Abstract
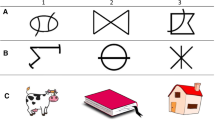
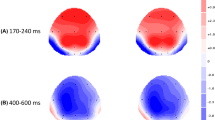
The question of the cognitive nature and the cerebral origins of the event-related potential (ERP) N400 component has frequently been debated. Here, the N400 effects were analyzed in three tasks. In the semantic task, subjects decided whether sequentially presented word pairs were semantically related or unrelated. In the phonologic (rhyme detection) task, they decided if words were phonologically related or not. In the image categorization task, they decided whether images were categorically related or not. Difference waves between ERPs to unrelated and related conditions (defined here as the N400 effect) demonstrated a greater amplitude and an earlier peak latency effect in the image than in semantic and phonologic tasks. In contrast, spatial correlation analysis revealed that the maps computed during the peak of the N400 effects were highly correlated. Source localization computed from these maps showed the involvement in all tasks of the middle/superior temporal gyrus. Our results suggest that these qualitatively similar N400 effects index the same cognitive content despite differences in the representational formats (words vs. images) and the types of mismatch (semantic vs. phonological) across tasks.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrett SE, Rugg MD (1989) Event-related potentials and the semantic matching of faces. Neuropsychologia 27:913–922
Barrett SE, Rugg MD (1990a) Event-related potentials and the phonological matching of picture names. Brain Lang 38:424–437
Barrett SE, Rugg MD (1990b) Event-related potentials and the semantic matching of pictures. Brain Cogn 14:201–212
Bentin S, McCarthy G, Wood CC (1985) Event-related potentials, lexical decision and semantic priming. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 60:343–355
Brandeis D, Naylor H, Halliday R, Callaway E, Yano L (1992) Scopolamine effects on visual information processing, attention and event-related potential map latencies. Psychophysiology 29:315–336
Brandeis D, Lehmann D, Michel CM, Mingrone W (1995) Mapping event-related brain potential microstates to sentence endings. Brain Topogr 8:145–159
Brown CM, Hagoort P (1993) The processing nature of the N400: evidence from masked priming. J Cogn Neurosci 5:34–44
Content A, Mousty P, Radeau M (1990) Brulex: Une base de données lexicales informatisée pour le français écrit et parlé. L’année Psychologique 90:551–566
Ganis G, Kutas M, Sereno MI (1996) The search for “common sense”: an electrophysiological study of the comprehension of words and pictures in reading. J Cogn Neurosci 8:89–106
Grave de Peralta Menedez R, Gonzalez Andino S, Lantz G, Michel CM, Landis T (2001) Noninvasive localization of electromagnetic epileptic activity. I. Method descriptions and simulations. Brain Topogr 14:131–137
Hagoort P (2008) The fractionation of spoken language understanding by measuring electrical and magnetic brain signals. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 363:1055–1069
Holcomb PJ (1993) Semantic priming and stimulus degradation: implications for the role of the N400 in language processing. Psychophysiology 30:47–61
Holcomb PJ, Grainger J (2007) Exploring the temporal dynamics of visual word recognition in the masked repetition priming paradigm using event-related potentials. Brain Res 1180:39–58
Khateb A, Annoni JM, Landis T, Pegna AJ, Custodi MC, Fonteneau E et al (1999) Spatio-temporal analysis of electric brain activity during semantic and phonological word processing. Int J Psychophysiol 32:215–231
Khateb A, Michel CM, Pegna AJ, O’Dochartaigh SD, Landis T, Annoni JM (2003) Processing of semantic categorical and associative relations: an ERP mapping study. Int J Psychophysiol 49:41–55
Khateb A, Pegna AJ, Landis T, Michel CM, Brunet D, Seghier ML et al (2007) Rhyme processing in the brain: an ERP mapping study. Int J Psychophysiol 63:240–250
Kondakor I, Pascual-Marqui RD, Michel CM, Lehmann D (1995) Event-related potential map differences depend on the prestimulus microstates. J Med Eng Technol 19:66–69
