Abstract
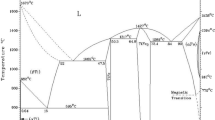
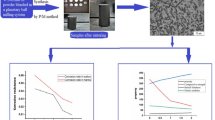
Titanium and titanium alloy with low density, high specific strength, good biological, excellent mechanical compatibility and easy to process have been widely used in the medical materials, but their application in orthopedics and dentistry often face bacterial infection, corrosion failure and stress shielding. In this paper, Ti–15Mo–7Cu (TM–7Cu) alloy was prepared by high vacuum non-consumable electric arc melting furnace and then treated by solution and aging treatment. The microstructure, mechanical properties, antibacterial properties and cytocompatibility were studied by X-ray diffraction, microhardness tester, electrochemical working station, antibacterial test and Live/Dead staining technology. The results have shown that the heat treatment significantly influenced the phase transformation, the precipitation of Ti2Cu phase, the elastic modulus and the antibacterial ability. With the extension of the aging time, the elastic modulus slightly increased and the antibacterial rate obviously increased. TM–7Cu alloy with a low elastic modulus of 83GPa and a high antibacterial rate of > 93% was obtained. TM–7Cu alloy showed no cytotoxicity to MC3T3. It was suggested that TM–7Cu might be a highly competitive medical material.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldhohrah T, Yang J, Guo J, Zhang H, Wang Y (2021) Ion release and biocompatibility of Co-Cr alloy fabricated by selective laser melting from recycled Co-Cr powder: an in vitro study. J Prosthetic Dentistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prosdent.2021.09.003
Bao X, Maimaitijuma T, Yu B, Li X, Xi G, Liu S, Cao Y, Zhang T (2022) Ti-Zr-Nb based BCC solid solution alloy containing trace Cu and Ag with low modulus and excellent antibacterial properties. Mater Today Commun 31:103180
Bazzano L, He J (2002) Copper in legumes may lower heart disease risk—reply. Arch Internal Med. 162(15):1780–1
Brogini S, Sartori M, Giavaresi G, Cremascoli P, Alemani F, Bellini D, Martini L, Maglio M, Pagani S, Fini M (2021) Osseointegration of additive manufacturing Ti–6Al–4V and Co–Cr–Mo alloys, with and without surface functionalization with hydroxyapatite and type I collagen. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 115:104262
Burghardt I, Lüthen F, Prinz C, Kreikemeyer B, Zietz C, Neumann H-G, Rychly J (2015) A dual function of copper in designing regenerative implants. Biomaterials 44:36–44
Cai D, Zhao X, Yang L, Wang R, Qin G, Chen D-F, Zhang E (2021) A novel biomedical titanium alloy with high antibacterial property and low elastic modulus. J Mater Sci Technol 81:13–25
Cao B, Zheng Y, Xi T, Zhang C, Song W, Burugapalli K, Yang H, Ma Y (2012) Concentration-dependent cytotoxicity of copper ions on mouse fibroblasts in vitro: effects of copper ion release from TCu380A vs TCu220C intra-uterine devices. Biomed Microdevices 14(4):709–20
Chen M, Zhang E, Zhang L (2016) Microstructure, mechanical properties, bio-corrosion properties and antibacterial properties of Ti–Ag sintered alloys. Mater Sci Eng C 62:350–360
Chen M, Yang L, Zhang L, Han Y, Lu Z, Qin G, Zhang E (2017) Effect of nano/micro-Ag compound particles on the bio-corrosion, antibacterial properties and cell biocompatibility of Ti-Ag alloys. Mater Sci Eng C 75:906–917
Cortizo MC, Lorenzo de Mele MF (2004) Cytotoxicity of copper ions released from metal. Biol Trace Elem Res 102(1):129–141
Cortizo MC, De Mele MF, Cortizo AM (2004) Metallic dental material biocompatibility in osteoblastlike cells. Biol Trace Elem Res. 100(2):151–68
Cui S, Liu S, Nie J, Chen D, Wu X, Qin G, Zhang E (2022) Design and preparation of a biomedical titanium alloy with low elastic modulus and high antibacterial property based on Ti-Mo-Ag system. J Alloys Compds 908:164639
