Abstract
Purpose
Research on the role of insulin resistance (IR) in breast cancer risk in premenopausal women is scarce. We aimed to investigate the relationship between IR and the development of breast cancer in premenopausal women.
Methods
We analyzed the prospective association of IR and incident breast cancer in premenopausal women without breast cancer at baseline using a subsample of the Kangbuk Samsung Health Study.
Results
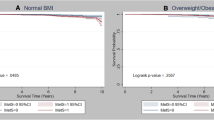
Among 134,488 Korean premenopausal women, 696 women developed incident breast cancers during a median follow-up of 4.34 years. After adjustment for dense breast and other potential confounders, HR (95% CI) for incident breast cancer comparing HOMA-IR quintiles 2, 3, 4, and 5 to the first quintile was 0.91 (0.71–1.17), 0.89 (0.69–1.15), 0.75 (0.57–0.98), and 0.87 (0.65–1.16), respectively (P for trend = 0.117), while HR (95% CI) comparing insulin quintiles 2, 3, 4, and 5 to the first quintile was 1.02 (0.80–1.30), 0.90 (0.69–1.16), 0.72 (0.54–0.96), and 0.96 (0.72–1.28), respectively (P for trend = 0.151). This pattern did not significantly differ by obesity. These results were attenuated and no longer significant in time-dependent analyses where updated status of insulin and other covariates over time were treated as time-varying covariates.
Conclusion
Our findings do not support the positive relationship of IR with the development of breast cancer in premenopausal women, unlike in postmenopausal women. Thus, the role of IR as a risk factor for breast cancer may differ by menopausal status.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the Kangbuk Samsung Health Study group, but restrictions apply to the availability of these data, which were used under the permission from the Institutional Review Board to distribute the data, and so are not publicly available. Data are, however, available from the authors upon reasonable request and with permission of the Kangbuk Samsung Health Study group.
Abbreviations
- aHR:
-
Adjusted hazard ratio
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- BP:
-
Blood pressure
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- CVD:
-
Cardiovascular disease
- HDL-C:
-
High-density lipoprotein cholesterol
- HEPA:
-
Health-enhancing physical activity
- HOMA-IR:
-
Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance
- HPEA:
-
Health-enhancing physical activity
- hsCRP:
-
High-sensitivity C-reactive protein
- IR:
-
Insulin resistance
- LDL-C:
-
Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol
- TNBC:
-
Triple-negative breast cancer
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68(6):394–424
Bray F, McCarron P, Parkin DM (2004) The changing global patterns of female breast cancer incidence and mortality. Breast Cancer Res 6(6):229–239
Kang SY, Kim YS, Kim Z, Kim HY, Kim HJ, Park S, Bae SY, Yoon KH, Lee SB, Lee SK et al (2020) Breast cancer statistics in Korea in 2017: data from a breast cancer registry. J Breast Cancer 23(2):115–128
Lin CH, Yap YS, Lee KH, Im SA, Naito Y, Yeo W, Ueno T, Kwong A, Li H, Huang SM et al (2019) Contrasting epidemiology and clinicopathology of female breast cancer in Asians vs the US population. J Natl Cancer Inst 111(12):1298–1306
Pan K, Chlebowski RT, Mortimer JE, Gunter MJ, Rohan T, Vitolins MZ, Adams-Campbell LL, Ho GYF, Cheng TD, Nelson RA (2020) Insulin resistance and breast cancer incidence and mortality in postmenopausal women in the Women’s Health Initiative. Cancer 126(16):3638–3647
Goodwin PJ (2015) Obesity, insulin resistance and breast cancer outcomes. Breast 24(Suppl 2):S56-59
Gunter MJ, Xie X, Xue X, Kabat GC, Rohan TE, Wassertheil-Smoller S, Ho GY, Wylie-Rosett J, Greco T, Yu H et al (2015) Breast cancer risk in metabolically healthy but overweight postmenopausal women. Cancer Res 75(2):270–274
Gunter MJ, Hoover DR, Yu H, Wassertheil-Smoller S, Rohan TE, Manson JE, Li J, Ho GY, Xue X, Anderson GL et al (2009) Insulin, insulin-like growth factor-I, and risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women. J Natl Cancer Inst 101(1):48–60
Kim BK, Chang Y, Ahn J, Jung HS, Kim CW, Yun KE, Kwon MJ, Suh BS, Chung EC, Shin H et al (2015) Metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance, and mammographic density in pre- and postmenopausal women. Breast Cancer Res Treat 153(2):425–434
Goodwin PJ, Stambolic V (2015) Impact of the obesity epidemic on cancer. Annu Rev Med 66:281–296
Lohmann AE, Goodwin PJ, Chlebowski RT, Pan K, Stambolic V, Dowling RJ (2016) Association of obesity-related metabolic disruptions with cancer risk and outcome. J Clin Oncol 34(35):4249–4255
