA CAIF inhibits autophagy and attenuates myocardial infarction by blocking p53-mediated myocardin transcription. Nat Commun. 2018;9:29.
Chen Z, Li Y, Wang Y, Qian J, Ma H, Wang X, et al. Cardiomyocyte-restricted low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 (LRP6) deletion leads to lethal dilated cardiomyopathy partly through Drp1 signaling. Theranostics. 2018;8:627–43.
Aghaei M, Motallebnezhad M, Ghorghanlu S, Jabbari A, Enayati A, Rajaei M, et al. Targeting autophagy in cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury: a novel therapeutic strategy. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(10):16768–78.
Zhang X, Wang Q, Wang X, Chen X, Shao M, Zhang Q, et al. Tanshinone IIA protects against heart failure post-myocardial infarction via AMPKs/mTOR-dependent autophagy pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;112:108599.
Shi B, Ma M, Zheng Y, Pan Y, Lin X. mTOR and Beclin1: two key autophagy-related molecules and their roles in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(8):12562–8.
Ma X, Liu H, Foyil SR, Godar RJ, Weinheimer CJ, Hill JA, et al. Impaired autophagosome clearance contributes to cardiomyocyte death in ischemia/reperfusion injury. Circulation. 2012;125:3170–81.
Eltzschig HK, Eckle T. Ischemia and reperfusion—from mechanism to translation. Nat Med. 2011;17:1391–401.
Liu H, Xu D, Zhong X, Xu D, Chen G, Ge J, et al. LncRNA-mRNA competing endogenous RNA network depicts transcriptional regulation in ischaemia reperfusion injury. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23:2272–6.
Mukhopadhyay P, Das S, Ahsan MK, Otani H, Das DK. Modulation of microRNA 20b with resveratrol and longevinex is linked with their potent anti-angiogenic action in the ischaemic myocardium and synergestic effects of resveratrol and gamma-tocotrienol. J Cell Mol Med. 2012;16:2504–17.
Hou Z, Qin X, Hu Y, Zhang X, Li G, Wu J, et al. Longterm exercise-derived exosomal miR-342-5p: a novel exerkine for cardio protection. Circ Res. 2019;124(9):1386–400.
Tang B, Bao N, He G, Wang J. Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR regulates autophagy via the miR-20b-5p/ATG7 axis in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. Gene. 2019;686:56–62.
Wang G, Wu Y, Zhu Y. Mechanism of MALAT1 preventing apoptosis of vascular endothelial cells induced by oxygen-glucose deficiency and reoxidation. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46:798–805.
Zhang X, Tang X, Liu K, Hamblin MH, Yin KJ. Long noncoding RNA Malat1 regulates cerebrovascular pathologies in ischemic stroke. J Neurosci. 2017;37(7):1797–806.
Vausort M, Wagner DR, Devaux Y. Long noncoding RNAs in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Circ Res. 2014;115:668–77.
Chen J, Jiang Z, Zhou X, Sun X, Cao J, Liu Y, et al. Dexmedetomidine preconditioning protects cardiomyocytes against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced necroptosis by inhibiting HMGB1-mediated inflammation. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2019;33:45–54.
Deng F, Wang S, Cai S, Hu Z, Xu R, Wang J, et al. Inhibition of caveolae contributes to propofol preconditioning-suppressed microvesicles release and cell injury by hypoxia-reoxygenation. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:3542149.
Wei R, Zhang L, Hu W, Wu J, Zhang W. Long non-coding RNA AK038897 aggravates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via acting as a ceRNA for miR-26a-5p to target DAPK1. Exp Neurol. 2019;314:100–10.
Deng F, Wang S, Zhang L, Xie X, Cai S, Li H, et al. Propofol through upregulating caveolin-3 attenuates post-hypoxic mitochondrial damage and cell death in H9C2 cardiomyocytes during hyperglycemia. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;44:279–92.
Zhu P, Yang M, Ren H, Shen G, Chen J, Zhang J, et al. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 downregulates cardiac transient outward potassium current by regulating miR-200c/HMGB1 pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119:10239–49.
Wang JJ, Bie ZD, Sun CF. Long noncoding RNA AK088388 regulates autophagy through miR-30a to affect cardiomyocyte injury. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(6):10155–63.
Li Z, Li J, Tang N. Long noncoding RNA Malat1 is a potent autophagy inducer protecting brain microvascular endothelial cells against oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced injury by sponging miR-26b and upregulating ULK2 expression. Neuroscience. 2017;354:1–10.
Ren L, Wei C, Li K, LncRNA LZ. MALAT1 up-regulates VEGF-A and ANGPT2 to promote angiogenesis in brain microvascular endothelial cells against oxygen-glucose deprivation via targetting miR-145. Biosci Rep. 2019;39.
Funding
This study was supported by Taihe Hospital Science and Technology Project in 2018 to Dr. Chen, Jingyi (grant numbers 2018JJXM046).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shuang Wang, Tao Yao, and Zhihua Ruan conceived and designed the project. Shuang Wang and Tao Yao performed the experiments with the help of Fan Deng, Wenqian Yu, Yiting Song, and Jingyi Chen. Fan Deng and Shuang Wang analyzed the data. Shuang Wang wrote the manuscript. All authors discussed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Yao, T., Deng, F. et al. LncRNA MALAT1 Promotes Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation and Reoxygenation Induced Cardiomyocytes Injury Through Sponging miR-20b to Enhance beclin1-Mediated Autophagy. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 33, 675–686 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-019-06902-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-019-06902-z