Abstract
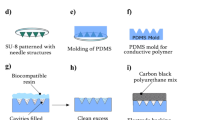
Electrophysiological devices are connected to the body through electrodes. In some applications, such as nerve stimulation, it is needed to minimally pierce the skin and reach the underneath layers to bypass the impedance of the first layer called stratum corneum. In this study, we have designed and fabricated surface microneedle electrodes for applications such as electrical peripheral nerve stimulation. We used molybdenum for microneedle fabrication, which is a biocompatible metal; it was used for the conductive layer of the needle array. To evaluate the performance of the fabricated electrodes, they were compared with the conventional surface electrodes in nerve conduction velocity experiment. The recorded signals showed a much lower contact resistance and higher bandwidth in low frequencies for the fabricated microneedle electrodes compared to those of the conventional electrodes. These results indicate the electrode-tissue interface capacitance and charge transfer resistance have been increased in our designed electrodes, while the contact resistance decreased. These changes will lead to less harmful Faradaic current passing through the tissue during stimulation in different frequencies. We also compared the designed microneedle electrodes with conventional ones by a 3-dimensional finite element simulation. The results demonstrated that the current density in the deep layers of the skin and the directivity toward a target nerve for microneedle electrodes were much more than those for the conventional ones. Therefore, the designed electrodes are much more efficient than the conventional electrodes for superficial transcutaneous nerve stimulation purposes.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
T.A. Anhoj, A.M. Jorgensen, D.A. Zauner, J. Hübner, J. Micromechanical Microeng. 16, 1819 (2006)
S. Aoyagi, H. Izumi, Y. Isono, M. Fukuda, H. Ogawa, Sensors Actuators A Phys. 139, 293–302 (2007)
A.J. Bard, L.R. Faulkner, Electrochem. Methods, 2nd edn. (Wiley, New York, 2001)
H. Becker, U. Heim, Sensors Actuators A Phys. 83, 130–135 (2000)
L. Beckmann, C. Neuhaus, G. Medrano, N. Jungbecker, M. Walter, T. Gries, et al., Physiol. Meas. 31, 233 (2010)
M.B. Chan-Park, J. Zhang, Y. Yan, C. Yue, Sensors Actuators B Chem. 101, 175–182 (2004)
J.-C. Chiou, L.-W. Ko, C.-T. Lin, C.-T. Hong, T.-P. Jung, S.-F. Liang, J.-L. Jeng, Using novel MEMS EEG sensors in detecting drowsiness application, in Biomedical circuits and systems conference, 2006. BioCAS 2006 (IEEE, 2006), 33–36 (2006)
Y.A. Chizmadzhev, A.V. Indenbom, P.I. Kuzmin, S.V. Galichenko, J.C. Weaver, R.O. Potts, J. Biophysics. 74, 843–856 (1998)
S.F. Cogan, Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 10, 275–309 (2008)
W. Dai, K. Lian, W. Wang, J. Microsyst. Technol. 11, 526–534 (2005)
T.P. DeMonte, P.D. Gadsby, P.F. Meyer, M.L. Joy, Measurement of edge effects in automatic external defibrillation electrodes using current density imaging, in Proc. 13th Annu. ISMRM Int. Conf. (2005)
P. Griss, P. Enoksson, H.K. Tolvanen-Laakso, P. Merilainen, S. Ollmar, G. Stemme, J. Microelectromech. Syst. 10, 10–16 (2001)
P. Griss, H.K. Tolvanen-Laakso, P. Merilainen, G. Stemme, IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 49, 597–604 (2002)
G.S. Guvanasen, L. Guo, R.J. Aguilar, A.L. Cheek, C.S. Shafor, et al., IEEE Trans. Neural Eng. Rehab. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2016.2629461