Capasso I, Esposito E, Pentimalli F, Montella M, Crispo A, Maurea N, D’Aiuto M, Fucito A, Grimaldi M, Cavalcanti E et al (2013) Homeostasis model assessment to detect insulin resistance and identify patients at high risk of breast cancer development: National Cancer Institute of Naples experience. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 32(1):14
Luque RM, Lopez-Sanchez LM, Villa-Osaba A, Luque IM, Santos-Romero AL, Yubero-Serrano EM, Cara-Garcia M, Alvarez-Benito M, Lopez-Mirand AJ, Gahete MD et al (2017) Breast cancer is associated to impaired glucose/insulin homeostasis in premenopausal obese/overweight patients. Oncotarget 8(46):81462–81474
Eliassen AH, Tworoger SS, Mantzoros CS, Pollak MN, Hankinson SE (2007) Circulating insulin and c-peptide levels and risk of breast cancer among predominately premenopausal women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 16(1):161–164
Kaaks R, Lundin E, Rinaldi S, Manjer J, Biessy C, Soderberg S, Lenner P, Janzon L, Riboli E, Berglund G et al (2002) Prospective study of IGF-I, IGF-binding proteins, and breast cancer risk, in northern and southern Sweden. Cancer Causes Control 13(4):307–316
Muti P, Quattrin T, Grant BJ, Krogh V, Micheli A, Schunemann HJ, Ram M, Freudenheim JL, Sieri S, Trevisan M et al (2002) Fasting glucose is a risk factor for breast cancer: a prospective study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 11(11):1361–1368
Kim EY, Chang Y, Ahn J, Yun JS, Park YL, Park CH, Shin H, Ryu S (2020) Mammographic breast density, its changes, and breast cancer risk in premenopausal and postmenopausal women. Cancer 126(21):4687–4696
Kim EY, Chang Y, Lee KH, Yun JS, Park YL, Park CH, Ahn J, Shin H, Ryu S (2019) Serum concentration of thyroid hormones in abnormal and euthyroid ranges and breast cancer risk: a cohort study. Int J Cancer 145(12):3257–3266
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC (1985) Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 28(7):412–419
Harlow SD, Gass M, Hall JE, Lobo R, Maki P, Rebar RW, Sherman S, Sluss PM, de Villiers TJ, Group SC (2012) Executive summary of the Stages of Reproductive Aging Workshop + 10: addressing the unfinished agenda of staging reproductive aging. Menopause 19(4):387–395
Consultation WHOE (2004) Appropriate body-mass index for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies. Lancet 363(9403):157–163
Hamajima N, Hirose K, Tajima K, Rohan T, Calle EE, Heath CW Jr, Coates RJ, Liff JM, Talamini R, Chantarakul N et al (2002) Alcohol, tobacco and breast cancer–collaborative reanalysis of individual data from 53 epidemiological studies, including 58,515 women with breast cancer and 95,067 women without the disease. Br J Cancer 87(11):1234–1245
Fernández-Solà J (2015) Cardiovascular risks and benefits of moderate and heavy alcohol consumption. Nat Rev Cardiol 12(10):576–587
Craig CL, Marshall AL, Sjostrom M, Bauman AE, Booth ML, Ainsworth BE, Pratt M, Ekelund U, Yngve A, Sallis JF et al (2003) International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity. Med Sci Sports Exerc 35(8):1381–1395
Pan K, Nelson RA, Wactawski-Wende J, Lee DJ, Manson JE, Aragaki AK, Mortimer JE, Phillips LS, Rohan T, Ho GYF et al (2020) Insulin resistance and cancer-specific and all-cause mortality in postmenopausal women: the Women’s Health Initiative. J Natl Cancer Inst 112(2):170–178
Goodwin PJ, Ennis M, Pritchard KI, Trudeau ME, Koo J, Madarnas Y, Hartwick W, Hoffman B, Hood N (2002) Fasting insulin and outcome in early-stage breast cancer: results of a prospective cohort study. J Clin Oncol 20(1):42–51
Ferroni P, Riondino S, Laudisi A, Portarena I, Formica V, Alessandroni J, D’Alessandro R, Orlandi A, Costarelli L, Cavaliere F et al (2016) Pretreatment insulin levels as a prognostic factor for breast cancer progression. Oncologist 21(9):1041–1049
Duggan C, Irwin ML, Xiao L, Henderson KD, Smith AW, Baumgartner RN, Baumgartner KB, Bernstein L, Ballard-Barbash R, McTiernan A (2011) Associations of insulin resistance and adiponectin with mortality in women with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 29(1):32–39
Del Giudice ME, Fantus IG, Ezzat S, McKeown-Eyssen G, Page D, Goodwin PJ (1998) Insulin and related factors in premenopausal breast cancer risk. Breast Cancer Res Treat 47(2):111–120
Biello F, Platini F, D’Avanzo F, Cattrini C, Mennitto A, Genestroni S, Martini V, Marzullo P, Aimaretti G, Gennari A (2021) Insulin/IGF axis in breast cancer: clinical evidence and translational insights. Biomolecules 11(1):125