Cui S, Liu S, Nie J, Chen D, Wu X, Qin G, Zhang E (2022) Design and preparation of a biomedical titanium alloy with low elastic modulus and high antibacterial property based on Ti-Mo-Ag system. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 908:164639
de Mello MG, Salvador CF, Cremasco A, Caram R (2015) The effect of Sn addition on phase stability and phase evolution during aging heat treatment in Ti–Mo alloys employed as biomaterials. Mater Charact 110:5–13
Du Z, Guo H, Liu J, Cheng J, Zhao X, Wang X, Liu F, Cui X (2020) Microstructure evolution during aging heat treatment and its effects on tensile properties and dynamic Young’s modulus of a biomedical β titanium alloy. Mater Sci Eng A 791:139677
Fu S, Zhang Y, Qin G, Zhang E (2021) Antibacterial effect of TiAg alloy motivated by Ag-containing phases. Mater Sci Eng C 128:112266
Fu S, Zhang Y, Yang Y, Liu X, Zhang X, Yang L, Xu D, Wang F, Qin G, Zhang E (2022) An antibacterial mechanism of titanium alloy based on micro-area potential difference induced reactive oxygen species. J Mater Sci Technol 119:75–86
Fu S, Zhao X, Yang L, Qin G, Zhang E (2022) A novel Ti-Au alloy with strong antibacterial properties and excellent biocompatibility for biomedical application. Mater Sci Eng C 133:112653
Gudkov SV, Simakin AV, Konushkin SV, Ivannikov AY, Nasakina EO, Shatova LA, Kolmakov AG, Sevostyanov MA (2020) Preparation, structural and microstructural characterization of Ti–30Nb–10Ta–5Zr alloy for biomedical applications. J Mater Res Technol 9(6):16018–16028
Gupta A, Khatirkar R, Singh J (2022) A review of microstructure and texture evolution during plastic deformation and heat treatment of β-Ti alloys. J Alloys Compds 899:163242
Hart EB, Steenbock H, Waddell J, Elvehjem CA, Van Donk E, Riising BM (1928) Iron in nutrition: VII Copper as a supplement to iron for hemoglobin building in the rat. J Biol Chem 77(2):797–812
Herath I, Davies J, Will G, Tran PA, Velic A, Sarvghad M, Islam M, Paritala PK, Jaggessar A, Schuetz M, Chatterjee K (2022) Anodization of medical grade stainless steel for improved corrosion resistance and nanostructure formation targeting biomedical applications. Electrochim Acta 416:140274
Jin-Chao Z, Xiao-Hong H, Qun Z, Ya-Ping L, Shu-Xiang W (2012) Effects of strontium nitrate on the proliferation, differentiation and mineralization function of primary mouse osteoblasts in vitro. Chin J Inorg Chem 28(2):374–80
Kuroda D, Niinomi M, Morinaga M, Kato Y, Yashiro T (1998) Design and mechanical properties of new β type titanium alloys for implant materials. Mater Sci Eng A. 243(1–2):244–9
Liu J, Li F, Liu C, Wang H, Ren B, Yang K, Zhang E (2014) Effect of Cu content on the antibacterial activity of titanium–copper sintered alloys. Mater Sci Eng C 35:392–400
Liu J, Zhang X, Wang H, Li F, Li M, Yang K, Zhang E (2014) The antibacterial properties and biocompatibility of a Ti-Cu sintered alloy for biomedical application. Biomed Mater 9(2):025013
Liuxin Q, Liyang X, Norman W, Mingju L, Yi G, Song G, Ping L (2016) Clinical effect of traditional Chinese spinal orthopedic manipulation in treatment of chondromalacia patellae. J Tradit Chin Med 36(6):718–723
Lodhi MJK, Deen KM, Greenlee-Wacker MC, Haider W (2019) Additively manufactured 316L stainless steel with improved corrosion resistance and biological response for biomedical applications. Addit Manuf 27:8–19
Lüthen F, Bergemann C, Bulnheim U, Prinz C, Neumann HG, Podbielski A, Bader R, Rychly J (2010) A dual role of copper on the surface of bone implants. In: Materials Science Forum 2010. Trans Tech Publications Ltd, vol 638, pp 600–605
Mohan P, Rajak DK, Pruncu CI, Behera A, Amigó-Borrás V, Elshalakany AB (2021) Influence of β-phase stability in elemental blended Ti-Mo and Ti-Mo-Zr alloys. Micron 142:102992
