Abstract
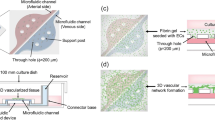
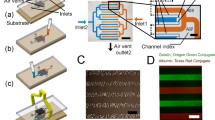
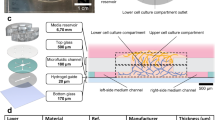
To study the effect of disturbed flow patterns on endothelial cells, the channels found within a modular tissue engineering construct were reproduced in a microfluidic chip and lined with endothelial cells whose resulting phenotype under flow was assessed using confocal microscopy. Modular tissue engineered constructs formed by the random packing of sub-millimetre, cylindrically shaped, endothelial cell-covered modules into a larger container creates interconnected channels that permit the flow of fluids such as blood. Due to the random packing, the flow path is tortuous and has the potential to create disturbed flow, resulting in an activated endothelium. At an average shear stress of 2.8 dyn cm−2, endothelial cells within channels of varying geometries showed higher amounts of activation, as evidenced by an increase in ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 levels with respect to static controls. VE-cadherin expression also increased, however, it appeared discontinuous around the perimeter of the cells. An increase in flow (15.6 dyn cm−2) was sufficient to reduce ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 expression to a level below that of static controls for many disturbed flow-prone channels that contained branches, curves, expansions and contractions. VE-cadherin expression was also reduced and became discontinuous in all channels, possibly due to paracrine signaling. Other than showing a mild correlation to VE-cadherin, which may be linked through a cAMP-initiated pathway, KLF2 was found to be largely independent of shear stress for this system. To gauge the adhesiveness of the endothelium to leukocytes, THP-1 cells were introduced into flow-conditioned channels and their attachment measured. Relative to static controls, THP-1 adhesion was reduced in straight and bifurcating channels. However, even in the presence of flow, areas where multiple channels converged were found to be the most prone to THP-1 attachment. The microfluidic system enabled a full analysis of the effect of the tortuous flow expected in a modular construct on endothelial cell phenotype.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.L. Akeson, C.W. Woods, J. Immunol. Methods 163, 181 (1993)
I. Barkefors, S. Le Jan, L. Jakobsson et al., J. Biol. Chem. 283, 13905 (2008)
P. Bausero, F. Cavaille, G. Meduri et al., Angiogenesis 2, 167 (1998)
B.C. Berk, Circulation 117, 1082 (2008)
A.R. Brooks, P.I. Lelkes, G.M. Rubanyi, Physiol. Genomics 2002, 27 (2002)
M.P. Burns, N. DePaola, Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 288, (2005)
T.M. Carlos, J.M. Harlan, Blood 84, 2068 (1994)
P.K. Chang, Separation of Flow (Pergamon, Oxford, 1970)
L. Chau, M. Doran, J. Cooper-White, Lab Chip 9, 1897 (2009)
C.N. Chen, S.F. Chang, P.L. Lee et al., Blood 107, 1933 (2006)
C. Cheng, F. Helderman, D. Tempel et al., Atherosclerosis 195, 225 (2007)
S. Chien, Ann. Biomed. Eng. 36, 554 (2008)
J.J. Chiu, D.L. Wang, S. Chien et al., J. Biomech. Eng. 120, 2 (1998)
M. Corada, M. Mariotti, G. Thurston et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 96, 9815 (1999)
K.S. Cunningham, A.I. Gotlieb, Lab Invest. 85, 9 (2005)
R.J. Dekker, S. Van Soest, R.D. Fontijn et al., Blood 100, 1689 (2002)
R.J. Dekker, J.V. Van Thienen, J. Rohlena et al., Am. J. Pathol. 167, 609 (2005)
R.J. Dekker, R.A. Boon, M.G. Rondaij et al., Blood 107, 4354 (2006)
Y. Du, E. Lo, S. Ali et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 105, 9522 (2008)
D.C. Duffy, J.C. McDonald, O.J.A. Schueller et al., Anal. Chem. 70, 4974 (1998)
L.K. Fiddes, N. Raz, S. Srigunapalan et al., Biomaterials 31, 3459 (2010)
J.O. Fledderus, J.V. Van Thienen, R.A. Boon et al., Blood 109, 4249 (2007)
R.W. Fox, A.T. McDonald, Introduction to Fluid Mechanics, 4th edn. (Wiley, Toronto, 1992)