Rose DP, Vona-Davis L (2010) Interaction between menopausal status and obesity in affecting breast cancer risk. Maturitas 66(1):33–38
Liu K, Zhang W, Dai Z, Wang M, Tian T, Liu X, Kang H, Guan H, Zhang S, Dai Z (2018) Association between body mass index and breast cancer risk: evidence based on a dose-response meta-analysis. Cancer Manag Res 10:143–151
Park JW, Han K, Shin DW, Yeo Y, Chang JW, Yoo JE, Jeong SM, Lee SK, Ryu JM, Park YM (2021) Obesity and breast cancer risk for pre- and postmenopausal women among over 6 million Korean women. Breast Cancer Res Treat 185(2):495–506
Jeong JH, Lee HM, Son HY, Lee I (2020) The clinical impact of body mass index on breast cancer in Korea: a nationwide population-based cohort study. J Breast Dis 8(1):51–57
Dartois L, Fagherazzi G, Baglietto L, Boutron-Ruault MC, Delaloge S, Mesrine S, Clavel-Chapelon F (2016) Proportion of premenopausal and postmenopausal breast cancers attributable to known risk factors: estimates from the E3N-EPIC cohort. Int J Cancer 138(10):2415–2427
Rebora P, Czene K, Reilly M (2008) Timing of familial breast cancer in sisters. J Natl Cancer Inst 100(10):721–727
Cust AE, Stocks T, Lukanova A, Lundin E, Hallmans G, Kaaks R, Jonsson H, Stattin P (2009) The influence of overweight and insulin resistance on breast cancer risk and tumour stage at diagnosis: a prospective study. Breast Cancer Res Treat 113(3):567–576
Mealey NE, O’Sullivan DE, Pader J, Ruan Y, Wang E, Quan ML, Brenner DR (2020) Mutational landscape differences between young-onset and older-onset breast cancer patients. BMC Cancer 20(1):212
Goodwin PJ CB, Gelmon KA, Whelan TJ, Ennis M, Lemieux J, Ligibel JA, Hershman DL, Mayer IA, Hobday TJ, Bliss JM, Rastogi P, Rabaglio-Poretti M, Mukherjee SD, Mackey RR, Abramson VG, Oja C, Wesolowski R, Thompson AM, Rea DW, Stos PM, Shepherd LE, Stambolic V, Parulerkar WR (2021) GS1-08 CCTGMA.32, a phase III randomized double-blind placebo controlled adjuvant trial of metformin (MET) vs placebo (PLAC) in early breast cancer (BC): results of the primary efficacy analysis (clinical trials.gov NCT01101438). In: San Antonio breast cancer symposium. San Antonio
Goodwin PJ, Dowling RJO, Ennis M, Chen BE, Parulekar WR, Shepherd LE, Burnell MJ, Vander Meer R, Molckovsky A, Gurjal A et al (2021) Effect of metformin versus placebo on metabolic factors in the MA.32 randomized breast cancer trial. NPJ Breast Cancer 7(1):74
Nestler JE (1997) Insulin regulation of human ovarian androgens. Hum Reprod 12(Suppl 1):53–62
Agnoli C, Grioni S, Sieri S, Sacerdote C, Ricceri F, Tumino R, Frasca G, Pala V, Mattiello A, Chiodini P et al (2015) Metabolic syndrome and breast cancer risk: a case-cohort study nested in a multicentre Italian cohort. PLoS ONE 10(6):e0128891
Stoll BA (1997) Impaired ovulation and breast cancer risk. Eur J Cancer 33(10):1532–1535
Katz A, Nambi SS, Mather K, Baron AD, Follmann DA, Sullivan G, Quon MJ (2000) Quantitative insulin sensitivity check index: a simple, accurate method for assessing insulin sensitivity in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85(7):2402–2410
Acknowledgements
We thank our staff members at the Kangbuk Samsung Health Study for their hard work, dedication, and continuing support. This study was supported by SKKU Excellence in Research Award Research Fund, Sungkyunkwan University, 2020.
Funding
None to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jeesun Lee and Yoosoo Chang contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Jeesun Lee, Yoosoo Chang, and Seungho Ryu. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Jeesun lee and Yejin Kim and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose and nothing to declare.
Ethical approval
This study used only available data that are available from the Kangbuk Samsung Health Study; therefore, it was waived the requirement for informed consent as we used only de-identified data obtained during regular health screening exams of the Kangbuk Samsung Health Study. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Kangbuk Samsung Hospital (KBSMC 2021-05-036).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J., Chang, Y., Kim, Y. et al. Insulin resistance and the development of breast cancer in premenopausal women: the Kangbuk Samsung Health Study. Breast Cancer Res Treat 192, 401–409 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-022-06513-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-022-06513-7