Moshokoa NA, Raganya ML, Machaka R, Makhatha ME, Obadele BA (2021) The effect of molybdenum content on the microstructural evolution and tensile properties of as-cast Ti-Mo alloys. Mater Today Commun 27:102347
Pathote D, Jaiswal D, Singh V, Behera CK (2022) Optimization of electrochemical corrosion behavior of 316L stainless steel as an effective biomaterial for orthopedic applications, Materials Today: Proceedings
Romero-Resendiz L, Rossi MC, Álvarez A, García-García A, Milián L, Tormo-Más MÁ, Amigó-Borrás V (2022) Microstructural, mechanical, electrochemical, and biological studies of an electron beam melted Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Mater Today Commun 31:103337
Ruzic J, Emura S, Ji X, Watanabe I (2018) Mo segregation and distribution in Ti–Mo alloy investigated using nanoindentation. Mater Sci Eng A 718:48–55
Seftel A (2004) Treatment of infections associated with surgical implants. J Urol 172(5, Part 1):2102
Shi A, Zhu C, Fu S, Wang R, Qin G, Chen D, Zhang E (2020) What controls the antibacterial activity of Ti-Ag alloy, Ag ion or Ti2Ag particles? Mater Sci Eng C 109:110548
Shi A, Cai D, Hu J, Zhao X, Qin G, Han Y, Zhang E (2021) Development of a low elastic modulus and antibacterial Ti-13Nb-13Zr-5Cu titanium alloy by microstructure controlling. Mater Sci Eng C 126:112116
Singh RP, Kumar S, Nada R, Prasad R (2006) Evaluation of copper toxicity in isolated human peripheral blood mononuclear cells and it’s attenuation by zinc: ex vivo. Mol Cell Biochem. 282(1):13–21
Somlyai-Sipos L, Baumli P, Sycheva A, Kaptay G, Szőri-Dorogházi E, Kristály F, Mikó T, Janovszky D (2020) Development of Ag nanoparticles on the surface of Ti powders by chemical reduction method and investigation of their antibacterial properties. Appl Surf Sci 533:147494
Wang K (1996) The use of titanium for medical applications in the USA. Mater Sci Eng A 213(1):134–137
Wu C, Zhou Y, Fan W, Han P, Chang J, Yuen J, Zhang M, Xiao Y (2012) Hypoxia-mimicking mesoporous bioactive glass scaffolds with controllable cobalt ion release for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 33(7):2076–85
Wu C, Zhou Y, Xu M, Han P, Chen L, Chang J, Xiao Y (2013) Copper-containing mesoporous bioactive glass scaffolds with multifunctional properties of angiogenesis capacity, osteostimulation and antibacterial activity. Biomaterials 34(2):422–33
Yi C, Yuan Y, Zhang L, Jiang Y, He Z (2021) Antibacterial Ti-35Nb-7Zr-xCu alloy with excellent mechanical properties generated with a spark plasma sintering method for biological applications. J Alloys Compds 879:160473
Yuan Y, Luo R, Ren J, Zhang L, Jiang Y, He Z (2022) Design of a new Ti-Mo-Cu alloy with excellent mechanical and antibacterial properties as implant materials. Mater Lett 306:130875
Zhang E, Li F, Wang H, Liu J, Wang C, Li M, Yang K (2013) A new antibacterial titanium–copper sintered alloy: preparation and antibacterial property. Mater Sci Eng C 33(7):4280–4287
Zhang E, Wang X, Chen M, Hou B (2016) Effect of the existing form of Cu element on the mechanical properties, bio-corrosion and antibacterial properties of Ti-Cu alloys for biomedical application. Mater Sci Eng C 69:1210–1221
Zhang E, Zhao X, Hu J, Wang R, Fu S, Qin G (2021) Antibacterial metals and alloys for potential biomedical implants. Bioactive Mater 6(8):2569–2612
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (No.31971253), Joint plan of key R & D projects in Liaoning Province (2020JH2/10300157) and Shenyang Science and technology plan in 2020 (20-205-4-023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, S., Shi, A., Xie, Y. et al. Feasibility study on Ti-15Mo-7Cu with low elastic modulus and high antibacterial property. Biometals 35, 1225–1241 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-022-00438-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-022-00438-w