D.L. Fry, Circ. Res. 22, 165 (1968)
F. Fukai, M. Mashimo, K. Akiyama et al., Exp. Cell Res. 242, 92 (1998)
S. Fukuhara, A. Sakurai, H. Sano et al., Mol. Cell Biol. 25, 136 (2005)
J.J. Fung, Transplantation 77, S41 (2004)
J. Gavard, J.S. Gutkind, Nat. Cell Biol. 8, 1223 (2006)
P.P. Hsu, S. Li, Y.S. Li et al., Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 285, 751 (2001)
J.P. Huddleson, N. Ahmad, S. Srinivasan et al., J. Biol. Chem. 280, 23371 (2005)
B. Imberti, D. Seliktar, R.M. Nerem et al., Endothelium 9, 11 (2002)
M. Inoue, H. Itoh, M. Ueda et al., Circulation 98, 2108 (1998)
M.W. Jackson, J.S. Roberts, S.E. Heckford et al., Cancer Res. 62, 854 (2002)
O.F. Khan, M.V. Sefton, Biomaterials 31, 8254 (2010)
T. Krakauer, Immunol. Lett. 45, 61 (1995)
M.G. Lampugnani, M. Corada, L. Caveda et al., J. Cell Biol. 129, 203 (1995)
K. Ley, Cardiovasc. Res. 32, 733 (1996)
J.C. McDonald, G.M. Whitesides, Acc. Chem. Res. 35, 491 (2002)
A.P. McGuigan, M.V. Sefton, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 11461 (2006)
A.P. McGuigan, M.V. Sefton, Tissue Eng. 13, 1079 (2007)
A.P. McGuigan, M.V. Sefton, Biomaterials 29, 2453 (2008)
H. Miao, Y.L. Hu, Y.T. Shiu et al., J. Vasc. Res. 42, 77 (2005)
M.R. Montminy, L.M. Bilezikjian, Nature 328, 175 (1987)
R. Morandini, G. Ghanem, A. Portier-Lemarie et al., Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 270, H807 (1996)
S. Noria, D.B. Cowan, A.I. Gotlieb et al., Circ. Res. 85, 504 (1999)
K.M. Parmar, H.B. Larman, G. Dai et al., J. Clin. Invest. 116, 49 (2006)
B. Prabhakarpandian, K. Pant, R.C. Scott et al., Biomed. Microdevices 10, 585 (2008)
P.H. Reinhardt, P. Kubes, Blood 92, 4691 (1998)
M. Rhodes, Introduction to Particle Technology, 2nd edn. (Wiley, Chichester, 2008)
K.S. Sakariassen, P.A.M.M. Aarts, P.G. De Groot, J. Lab. Clin. Med. 102, 522 (1983)
U.Y. Schaff, M.M.Q. Xing, K.K. Lin et al., Lab Chip 7, 448 (2007)
H. Schlichting, Boundary-Layer Theory, 7th edn. (McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York, 1979)
S. SenBanerjee, Z. Lin, G.B. Atkins et al., J. Exp. Med. 199, 1305 (2004)
J.W. Song, W. Gu, N. Futai et al., Anal. Chem. 77, 3993 (2005)
E. Tkachenko, E. Gutierrez, M.H. Ginsberg et al., Lab Chip 9, 1085 (2009)
P.S. Tsao, N.P. Lewis, S. Alpert et al., Circulation 92, 3513 (1995)
P.S. Tsao, R. Buitrago, J.R. Chan et al., Circulation 94, 1682 (1996)
E. Tzima, M. Irani-Tehrani, W.B. Kiosses et al., Nature 437, 426 (2005)
H. Ulbrich, E.E. Eriksson, L. Lindbom, Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 24, 640 (2003)
A.D. Van Der Meer, K. Vermeul, A.A. Poot et al., Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 298, H719 (2010)
P.L. Walpola, A.I. Gotlieb, M.I. Cybulsky et al., Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 15, 2 (1995)
N. Wang, H. Miao, Y.S. Li et al., Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 341, 1244 (2006)
E.L. Yellin, Circ. Res. 19, 791 (1966)
T. Yeung, P.C. Georges, L.A. Flanagan et al., Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 60, 24 (2005)
E.W.K. Young, C.A. Simmons, Lab Chip 10, 143 (2010)
E.W. Young, A.R. Wheeler, C.A. Simmons, Lab Chip 7, 1759 (2007)
H. Yuan, D.J. Goetz, M.W. Gaber et al., Radiat. Res. 163, 544 (2005)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support of the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the US National Institutes of Health (EB 001013). O.F. Khan acknowledges scholarship support from the Ontario Graduate Scholarship Program. The authors thank Alison P. McGuigan for the μCT images used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, O.F., Sefton, M.V. Endothelial cell behaviour within a microfluidic mimic of the flow channels of a modular tissue engineered construct. Biomed Microdevices 13, 69–87 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-010-9472-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-010-9472-8