Kramer AF, Donchin E (1987) Brain potentials as indices of orthographic and phonological interaction during word matching. J Exp Psychol Learn Mem Cogn 13:76–86
Kutas M, Federmeier KD (2000) Electrophysiology reveals semantic memory use in language comprehension. Trends Cogn Sci 4:463–470
Kutas M, Hillyard SA (1980) Reading senseless sentences: brain potentials reflect semantic incongruity. Science 207:203–205
Kutas M, Hillyard SA (1982) The lateral distribution of event-related potentials during sentence processing. Neuropsychologia 20:579–590
Lau EF, Phillips C, Poeppel D (2008) A cortical network for semantics: (de)constructing the N400. Nat Rev Neurosci 9:920–933
Martin CD, Thierry G (2008) Interplay of orthography and semantics in reading: an event-related potential study. Neuroreport 19:1501–1505
Moreno EM, Kutas M (2005) Processing semantic anomalies in two languages: an electrophysiological exploration in both languages of Spanish-English bilinguals. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res 22:205–220
Munte TF, Brack M, Grootheer O, Wieringa BM, Matzke M, Johannes S (1998) Brain potentials reveal the timing of face identity and expression judgments. Neurosci Res 30:25–34
Murray MM, Brunet D, Michel CM (2008) Topographic ERP analyses: a step-by-step tutorial review. Brain Topogr 20:249–264
Nigam A, Hoffman JE, Simons RF (1992) N400 to semantically anomalous pictures and words. J Cogn Neurosci 4:15–22
Perez-Abalo MC, Rodriguez R, Bobes MA, Gutierrez J, Valdes-Sosa M (1994) Brain potentials and the availability of semantic and phonological codes over time. Neuroreport 5:2173–2177
Perrin F, Pernier J, Bertrand O, Echallier JF (1989) Spherical splines for scalp potential and current density mapping. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 72:184–187
Ritter W, Simson R, Vaughan HG Jr (1983) Event-related potential correlates of two stages of information processing in physical and semantic discrimination tasks. Psychophysiology 20:168–179
Rodriguez-Fornells A, Munte TF, Clahsen H (2002) Morphological priming in Spanish verb forms: an ERP repetition priming study. J Cogn Neurosci 14:443–454
Rugg MD (1984a) Event-related potentials and the phonological processing of words and non-words. Neuropsychologia 22:435–443
Rugg MD (1984b) Event-related potentials in phonological matching tasks. Brain Lang 23:225–240
Rugg MD (1985) The effects of semantic priming and work repetition on event-related potentials. Psychophysiology 22:642–647
Rugg MD, Coles MGH (1995) The ERP and cognitive psychology: conceptual issues. In: Rugg MD, Coles MGH (eds) Electrophysiology of Mind - Event Related Potentials and Cognition. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 27–39
Snodgrass JG, Vanderwart M (1980) A standardized set of 260 pictures: norms for name agreement, image agreement, familiarity and visual complexity. J Exp Psychol 6:174–215
Szucs D, Soltesz F, Czigler I, Csepe V (2007) Electroencephalography effects to semantic and non-semantic mismatch in properties of visually presented single-characters: the N2b and the N400. Neurosci Lett 412:18–23
van den Brink D, Brown CM, Hagoort P (2001) Electrophysiological evidence for early contextual influences during spoken-word recognition: N200 versus N400 effects. J Cogn Neurosci 13:967–985
Willems RM, Ozyurek A, Hagoort P (2008) Seeing and hearing meaning: ERP and fMRI evidence of word versus picture integration into a sentence context. J Cogn Neurosci 20:1235–1249
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation grants no’ 325100-118362 and 320030-125196, and the EEG Brain Mapping Core of the Center for Biomedical Imaging (CIBM) of Geneva and Lausanne. We thank Drs Rolando Grave de Peralta Menedez and Sara Gonzales Andino for the inverse solutions, and Tatiana Aboulafia for her contribution to the analysis of part of the data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khateb, A., Pegna, A.J., Landis, T. et al. On the Origin of the N400 Effects: An ERP Waveform and Source Localization Analysis in Three Matching Tasks. Brain Topogr 23, 311–320 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-010-0149-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-010-0149-7