Abstract
Background
Prolactin is a polypeptide hormone that promotes normal breast proliferation and differentiation, but it is also implicated in the development and growth of mammary tumors. Mammographic density is a strong, independent predictor of breast cancer and, therefore, a potential surrogate indicator of breast cancer risk.
Methods
To test the hypothesis that serum prolactin is positively related to mammographic density, we conducted a cross-sectional analysis of baseline data from the Postmenopausal Estrogen/Progestin Interventions (PEPI) Mammographic Density Study. Based on prior work, we further hypothesized that this association would be apparent only in women who had not recently used postmenopausal hormone therapy (HT).
Results
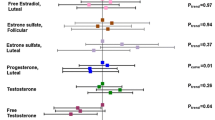
In linear regression models adjusted for age, body mass index, race, smoking, alcohol use, parity and physical activity, among the 400 women who were not recent users of HT, prolactin was positively and statistically significantly associated with mammographic density (Beta log base 2 prolactin 0.0369 [95% CI: 0.0094–0.0645]. Thus, for each doubling of serum prolactin, there was an absolute increase in mammographic density of 3.69%. Additional adjustment for serum levels of estradiol, progesterone, sex hormone binding globulin and age at first pregnancy did not affect this result. There was no association between prolactin and mammographic density among the 169 participants who had recently used HT.
Conclusion
The correspondence between higher prolactin and higher mammographic density is consistent with prolactin’s mitogenic properties and the associations between prolactin and breast tumor promotion. These results support the thesis that prolactin deserves investigation as a target for breast cancer risk reduction.

Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Wolfe JN, Saftlas AF, Salane M (1987) Mammographic parenchymal patterns and quantitative evaluation of mammographic densities: a case–control study. Am J Radiol 148:1087–1092
Boyd NF, Byng JW, Jong RA et al (1995) Quantitative classification of mammographic densities and breast cancer risk: results from the Canadian National Breast Screening Study. J Natl Cancer Inst 87:670–675
Ursin G, Astrahan MA, Salane M et al (1998) The detection of changes in mammographic densities. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 7:43–47
Saftlas AF, Szklo M (1987) Mammographic parenchymal patterns and breast cancer risk. Epidemiol Rev 9:146–174
Oza AM, Boyd NF (1993) Mammographic parenchymal patterns: a marker of breast cancer risk. Epidemiol Rev 15:196–208
Warner E, Lockwood G, Tritchler D, Boyd NF (1992) The risk of breast cancer associated with mammographic parenchymal patterns: a meta-analysis of the published literature to examine the effect of method of classification. Cancer Detect Prev 16:67–72
Boyd NF, Lockwood GA, Martin LG et al (1998) Mammographic densities and breast cancer risk. Breast Dis 10:126–133
Byrne C, Schairer C, Wolfe J et al (1995) Mammographic features and breast cancer risk: effects with time, age and menopause status. J Natl Cancer Inst 87:1622–1629
Ursin G, Ma H, Wu AH et al (2003) Mammographic density and breast cancer in three ethnic groups. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 12:332–338
Bright RA, Morrison AS, Brisson J et al (1988) Relationship between mammographic and histologic features of breast tissue in women with benign biopsies. Cancer 61:266–271
Urbanski S, Jensen HM, Cooke G et al (1988) The association of histological and radiological indicators of breast cancer risk. Br J Cancer 58:474–479
Bartow SA, Pathak DR, Mettler FA (1990) Radiographic microcalcification and parenchymal pattern as indicators of histologic “high-risk” benign breast disease. Cancer 66:1721–1725
Boyd NF, Jensen HM, Cooke G, Han HL (1992) Relationship between mammographic and histological risk factors for breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 84:1170–1195
Wellings SR, Wolfe JN (1978) Correlative studies of the histological and radiographic appearance of the breast parenchyma. Radiology 129:299–306
Fisher ER, Palekar A, Kim WS, Redmond C (1978) The histopathology of mammographic patterns. Am J Clin Pathol 69:421–426
Moskowitz M, Gartside P, McLaughlin C (1980) Mammographic patterns as markers for high-risk benign breast disease and incident cancers. Radiology 134:293–295
Arthur JE, Ellis IO, Flowers C, Roebuck E, Elston CW, Blamey RW (1990) The relationship of “high risk” mammographic patterns to histological risk factors for development of cancer in the human breast. Br Radiol 63:845–849
Pike MC, Bernstein L, Spicer DV (1993) Exogenous hormones and breast cancer risk. In: Niederhuber JE (ed) Current therapy in oncology, Mosbey, St. Louis
Pike MC, Spicer DV, Dahmoush L, Press MF (1993) Estrogens, progestogens, normal breast cell proliferation, and breast cancer risk. Epidemiol Rev 15:17–35
Vonderhaar BK. (1998) Prolactin: the forgotten hormone of human breast cancer. Pharmacol Ther 79:169–178
Goffin V, Binart N, Touraine P, Kelly PA (2002) Prolactin: the new biology of an old hormone. Annu Rev Physiol 64:47–67
Harris J, Stanford PM, Oakes SR, Ormandy CJ (2004) Prolactin and the prolactin receptor: new targets of an old hormone. Ann Med 36:414–425
Clevenger CV, Furth PA, Hankinson SE, Schuler LA (2003) The role of prolactin in mammary carcinoma. Endocr Rev 24:1–27
Hankinson SE, Willet WC, Michaud DS (1999) Plasma prolactin levels and subsequent risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women. J Natl Cancer I 91:629–634
