Summary
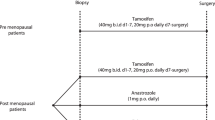
Prevention trials using incidence or mortality as endpoints require a large number of participants and long follow-up. Trials using biomarkers as endpoints would potentially require fewer participants, less time, and significantly less resources to test promising new agents for breast cancer prevention. To test this idea, a randomized trial of tamoxifen for 1 year versus observation for 1 year was conducted to determine whether tamoxifen can cause regression of hyperplastic breast tissue, whether it changes the biomarker phenotype of premalignant disease or normal breast epithelium, and if biomarkers can be used as early surrogate indicators of response to tamoxifen. Women were identified by having an abnormal mammogram and ductal hyperplasia diagnosed by core needle biopsy. Image-directed needle biopsy was repeated in the same site of the breast after 1 year. Approximately 3000 women were screened, and 265 were eligible. Sixty-three women were randomized and paired biopsies from 45 subjects were available for analysis. There was no evidence of substantial regression of hyperplasia – fewer samples showed hyperplasia at 1 year follow-up, but this was seen in both untreated and tamoxifen-treated women. There were trends for reductions in ER and PgR and trends for increases in bcl-2 in normal and hyperplastic tissue in the tamoxifen-treated arm, though these changes did not reach statistical significance. Proliferation, determined by Ki67 staining, was not significantly changed. Clinical trials of this type are difficult to carry out and modifications in trial design are needed to make this process more efficient.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Tamoxifen for early breast cancer: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet 351 (1998) 1451-1467
B Fisher, J Costantino, DL Wickerham, C Redmond, MT Kavanah, WM Cronin, V Vogel, A Robidoux, NV Dimitrov, J Atkins, M Daly, S Wieand, E Tan-Chiu, L Ford and N Wolmark, Tamoxifen for prevention of breast cancer: report of the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project P-1 Study. J Natl Cancer Inst 90 (1998) 1371-1388
JA Hage van der, C Velde van de, J-P Julien, M Tubiana-Hulin, C Vandervelden and L Duchateau, Preoperative chemotherapy in primary operable breast cancer: results from the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Trial 10902. J Clin Oncol 19 (2001) 4224-4237
B Fisher, A Brown, E Mamounas, S Wieand, A Robidoux, RG Margolese, AB Cruz Jr., ER Fisher, DL Wickerham, N Wolmark, A DeCillis, JL Hoehn, AW Lees and NV Dimitrov, Effect of preoperative chemotherapy on local-regional disease in women with operable breast cancer: findings from National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project B-18. J Clin Oncol 15 (1997) 2483-2493
ATAC, Trialist's Group. Anastrozole alone or in combination with tamoxifen versus tamoxifen alone for adjuvant treatment of postmenopausal women with early breast cancer: first results of the ATAC randomized trial. The Lancet 359: 2131–2139, 2002
Dowsett, M., Smith, I.E., Trialists, I. Greater Ki67 response after 2 weeks neoadjuvant treatment with anastrozole (A) than with tamoxifen (T) or anastrozole plus tamoxifen (C) in the IMPACT trial: a potential predictor of relapse-free survival. Breast Cancer Res Treatment 82: 56, 2003
WD DuPont and DL Page, Risk factors for breast cancer in women with proliferative breast disease. New Engl J Med 312 (1985) 146-151
SJ London, JL Connolly, SJ Schnitt and GA Colditz, A prospective study of benign breast disease, the risk of breast cancer. JAMA: The J Am Med Assoc 267 (1992) 941-944
WD Dupont, FF Parl, WH Hartmann, LA Brinton, AC Winfield, JA Worrell, PA Schuyler and WD Plummer, Breast cancer risk associated with proliferative breast disease and atypical hyperplasia. Cancer 71 (1993) 1258-1265
MC Pike, DV Spicer, L Dahmoushm and M Press, Estrogens, progestogens, normal breast cell proliferation, and breast cancer risk. Epidemiol Rev 15 (1993) 17-35
BS Katzenellenbogen, I Choi, R Delage-Mourroux, T Ediger, PGV Martini, M Montano, J Sun, K Weis and JA Katzenellenbogen, Molecular mechanisms of estrogen action: selective ligands and receptor pharmacology. Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 74 (2000) 279-285
DC Allred and S Mohsin, Biological features of premalignant disease in the human breast. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 5 (2000) 351-364
D Giri, S Dundas, J Nottingham and J Underwood, Oestrogen receptors in benign epithelial lesions and intraduct carcinomas of the breast: an immunohistological study. Histopathology 15 (1989) 575-584