M. Han, D.-H. Hyun, H.-H. Park, S.S. Lee, C.-H. Kim, C. Kim, J. Micromechanical Microeng. 17, 1184 (2007)
C.Y. Jin, M.H. Han, S.S. Lee, Y.H. Choi, Biomed. Microdevices 11, 1195–1203 (2009)
T. Keller, A. Kuhn, J. Autom. Control. 18, 35–45 (2008)
K. Kim, D.S. Park, H.M. Lu, W. Che, K. Kim, J.-B. Lee, et al., J. Micromechanical Microeng. 14, 597 (2004)
A. Kuhn, T. Keller, M. Lawrence, M. Morari, J. Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing. 47, 279 (2009)
C. Liu, Adv. Mater. 19, 3783–3790 (2007)
T. Maeda, N. Arakawa, M. Takahashi, Y. Aizu, J. Optial Rev. 3, 223–229 (2010)
M. Matteucci, R. Carabalona, M. Casella, E. Di Fabrizio, F. Gramatica, M. Di Rienzo, et al., Microelectron. Eng. 84, 1737–1740 (2007)
E. McAdams, in Integrated Circuits and Systems, ed. By H. J. Yoo, C. van Hoof (Springer, New York, 2011), p. 31
E. McAdams, J. Jossinet, EMBS Conf. 13, 1728–1729 (1991)
E. McAdams, A. Lackermeier, J. McLaughlin, D. Macken, J. Jossinet, Biosens. Bioelectron. 10, 67–74 (1995)
D.B. McCreery, W.F. Agnew, T.G. Yuen, L. Bullara, IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 37, 996–1001 (1990)
D.R. Merrill, M. Bikson, J.G. Jefferys, J. Neurosci. Methods 141, 171–198 (2005)
K.L. Mittal, Adhesion measurement of thin films. ElectroComponent Science and Technology 3(1), 21–42 (1976)
H. W. Moses, J. C. Mullin, A practical guide to cardiac pacing. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins (2007)
K.V. Nemani, K.L. Moodie, J.B. Brennick, A. Su, B. Gimi, J. Mater. Sci. Eng. 33, 4453–4459 (2013)
A. Norlin, J. Pan, C. Leygraf, Biomol. Eng. 19, 67–71 (2002)
T.I. Oh, H. Koo, K.H. Lee, S.M. Kim, J. Lee, S.W. Kim, et al., Physiol. Meas. 29, 295 (2008)
J.H. Park, Y.K. Yoon, S.O. Choi, M.R. Prausnitz, M.G. Allen, IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 54, 903–913 (2007)
V. Parker, J. Warman Chardon, J. Mills, C. Goldsmith, P. R. Bourque, (2016). https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6796270
J.N. Patel, B. Kaminska, B.L. Gray, B.D. Gates, J. Micromechanical Microeng. 18, 095028 (2008)
A.M. Ribeiro, T.H. Flores-Sahagun, R.C. Paredes, J. Mater. Sci. 51, 2806–2816 (2016)
M. Sawan, F. Mounaim, G. Lesbros, Analog Integr. Circ. Sig. Process 55, 103–114 (2008)
M. Schaldach, M. Hubmann, A. Weikl, R. Hardt, Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 13, 1891–1895 (1990)
T.M. Suhonen, J.A. Bouwstra, A. Urtti, J. Control. Release 59, 149–161 (1999)
Y.K. Yoon, J.H. Park, M.G. Allen, J. Microelectromech. Syst. 15, 1121–1130 (2006)
L. Yu, F. Tay, D. Guo, L. Xu, K. Yap, Sensors Actuators A Phys. 151, 17–22 (2009)
D. Zhou, R. Greenberg, 25th EMBS Conf. (2003). https://doi.org/10.1109/IEMBS.2003.1279831
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by CMC Microsystems (MNT # 3923). The fabrication process was done in Nano-Systems Fabrication Laboratory at the University of Manitoba. The authors declare no commercial or financial conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Biomedical MicroNeedles
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soltanzadeh, R., Afsharipour, E., Shafai, C. et al. Molybdenum coated SU-8 microneedle electrodes for transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation. Biomed Microdevices 20, 1 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-017-0241-9
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-017-0241-9