Tworoger SS, Sluss P, Hankinson SE (2006) Association between plasma prolactin concentrations and risk of breast cancer among predominately premenopausal women. Cancer Res 66:2476–2482
Greendale GA, Reboussin BA, Slone S et al (2003) Postmenopausal hormone therapy and change in mammographic density. J Natl Cancer Inst 95:30–37
Greendale GA, Palla SL, Ursin G et al (2005) The association of endogenous sex steroids and sex steroids binding proteins with mammographic density: results from the postmenopausal estrogen/progestin interventions mammographic density study. Am J Epidemiol 162:826–834
The PEPI Investigators (1995) Rationale, design and conduct of the PEPI Trial. Controlled Clin Trials 16:3S-19S
Greendale GA, Bodin-Dunn L, Ingles S, Hail R, Barrett-Connor E (1996) Leisure, home and occupational physical activity and cardiovascular risk factors in postmenopausal women: the postmenopausal estrogen/progestins intervention (PEPI) study. Arch Intern Med 156:418–424
Greendale GA, James MK, Espeland M, Barrett-Connor E (1997) Can we measure postmenopausal estrogen/progestin use? The postmenopausal estrogen/progestin interventions trial. Am J Epidemiol 146:763–770
Block G, Hartman AM, Dresser CM et al (1986) A data-based approach to diet questionnaire design and testing. Am J Epidemiol 124:453–469
Anderson DC, Hopper BR, Lasley BL, Yen SS (1976) A simple method for the assay of eight steroids in small volumes of plasma. Steroids 28:179
Tremblay RR, Dube JY (1974) Plasma concentrations of free and non-TeBG bound testosterone in women on oral contraceptives. Contraception 10:599
Greendale GA, Reboussin BA, Sie A et al (1999) Effects of estrogen and estrogen–progestin on mammographic parenchymal density. Ann Intern Med 130:262–269
Byng JW, Boyd NF, Little L et al (1996) Symmetry of projection in the quantitative analyses of mammographic images. Eur J Cancer Prev 5:319–327
Crandall C, Palla S, Reboussin BA, Ursin G, Greendale G (2005) Positive association between mammographic breast density and bone mineral density in the Postmenopausal Estrogen/Progestin Interventions Study. Breast Cancer Res 7:R922–R928
Wang DY, de Stavola BL, Bulbrook RD et al (1988) The permanent effect of reproductive events on blood prolactin levels and its relation to breast cancer risk: a population study of postmenopausal women. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol 24:1225–1231
Heuson JC, Coune A, Staquet M (1972) Clinical trial of 2-BR-alpha-ergocryptine (CB154) in advanced breast cancer. Eur J Cancer 8:155–156
Peyrat JP, Vennin PH, Bonneterre J et al (1984) Effect of bromocriptine treatment on prolactin and steroid and steroid receptor levels in human breast cancer. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol 20:1363–1367
Gill S, Peston D, Vonderhaar BK, Shousha S (2001) Expression of prolactin receptors in normal, benign, and malignant breast tissue: an immunohistological study. J Clin Pathol 54:956–960
Mertani HC, Garcia-Cabellero T, Lambert A et al (1998) Cellular expression of growth hormone and prolactin receptors in human breast disorders. Int J Cancer 79:202–211
Reynolds C, Montone KT, Powell CM, Tomaszewski JE, Clevenger CV (1997) Expression of prolactin and its receptor in human breast carcinoma. Endocrinology 138:5555–5559
Touraine P, Martini JF, Zafrani B et al (1998) Increased expression of prolactin gene assessed by quantitative polymerase chain reaction in human breast tumors versus normal breast tissues. J Clin Endocr Metab 83:667–674
Ingram DM, Nortage EM, Roberts AN (1990) Prolactin and breast cancer risk. Med J Aust 153:469–473
Boyd NF, Stone J, Martin LJ et al (2002) The association of breast mitogens with mammographic densities. Br J Cancer 87:876–882
Tamimi RM, Hankinson SE, Colditz GA, Byrne C (2005) Endogenous sex hormone levels and mammgraphic density among postmenopausal women. Cancer Epidem Biomar 14:2641–2647
Hankinson SE, Willet WC, Manson JE et al (1995) Alcohol, height, and adiposity in relation to estrogen and prolactin levels in postmenopausal women. J Natl Cancer I 87:1297–1302
Koenig KL, Toniolo P, Bruning PF et al (1993) Reliability of serum prolactin measurements in women. Cancer Epidem Biomar 2:411–414
Muti P, Trevisan M, Micheli A et al (1996) Reliability of serum hormones in premenopausal and postmenopausal women over a one-year period. Cancer Epidem Biomar 5:917–922
Ehara Y, Siler TM, Yen SS (1976) Effects of large doses of estrogen on prolactin and growth hormone release. Am J Obstet Gynecol 125:455–458
Yen SS, Ehara Y, Siler TM Augmentation of prolactin secretion by estrogen in hypogonadal women. J Clin Invest 53:652–655
Chang RJ, Davidson BJ, Carlson HE, Judd HL (1982) Circadian pattern of prolactin secretion in postmenopausal women receiving estrogen with or without progestin. Am J Obstet Gynec 144:402–407
Yen SS, Lasley B, Wang C, Ehara Y (1975) Steroid modulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary system in the secretion of reproductive hormones. J Steroid Biochem 6:1047–1053
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the women who generously participated in the Postmenopausal Estrogen/Progestin Intervention Trial.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Greendale, G.A., Huang, MH., Ursin, G. et al. Serum prolactin levels are positively associated with mammographic density in postmenopausal women. Breast Cancer Res Treat 105, 337–346 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-006-9454-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-006-9454-y