RM Elledge, GM Clark, SA W Fuqua, Y-Y Yu and DC Allred, p53 protein accumulation detected by five different antibodies: relationship to prognosis and heat shock Protein 70 in breast cancer. Cancer Res 54 (1994) 3752-3757
S London, J Connolly, SJ Schnitt and GA Colditz, A prospective study of benign breast disease, the risk of breast cancer. JAMA: The J Am Med Assoc 267 (1992) 941-944
FW Foote and FW Stewart, Comparative studies of cancerous versus non-cancerous breasts. Ann Surg 121 (1945) 197
SA Bartow, DR Pathak, WC Black, CR Key and SR Teaf, Prevalence of benign, atypical, and malignant breast lesions in populations at different risk for breast cancer. A forensic autopsy study. Cancer 60 (1987) 2751-60
P O'Connell, V Pekkel, SA Fuqua, CK Osborne, GM Clark and DC Allred, Analysis of loss of heterozygosity in 399 premalignant breast lesions at 15 genetic loci. J Natl Cancer Inst 90 (1998) 697-703
KJ Walker, JM Price-Thomas, W Candish and RI Nicholson, Influence of the antioestrogen tamoxifen on normal breast tissue. Br J Cancer 64 (1991) 764-768
CJ Fabian, BF Kimler, J Anderson, OW Tawfik, MS Mayo, WE Burak Jr., JA O'Shaughnessy, KS Albain, DM Hyams, GT Budd, PA Ganz, ER Sauter, SW Beenken, WE Grizzle, JP Fruehauf, DW Arneson, JW Bacus, MD Lagios, KA Johnson and D Browne, Breast cancer chemoprevention phase I evaluation of biomarker modulation by arzoxifene, a third generation selective estrogen receptor modulator. Clin Cancer Res 10 (2004) 5403-5417
RJ Jackman, KW Nowels, J Rodriguez-Soto, F Marzoni, S Finkelstein and MJ Shepard, Stereotactic, automated, large-core needle biopsy of nonpalpable breast lesions: False-negative and histologic underestimation rates after long-term follow-up. Radiology 210 (1999) 799-805
K Dmytrasz, PI Tartter, H Mizrachy, L Chinitz, SR Smith and A Estabrook, The Significance of Atypical Lobular Hyperplasia at Percutaneous Breast Biopsy. The Breast J 9 (2001) 10-12
CJ Fabian, BF Kimler, DA Brady, MS Mayo, CH Chang, JA Ferraro, CM Zalles, AL Stanton, S Masood, WE Grizzle, NF Boyd, DW Arneson and KA Johnson, A phase II breast cancer chemoprevention trial of oral alpha-difluoromethylornithine: breast tissue, imaging, and serum and urine biomarkers. Clin Cancer Res 8 (2002) 3105-3117
CJ Fabian, BF Kimler, CM Zalles, JR Klemp, S Kamel, S Zeiger and MS Mayo, Short-term breast cancer prediction by random periareolar fine-needle aspiration cytology and the Gail risk model. J Natl Cancer Inst 92 (2000) 1217-1227
LJ t Veer van, H Dai, MJ Vijver van de, YD He, AA Hart, M Mao, HL Peterse, K Kooy van der, MJ Marton, AT Witteveen, GJ Schreiber, RM Kerkhoven, C Roberts, PS Linsley, R Bernards and SH Friend, Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer. Nature 415 (2002) 530-536
CM Perou, T Sorlie, MB Eisen, M van de Rijn, SS Jeffrey, CA Rees, JR Pollack, DT Ross, H Johnsen, LA Akslen, O Fluge, A Pergamenschikov, C Williams, SX Zhu, PE Lonning, AL Borresen-Dale, PO Brown and D Botstein, Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 406 (2000) 747-752
L Wilson, A Vlahou, B Gregory, RR Perry, D McGaughey, O Semmes, GL Wright Jr and C Laronga, A blood test for breast cancer detection. Breast Cancer Res Treatment 76 (2002) S-34
JA O'Shaughnessy, BM Ljung, WC Dooley, J Chang, HM Kuerer, DT Hung, MD Grant, SA Khan, RF Phillips, K Duvall, DM Euhus, BL King, BO Anderson, SL Troyan, J Kim, U Veronesi and M Cazzaniga, Ductal lavage and the clinical management of women at high risk for breast carcinoma: a commentary. Cancer 94 (2002) 292-298
WC Dooley, Ductal lavage, nipple aspiration, and ductoscopy for breast cancer diagnosis. Curr Oncol Rep 5 (2003) 63-5
WC Dooley, A Spiegel, C Cox, R Henderson, L Richardson and J Zabora, Ductoscopy: defining its role in the management of breast cancer. Breast J 10 (2004) 271-272
K Mokbel and AE Elkak, The evolving role of mammary ductoscopy. Curr Med Res Opin 18 (2002) 30-32
D Yamamoto and K Tanaka, A review of mammary ductoscopy in breast cancer. Breast J 10 (2004) 295-297
OW Sartorius, HS Smith, P Morris, D Benedict and L Friesen, Cytologic Evaluation of Breast Fluid in the detection of breast disease. J Natl Cancer Inst 59 (1977) 1073-1078
M Wrensch, N Petrakis, E King, R Miike, L Mason, K Chew, M Lee, VL Ernster, JF Hilton, R Schweitzer, WH Goodson III and TK Hunt, Breast Cancer Incidence in Women with Abnormal Cytology in Nipple Aspirates of Breast Fluid. Am J Epidemiol 135 (1992) 130-140
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohsin, S.K., Allred, D.C., Osborne, C.K. et al. Morphologic and Immunophenotypic Markers as Surrogate Endpoints of Tamoxifen Effect for Prevention of Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 94, 205–211 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-005-4896-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-005-4896-1